Magnetotherapy (13) Infrared and phototherapy (8) Vibroacoustic therapy (6) Laser therapy (4) Quantum therapy (1) Thermotherapy (2) Electrophoresis and Galvanization (5) Electrical stimulation (3)
UHF therapy for lactostasis helps eliminate stagnation of breast milk during lactation in women, and is carried out using an electric field with ultra-high frequency. The action of the UHF field is directed deep into the tissues and affects:
- acceleration of blood flow in the mammary gland;
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- severity of edema;
- speed of anti-inflammatory processes;
- dilation of blood vessels and ducts of the mammary glands.
Absolute contraindications for UHF therapy should be taken into account:
- acute mastitis;
- fibroadenomatosis of one or two mammary glands;
- mastopathy;
- hypotension;
- pregnancy;
- oncology.
The advantages of UHF therapy for lactostasis are due to the painlessness of the procedure and its safety for both the nursing mother and the child.
Positive changes are noted after 1 session. The frequency and duration of procedures is determined only by the doctor. Depending on the severity of the condition, the duration of the procedure can vary from five to fifteen minutes, the course can range from 1 to 15 sessions. You should only visit specialized physiotherapy rooms equipped with wooden furniture. Subjective sensations should vary within the limits of moderate heat and no higher, in order to avoid burns in the treated area.
To consolidate the effect of UHF therapy for lactostasis, it is recommended to perform a light massage of the mammary gland before each feeding.
Magnetic therapy devices
[td]
Ultrasound as a method of physiotherapy
The use of physiotherapeutic methods of treatment for problems with the mammary glands during breastfeeding has recently become quite widespread. One of them is ultrasound. This painless and effective method brings relief to the young mother after the first 2-3 sessions. With its help, the functioning of the thoracic ducts is significantly improved, milk production is enhanced and the risk of inflammatory processes in the mammary gland is reduced. The procedure is combined with mandatory pumping, which is performed by an experienced specialist.
Ultrasound has a complex effect on the mammary gland. With its help, the patency of the thoracic ducts increases, the blood vessels of the chest expand, and the pain syndrome is completely relieved.
This effect is achieved due to the massage properties of ultrasound and its contribution to enhancing the nutrition of breast tissue by dilated blood vessels.
The procedure itself is carried out by a functionalist doctor. Using the ultrasound device's sensor, it processes the entire surface of the mammary gland, with the exception of the nipple and areola. The entire therapeutic effect on the breast lasts about 15-20 minutes, and the sessions themselves require 4-8, depending on the severity of the condition and the neglect of the process.
After the manipulation, a mandatory pumping procedure takes place, which, provided the mammary gland is warmed up and softened, does not cause any unpleasant sensations. If necessary, the young mother will be assisted in pumping by an experienced medical professional.
Other reasons
There are also a number of negative factors that can cause lactostasis in a nursing mother. Treatment may depend on the causes of the disease.
Typically occurs as a result of the following conditions:
- Infectious diseases of the respiratory tract in the mother (the reason in this case is also tissue swelling).
- Hyperlactation (increased milk content in the mammary glands). This condition usually develops as a result of irrational frequent pumping.
- Swelling of the breast tissue can occur when wearing incorrectly selected underwear. The seams of your bra can put excessive pressure on you.
- Breast injury (tissues in the area of impact may swell, the ducts become compressed, and milk does not drain as expected).
- Anatomical features: in many women, the ducts of the mammary glands are too narrow or excessively tortuous.
- Sagging breasts.
- Sleeping on your side or stomach with compression of the mammary glands.
- Physical overexertion.
- Psycho-emotional stress.
Stagnation of milk in the duct can cause an increase in pressure in the entire lobule. As a result, tissue swelling occurs, which can turn into painful compaction. Milk, having no outflow tract, can be partially absorbed into the blood. This causes an increase in body temperature. Due to prolonged hypertension in the lobules, milk production is reduced until lactation completely stops. This condition is called total lactostasis.
Purulent mastitis
The inflammatory process, accompanied by suppuration in the tissues, refers to infectious or purulent mastitis. In children, immunity is poorly developed, so there is a high probability of generalization of the process. The disease is serious and, in the absence of adequate and timely treatment, leads to serious consequences. The pathology is provoked by an infection that enters the baby’s body in various ways.
In the absence of timely treatment, irreparable things can happen. Sometimes parents themselves provoke purulent mastitis by improperly caring for the child or by self-treatment of physiological swelling of the mammary glands. Rubbing, compresses and other manipulations with the baby’s delicate skin lead to infection and, as a result, mastitis. In addition to this reason, there are other factors that can provoke the disease:
- Pressing on the breasts to extract as much nipple discharge as possible.
- Insufficient infant hygiene, rare water procedures.
- Tight clothing, as well as made from synthetic materials. Although most baby clothes are made from natural fabrics, some clothes contain synthetics, which can be a source of irritation.
- Congenital pathologies.
- Infection through contact with the mother, who may be a carrier of infections.
Signs of pathology appear clearly and cause great concern to the newborn. Typical symptoms of mastitis include:
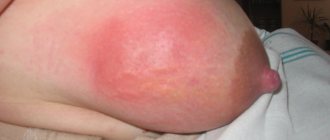
- Swelling, swelling of tissues. Usually problems occur on one side, but the infection can spread to both breasts at once.
- Redness of a separate area on the chest, sometimes the skin may take on a purple color.
- An increase in temperature, the jump can be sharp immediately up to 39-40 C°.
- Behavioral changes. The baby becomes lethargic, whiny, and refuses to eat.
- Discharge in the form of pus, there may be a specific smell.
If a newborn develops similar symptoms, then contacting a doctor should be done immediately . Self-medication, lotions and compresses with drugs whose effect has not been confirmed by doctor’s recommendations are contraindicated. Such actions can aggravate the situation, the infection will begin to rapidly spread throughout the body.
Mastitis in newborns can be successfully treated, the main thing is to seek help from a doctor in a timely manner. The therapeutic regimen may differ depending on the clinical picture of the disease.
If mastitis has reached the stage when foci of suppuration have formed, then complex treatment is carried out, including surgical methods. For each child, a specific, most gentle therapeutic regimen is selected and may include:
- Surgical intervention to remove formed pus. As a rule, drainage is not used in such cases. Subsequently, topical antiseptic drugs are prescribed, which are necessary to prevent repeated relapses.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics, but adapted for newborns regarding the active component and dose.
- Vitamin complex. If the baby is breastfed, special nutrition and supplements can be recommended for the mother herself.
- Physiotherapy.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, even if pus forms in the mammary glands, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Complications are likely if left untreated , which leads to phlegmon and the spread of infection throughout the body. Such conditions are critical and lead to death.
Contraindications to physical methods of treatment
Physiotherapy for lactostasis is not carried out if the following contraindications are present:
- acute stage of mastitis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- mastopathy;
- fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands.
Lactostasis is not only discomfort and pain for a young mother, but also, in advanced cases, a threat to health. This is a condition that all expectant mothers should know about, because it is easier to prevent than to treat. But even if lactostasis occurs, timely and correct actions by a woman will help quickly cope with the problem.
Lactostasis
It is considered a condition in a lactating woman in which either increased milk production occurs or its obstructed outflow from the mammary glands. This problem often arises in situations where a young mother does not have an established breastfeeding technique - feeding not “on demand”, using nipples, bottles with formula to supplement the baby’s feeding, supplementing with water in the first months of the child’s life, not regularly putting the baby to the breast ( for example, due to an early return to work, mother’s illness), regular pumping (which leads to excessive milk production and stagnation). Also, the risk of lactostasis occurs when wearing underwear that is too tight, preceded by long-term mastopathy with the formation of fibrous tissue. Lactostasis manifests itself as a feeling of heaviness in the chest and a feeling of fullness; a limited area of compaction can be felt.
Why is the development of lactostasis dangerous?
If congestion in the mammary gland is not corrected in a timely manner during lactostasis, a dangerous disease can develop - mastitis with the formation of inflammatory processes in the tissues of the mammary gland. With mastitis, in addition to severe bursting pain in the chest, its swelling and redness, there is an increase in the temperature of both the chest itself and the general one, with chills and a sharp deterioration in well-being. Advanced mastitis can lead to tissue necrosis and the development of sepsis. That's why it's so important to fight lactostasis.
Lactostasis initially develops only in a few lobules of the mammary gland, in which milk stagnation occurs, and has a very limited localization that can be palpated. If you start preventive measures at this stage, then you can completely avoid unpleasant consequences.
What can you do yourself?
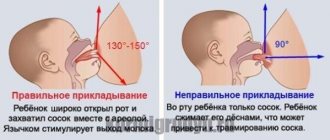
It is urgent to establish the technique of attaching the baby to the breast, make sure that the baby correctly grasps the breast along with the areola, try to initially attach the baby to this breast and not tear him off before he releases the breast. During feeding, you need to massage the area of the breast where the tightness is felt - from the periphery to the center of the mammary gland, freeing it from milk. Pumping too hard can cause a reflex increase in milk production and make the situation worse. Before feeding, you can put a warm diaper on your chest, this will improve the flow of milk when the baby sucks. When expressing, you need to remember that you should not try to express “to the last drop,” but to release the stagnant lobules of the mammary gland.
If you feel that you cannot cope on your own, do not hesitate and within 2 days contact a gynecologist, mammologist or pediatrician
. You will be immediately prescribed drug therapy, physical therapy methods, and taught how to properly drain congestive breasts.
From physiotherapeutic methods
Ultrasound therapy
is the most commonly prescribed . Its mechanism of action for mastitis is to improve the outflow of milk, blood and lymph flow due to a local increase in temperature and micromassage effect, ultrasound also has an anti-inflammatory effect, which is important for the prevention of mastitis.
Ultrasound treatment is carried out in advanced cases, when there is a risk of developing mastitis (inflammation of the mammary gland due to infection of its excretory ducts). Ultrasound therapy is used in this case as a method that restores the regeneration of inflamed tissues and improves local blood and lymph flow. Ultrasound waves pass deep into the tissue and are well absorbed by adipose tissue; the pulsed technique, when affecting milk clots in the lobules, improves their outflow from the mammary glands. The technique is quite simple and painless: the procedure is performed locally on the area of the mammary gland (excluding the areola), using soft circular movements, the mode is set to pulse, the duration of the procedure is only about 10 minutes. For a full course of treatment, 5-8 daily procedures or every other day are prescribed. After the ultrasound treatment procedure, you need to express milk, focusing on the stagnant area; as a rule, this is quite easy. A noticeable improvement will already be noticeable after the 3rd procedure. At the same time, it must be remembered that ultrasound therapy is carried out in combination with methods that regulate increased milk production or improve its outflow. At the same time, vegetative-vascular dysfunction is corrected and the adrenal cortex is stimulated.
Contraindications to ultrasound exposure
with lactostasis:
Mastopathy
Fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands
Acute mastitis
Malignant neoplasms
Organic lesions of the central nervous system.
In all other cases, ultrasound is the most important auxiliary method for correcting congestion in the chest during lactostasis.
Many mothers, suspecting that they have lactation mastitis, immediately rush to search for a remedy that will relieve them of this disease. Everything is used - advice from grandmothers and friends, folk recipes, etc. Often, as a result of such “treatment”, mastitis in a nursing mother does not go away, but takes on a more severe form, in which surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
To understand what exactly the treatment of mastitis is, let’s look at its main causes and give a brief description of the problem.