Breastfeeding is not only about moments filled with happiness and togetherness with your baby. Often there are many troubles associated with lactation: cracks, lack of milk or, conversely, hyperlactation. One of these problems may be the formation of lumps in the mammary gland in a nursing mother. In addition to pain and discomfort, they can lead to serious complications.
What it is
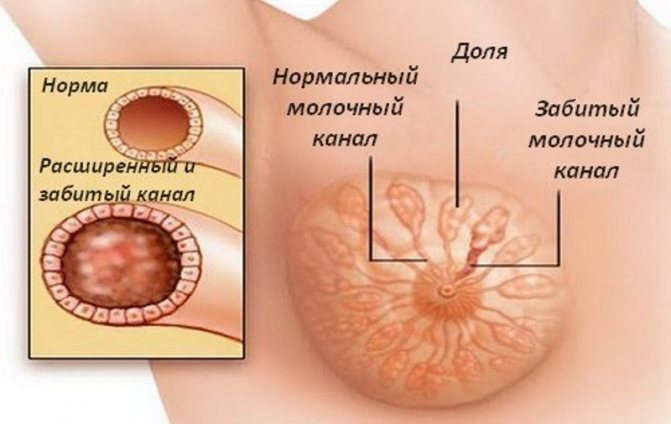
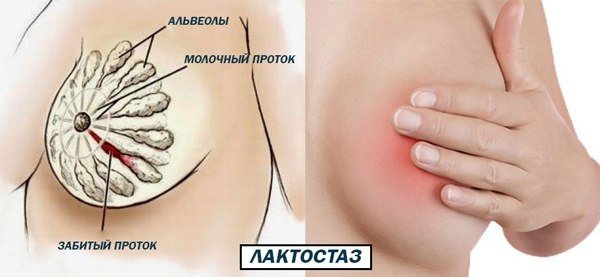
Most often, lumps in the breast that occur during feeding are lactostasis. This is a stagnant formation that occurs when the milk duct is blocked and the lobe cannot be cleared of milk.
In itself, this nuisance does not pose any threat to the mother or baby, and it is quite common. But it is imperative to get rid of lactostasis in a short time, since the advanced form leads to the formation of mastitis. Purulent mastitis, which is subject to surgical intervention, is especially dangerous.
Symptoms
Symptoms of lactostasis manifest themselves in a fairly noticeable way:
- soreness;
- the presence of lumps in the breasts during lactation, which may disappear after a massage;
- uneven flow of milk from a painful breast;
- increase in breast volume - due to the presence of a large volume of milk in the breast;
- increase in body temperature - up to 40 degrees, occurs with advanced lactostasis;
- swelling and redness - occurs above the site of compaction and indicates that inflammation is occurring in the mammary gland.

Symptoms of the condition
The symptoms of the presented condition are more than eloquent and they are expressed in painful sensations in the mammary gland. In the vast majority of cases, lumps form in only one breast, which is where the pain occurs. Serious difficulties may also arise when trying to feed the baby with this particular breast. Lactostasis, as a pathological condition, begins to be felt quite quickly.
In addition, a nursing mother may exhibit other symptoms, for example, an increase in body temperature or a deterioration in general well-being, apathy, and loss of appetite.
In the most complex and advanced situations, especially if a woman has attempted self-treatment, a purulent form may occur. Of course, it is characterized by much more vivid manifestations: fever, temperature above 38-39 degrees and much more. In many ways, the symptoms depend on the woman’s age, her general health, and the absence or presence of chronic diseases. In any case, if lumps have formed in the mammary gland during breastfeeding or pregnancy, you must contact a mammologist for step-by-step diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Features and causes of aching chest pain
Causes
Incorrect actions of the mother or the characteristics of the baby lead to the formation of compaction in the mammary glands during feeding. There are many reasons that cause lactostasis, but they all boil down to the fact that milk does not come out of some parts of the breast.
This is facilitated by:
- improper feeding of the baby;
- increased lactation, when too much milk is produced that the baby is not able to eat;
- the baby does not suckle actively;
- introduction of complementary foods, which significantly reduces the time the baby spends at the breast;
- uncomfortable posture during night sleep;
- blockage of the milk duct, which occurs due to cracked nipples or very fatty milk;
- incorrect posture when feeding or supporting the breast with your hand, in which some lobules of the mammary gland are pinched and are not emptied.
One of the common causes of breast lumps during breastfeeding is a monotonous feeding position. For example, the largest axillary lobe is poorly released from milk when the baby takes the breast in a standard “sitting” position. If the blockage occurs in the center of the upper part of the breast, then, most likely, the mother, while feeding the baby, holds the breast so that the nipple is pinched on top with the index finger, and on the bottom with the middle finger.
Causes
There are many factors that can cause milk stagnation. However, one reason cannot lead to the development of the disease - only a combination of several factors together causes the disease. Provocateurs of lactostasis:
- Prolonged hypothermia of the chest. Low temperatures reflexively narrow all vessels and channels. Thus, the excretory ducts are pinched and milk stagnates in the acini.
- Incorrect feeding process, in which the baby does not completely cover the nipple with his mouth.
- Large glands: large breasts sag, and their own weight compresses the channels that remove milk.
- Diet: with excessive fat consumption, the lumen of the excretory ducts is narrowed by fatty deposits.
- Incomplete emptying of the thoracic acini. After breastfeeding, mothers often do not sufficiently empty the glands in which milk remains.
- A bra that is tight to the skin: the fabric restricts the air flow and local ventilation of the skin is disrupted.
- Frequently sleep on your stomach. This reason is also associated with a violation of oxygen supply.
- Congenital features - narrow thoracic ducts that pass milk worse.
- Hyperlactation - milk production is greater than normal. This phenomenon is often observed at the beginning of lactation (the first week after birth).
- Injuries to the gland: bruises, blows to the chest. Tissue damage causes inflammation, followed by local swelling, compressing the excretory canals.
- Cracks on areolas and nipples. The integrity of the skin is compromised - a direct path to bacterial infection.
- Hypohydration is low water content in the body.
- Tumors. The neoplasm is mechanically compressed by the acini.
- Psychological factors: severe fatigue, lack of sleep and chronic stress.
Possible complications
The main complication that can result from stagnation of milk with hardening in the mammary gland in a nursing woman is mastitis, and especially purulent one. It is a consequence of bacteria entering the breast tissue. This can happen if there are chronic infectious diseases or damage to the skin in the nipple area.
In most cases, a woman’s immune system copes with bacteria, but stagnation of milk in the ducts is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms. If the lump cannot be broken for a long time - more than 3 days, and the temperature rises, the chest swells and turns red in places, most likely, the inflammatory process is already underway.
In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, since advanced purulent mastitis is an indication for surgical intervention. How to remove lumps in the chest? If you consult a specialist in time, it is possible to remove inflammation using ultrasound and other physiotherapeutic methods.
First aid for yourself
If signs of lactostasis are detected, precise measures should be taken. These include taking medications and manual methods. It is important to remember that if lactostasis is detected, you need to take action immediately. Otherwise, the still harmless blockage easily turns into inflammation of the mammary glands.
So, first of all, you should take an antispasmodic. Among the drugs of choice, the most popular is drotaverine. The essence of its action is to relax the excretory ducts. The drug reduces tension and allows the duct to continue to function. In addition, if you have a fever, you can take paracetamol. This remedy not only lowers body temperature, but also suppresses inflammatory processes in the chest. Paracetamol also relieves pain. At the same time, you should not be afraid of the active substance getting into the milk. A one-time dose does not have a negative effect on either the milk or the baby.
Complex treatment
Treatment of lumps in the sternum in women that arise during breastfeeding requires an integrated approach. The fight against lactostasis should begin immediately after its detection. After 12 hours, this is much more difficult to do, the woman’s well-being may worsen, and the likelihood of an infectious process increases significantly.
If there is no temperature yet and the mother’s condition is satisfactory, a number of measures can be taken to help eliminate the bumps. To do this, you need to clear the stagnation and completely empty the breast lobe of milk. How to get rid of lumps in the chest?

Proper preparation
Before taking direct measures to get rid of balls in the chest during breastfeeding, it is necessary to prepare the chest. The most preferable is a warm shower or compress for a few minutes, after which the area of the lump is lightly kneaded until it becomes softer.
Under no circumstances should these measures be resorted to in the case of advanced lactostasis and elevated temperature, since it is not known at what stage of inflammation the damaged lobule of the mammary gland is located.
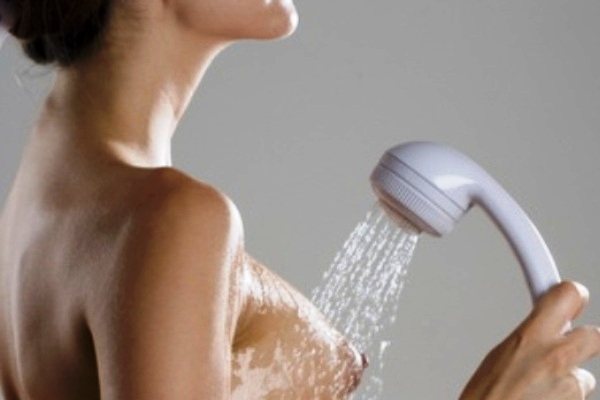

Frequent applications
The best way to deal with such a problem is to try to get the child to resolve the stagnation. If you apply the baby more often to the affected breast at the beginning of lactostasis, there is a high probability that he will cope with it. Before feeding, it is advisable to express a little milk - this will help the baby suck more actively.
In order for the sucking process to be most effective, an important rule should be observed - the area of compaction in the chest during feeding should be under the child’s lower jaw. In the case where the feeding position is extremely uncomfortable, for example, the upper part of the chest is affected, you can lie down with the baby on the bed in a certain way.

Compresses
They help soften the lump in the mammary gland during feeding, and also somewhat reduce pain. Depending on the compress itself, it may have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect.
The most effective and easiest to use is a napkin or towel moistened with warm water, which is applied to the sore chest. It is kept until it cools down. A cabbage compress is very common and quite effective for breast diseases. The cabbage leaf is beaten until the juice is released and applied to the sore spot. It is believed to help with inflammatory diseases of the mammary gland.
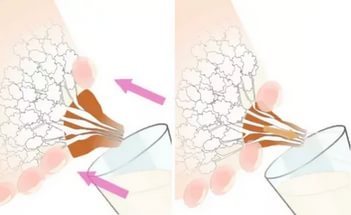
Pumping
If your baby’s help fails to dissolve a lump in the mammary gland while breastfeeding, you can try to do it yourself.
To do this correctly, you need to follow a certain technique that will not make the situation worse. If lactostasis has already occurred, and there is an excess of milk, you should express a little yourself after finishing feeding so that it does not stagnate in the breast for a long time.
excellent selection of tips for blocked ducts / lactostasis
1. Rest, get enough sleep, don’t be nervous - stress hormones inhibit the production of oxytocin. Drink a sedative - motherwort, hawthorn, valerian. Be careful, small children can react to a sedative after receiving it through mother’s milk. If the temperature is severe, bring it down with something compatible with breastfeeding - Tylenol, paracetamol, for example. 2. Try to find out and eliminate the causes of lactostasis. Check to see if the breasts are being pinched by an uncomfortable bra, grip, feeding position (the “uncomfortable” lobe is not being sucked out), sleeping in an uncomfortable position that compresses the chest, for example, on the stomach. 3. The duct can be clogged with a “white dot” - walk around with a cotton swab moistened olive oil on the nipple, hold the nipple in warm water or carefully pierce the white bubble on the top of the nipple with a sterile needle. After this, express or let the baby suck.4. Attach the baby as often as possible, avoid long night breaks in feeding. 5. Immediately before feeding, apply heat to the breast to expand the spasmodic ducts and facilitate the flow of milk. You can wet it with warm water, wring it out and apply a towel. Some midwives suggest applying it on the breast as an option. 40-50 minutes before feeding the flatbread: oil (fat) + vodka + honey 1 tablespoon + flour to the desired consistency, or grated apple + flour + fat. But you need to remember that alcohol compresses are not recommended. 6. Then a gentle massage . If there is no high temperature, it is very convenient to massage and express (no more than once a day) under a warm shower or while sitting in a warm bath, immersing your breasts in water. This way it’s easier to strain the right places: stagnant milk is much richer than usual, it will come out in “strings”, and sometimes these strings will float in the water for some time without dissolving. Try so that the milk begins to flow out of all the ducts (there are on average 6 of them). Place the baby on the expressed breast. 7. Place the baby’s chin in the direction of the seal. Then there is a greater chance that it will “break through” the blockage. Choose a position suitable for this - from the armpit, on all fours hanging over the child, lying in a jack - the child is on the pillow from behind the head.8. While applying, carefully massage the seals with your full palm towards the nipple or squeeze the breast, this improves the outflow of milk from the sore lobe.9. After feeding, use cold to reduce inflammation, swelling, and milk production. Depending on the severity of the condition, apply ice according to the scheme: 10 minutes ice, 20 minutes break, or once for no more than 20 minutes, stop sufficient time before feeding.10. Then or immediately spread cold cottage cheese from the refrigerator (not from the freezer) onto a bandage and apply it as a compress for at least 20 minutes until it begins to dry out and warm up. 11. Then, or instead, apply a cabbage leaf, you can break it with a hammer or prick the veins with a knife. You can wear it constantly, changing it as it fades and when it starts to warm up. Can be left overnight. But this may reduce your milk supply. Red cabbage is sometimes recommended.12. Apply a lotion of mumiyo, dissolved in water to the consistency of strong tea, to the sore spot until it dries. Apply with agents that reduce inflammation and swelling - traumeel C, homeopathic arnica ointment.13. As an option - magnesium lotions.14.As an option - massage the seal with homeopathic arnica ointment.16. Devices. Vitafone at home. Before feeding.17 At the clinic.Newman recommends an ultrasound. Dose “watts/cm, continuously, for 5 minutes. to the damaged area, 1 r per day up to 2 doses. With caution, according to some consultants, ultrasound is harmful to the mammary gland, and this procedure can only be done once.18. A folk recipe is to place a flatbread made of rye flour with cumin mixed with honey on the seal overnight for 6 hours (it is also recommended to use honey with caution, preferably once).19. .Diet. Drink sour drinks, avoid meat, fatty, and sweet foods for several days. , dairy, butter. Include beets, baked apples, dried apricots, prunes. 20. Homeopathy. Anti-inflammatory herbal preparations.21. Newman recommends lecithin for recurring lactostasis. 1200 mg 3-4 times a day. It is worth choosing the preparation carefully so that the lecithin is of good quality, it is better to choose egg lecithin, for example, moslecithin.22. Exercise: stand in front of the doorway, fists to your shoulders, elbows to the sides. You rest your elbows on the doorposts. Press for a few seconds, then sag, stretching the muscles running from the chest to the elbows. Repeat several times. Then you move your elbows higher on the jambs - press several times, sag. Then repeat the same with your elbows in the lower position. To overcome stagnation, as a rule, it is enough to do such exercises several times. Measures to overcome stagnation must be taken immediately. Systematically and in a comprehensive manner. Select what is suitable for this particular case. These measures should result in improvement. Stagnation should not last more than 2-3 days. List of “don’ts”: 1. Do not limit the total amount of fluid per day. But it is better not to drink a warm drink between feedings, but to drink before feeding, this widens the ducts, increasing the chances of “breaking through” stagnation. 2. Do not apply warm compresses between feedings, this can increase swelling, especially alcohol and camphor compresses - they make the receptors insensitive to oxytocin , making it difficult to release milk. 3. Do not strain the breast hard, kneading the lumps - there is a high risk of injuring the tissue, this aggravates the inflammation. 4. Do not let your husband dissolve the breast - there is a risk of infection, and the child (or breast pump) will do it better. 5. Do not express the sore breast “to the end” after feeding - this will increase the flow of milk, exacerbating lactostasis. 6. Do not drink teas with mint, sage and other remedies that reduce the amount of milk - then you will have to cope with the lack of milk 7. Do not randomly try all the tips in a row. Links: Technique for softening the areola https://users.iptelecom.net.ua/~vylkas/rps.html Jack Newman's website https://www.drjacknewman.com/ Mastitis and lactostasis (translation of D. Newman's article) https:// users.iptelecom.net.ua/~vylkas/newman/mastitis.html breast compression (translation of D. Newman's article) https://users.iptelecom.net.ua/~vylkas/newman/BreastCompression.html cabbage leaves, herbs, lecithin (translation of an article by D. Newman) https://users.iptelecom.net.ua/~vylkas/newman/herbslecithin.html Questions and answers from the La Leche League website https://www.llli.org//russian/FAQ .html Article about lactostasis https://rus.delfi.lv/news/delfi_woman/dom/article.php?id=16108100
Tags: GW
How to strain correctly
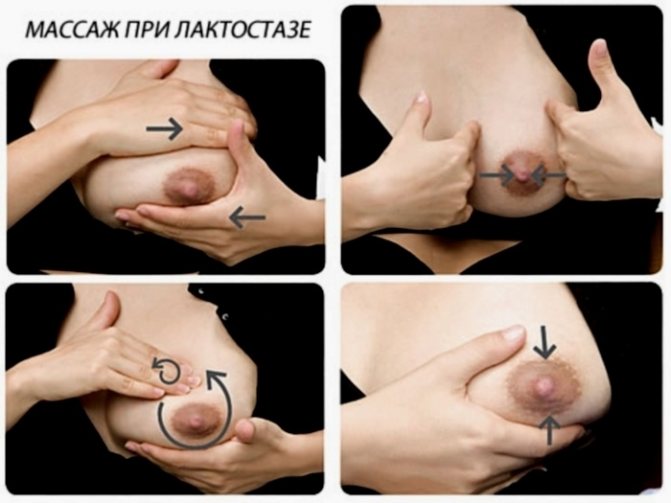
The technique of straining stagnation is not complicated. It should be remembered that this procedure should not cause significant pain. Excessive pressure and active massage should also be avoided. All movements should be soft and smooth.
Let's look at how to break up lumps when breastfeeding:
- Before pumping, prepare the breasts with heat and a little massage, and wash your hands and mammary glands well.
- The chest should be grasped as follows: the thumb is opposed to the other 4 fingers. For example, the thumb is on the top of the chest, and the other four support the chest from below.
- Your fingers should be near the edge of the areola. Pressure is applied not to the lobules of the gland, but to the edge of the areola, while slightly pressing it into the chest.
- The lump in the breast during breastfeeding, which is located under the thumb, will be cleared.
- If milk is no longer released, you need to massage the clogged part of the breast a little more and try again.
- You should not focus only on working on the seal; it is better to express the entire breast.
After feeding or pumping, apply a cold compress to your breasts to reduce milk flow. For the same reason, it is better to reduce the amount of fluid you drink at this time.
Mastitis
Lumps in the breasts while breastfeeding may be a sign of mastitis. Lactation mastitis occurs in women who are just starting to breastfeed or when they wean their baby. The reasons may be stagnation of milk, chronic diseases (sinusitis, sore throat, etc.), fatigue, hypothermia, improper care or cracks in the chest.
As soon as the baby is born, the woman begins lactation, but during this period more milk is produced than the baby needs, so swelling may appear in the mammary gland, which blocks the milk ducts. This is lactostasis.
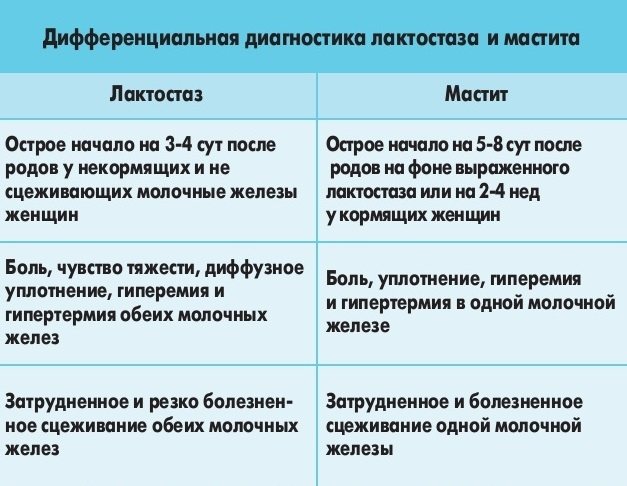
If a woman does not take any measures, she may develop serous mastitis, which has the following symptoms:
- temperature up to 38° C and above;
- heaviness and soreness of the mammary gland;
- milk flows poorly, often the child cannot get a drop of milk;
- the diseased breast differs in size from the healthy one;
- The mammary gland may turn red.
After serous mastitis, the next stage may occur - interstitial. At this stage, the symptoms become stronger, the breasts become hard, the temperature is high, the woman shudders, and joint weakness appears.
The lump in the breast when feeding the baby becomes painful, milk does not pass through the ducts, the baby refuses to eat, and it is impossible to express milk. If adequate treatment is not undertaken, within 2 days interstitial mastitis will turn into a purulent form, which requires urgent surgical intervention.
In this case, the temperature rises to 40° C, the breasts become very hard and painful, the woman has all the symptoms of intoxication (fever, thirst, chills, severe sweating), and pus may be released from the mammary gland. It is important to know that purulent mastitis is a life-threatening condition; you should immediately seek medical help.
What not to do with purulent mastitis:
- You cannot self-medicate. If the high temperature lasts for 2 days, there is no improvement in your condition, you need to go for an ultrasound.
- You cannot crush, press, or rub your breasts. Such actions will lead to increased swelling and the problem will worsen. Only a doctor can show you how to do a special massage.
- As with any other inflammatory process, breasts with mastitis should not be heated, heating pads should not be applied, baths, hot compresses should be made, even a shower should be at body temperature.
- You should not limit yourself to liquid; many believe that this way you can reduce the volume of milk. This is not so, the amount of milk will remain the same, but the symptoms of the disease will only intensify.
You must definitely try to feed the child. With feeding, the signs of mastitis may not only decrease, but also disappear.
What not to do
There are certain actions that should be avoided so as not to aggravate lactostasis and not provoke the development of mastitis:
- Alcohol compresses should not be used. They inhibit the production of the hormone oxytocin, which helps effectively remove milk from the mammary gland. The consequence is heavy milk production, the baby gets tired of sucking it and doesn’t get enough, and the likelihood that lactostasis will go away also decreases.
- Hot compresses are contraindicated, especially at high temperatures, when there is a high probability that mastitis has begun.
- Aggressive massage should not be used. Inexperienced or too active actions near the lump can further injure the mammary gland and form new lumps in the mammary glands. In addition, if suddenly mastitis has already begun, pressing on the bag of pus can lead to its rupture.










