A sharp decrease in the immunity of a nursing mother after a successful delivery makes her body vulnerable to bacteriological and viral microorganisms that contribute to the development of various pathologies. In more than 75% of cases, young mothers are faced with a disease such as candidiasis, or thrush, the causative agents of which are mycotic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. In addition to the vaginal form of candidiasis, women quite often encounter thrush on the mammary glands during breastfeeding, which can be quite problematic to diagnose in a timely manner. Let's take a closer look at what symptomatic signs are caused by nipple thrush, why it appears, why it is dangerous and how it is treated.
Symptomatic signs of pathology
Breast candidiasis often develops with hidden symptomatic signs, making its differential diagnosis from other diseases much more complicated. In order not to start candidal pathology and not infect the baby, you should know what incipient thrush on the nipples looks like.
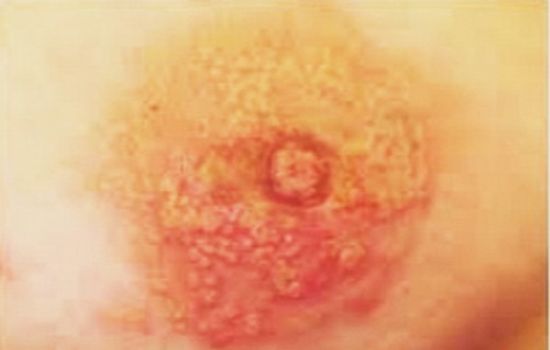
Its first symptomatic signs are:
- the appearance of microcracks and bright red spots in the areola area;
- swelling in the nipple area;
- peeling and the formation of thin films in the areola area are observed;
- less often, a whitish coating may form, as well as small blistering rashes near the nipple, and along the entire perimeter of the areola;
- the occurrence of pain in the nipple area while feeding the baby, as well as when the nipples come into contact with underwear;
- the appearance of varying degrees of severity of itching.
It is important to remember that the symptoms of breast thrush during breastfeeding can be combined with symptomatic signs of developing vulvaginal candidiasis in the vaginal cavity, which signals an extremely low level of the immune defense system.
Symptoms of thrush in a child
Thrush on the nipples is a fairly contagious pathology that can be transmitted from mother to child during breastfeeding. Diagnosing thrush in a baby is much easier, since the pathology in the child manifests itself with pronounced symptomatic signs.
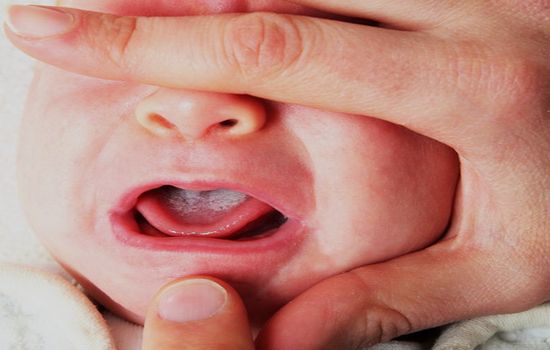
- First of all, a nursing mother notices the appearance of white plaque in the baby’s mouth, which can appear with varying intensity, from small white spots to an impressive white layer with a dense consistency that affects the entire oral cavity of the baby.
- With an intensively developing pathology, the behavior of the baby may change, who becomes whiny, irritable, and often refuses to eat (against the background of acute pain during breastfeeding).
- A child may develop small ulcers with a bright red color in the groin area and axillary folds, which do not heal over a long period of time.
- It is possible that the baby's temperature may increase.
Candidiasis can manifest itself in the form of developing irritation on the surface of the butt, manifested by a small blistering rash that does not go away with the use of various diaper rash remedies.
Blood in breast milk - what could it be?
Sometimes during lactation, nursing mothers notice unusual discharge from the breasts. Such discharge may have a reddish, pinkish or rusty tint. You should always pay close attention to such discharges, because... they may be a sign of blood in the milk.
Most often, blood gets into the milk from external damage to the nipple and areola, for example, with deep cracks or abrasions in the nipple area, the blood often mixes with the milk and turns it pink. In this case, the reason for the presence of blood in the milk lies on the surface and usually does not raise questions, but only requires correction of the baby’s attachment to the breast and additional treatment of the nipples for the speedy healing of cracks.
However, there are also less obvious reasons for the appearance of blood in milk, when there is no visible damage to the breast. Different studies on this problem describe different clinical cases, for example, one mother with severely inverted nipples had painless bleeding from the breast after wearing milk collection pads in late pregnancy. After she reduced the time she wore the pads, the bleeding stopped [2].
Another reason for the appearance of blood in milk may be damage to the capillaries inside the breast tissue due to careless manual expression or improper use of the breast pump [4].
There is also a study that says that the milk of some breastfeeding mothers during the first weeks after birth can resemble rusty water, which can be seen in water pipes that have not been used for a long time. This phenomenon is called “rusty pipe syndrome” . According to researchers, a similar syndrome occurs more often in first-time mothers during the early stages of lactogenesis and is most often not associated with any discomfort [3]. In addition, dairy farm owners report the appearance of “rusty” milk in cows calving for the first time. This is thought to be due to slight internal bleeding from the edema during the cow's first let-down [4].
O'Callaghan, who also studied rusty pipe syndrome, reports 37 clinical cases of its manifestation [5]. The earliest manifestation of the syndrome was noted during the fourth month of pregnancy and in most cases was associated with mechanical compression of the breast during the prenatal period. With this syndrome, blood in milk can appear in both breasts and disappears, as a rule, within 3-7 days after the start of lactation.
Bright red bleeding from the breast in the absence of pain or cracked nipples indicates that the nursing mother needs to see a doctor (mammologist or surgeon) as soon as possible. First of all, the study is carried out for intraductal papilloma.
An intraductal papilloma is a small, benign, wart-like growth on the inside of the milk duct that may bleed as it grows or breaks down. Usually, no lumps or swelling are palpable in the chest, and there may be no discomfort. Typically, with intraductal papilloma, bleeding is observed only from one breast. Often the bleeding stops spontaneously, without any treatment [2], but nevertheless, a nursing mother should still consult a doctor to identify its causes.
To identify the causes of blood in milk in the absence of soreness and cracked nipples, it will be useful to conduct a cytological examination, mammography, and ultrasound [1]. If, based on the results of the study, there is a need for surgical intervention, the doctor will remove the formation inside the duct. After this, the formation will be histologically examined to confirm that it is an intraductal papilloma, and not something more serious, such as an intraductal malignant tumor .
In a situation with bleeding from the breast of unknown origin, a nursing mother can gently express her breasts to maintain lactation until the cause of the bleeding is identified. It is advisable to choose hand expression and carefully follow the correct gentle expression technique, as rough expression or expression with a breast pump can aggravate the problem.
In any case, if the mother notices that the child accidentally received milk with a small admixture of blood, there is no need to panic - the baby will not be harmed by small amounts of serous-hemorrhagic discharge [2]. A relatively large amount of blood in milk can lead to the baby regurgitating bloody milk.
Call a consultant Do you have any questions? +7 (812) 956-3-954
Literature:
Literature:
- Berens PD , Prenatal, intrapartum, and postpartum support of the lactating mother. In: Schanler, R. J., ed. Breastfeeding, Part II: the management of breastfeeding, Pediatric Clin No Americal 48:365–75, 2002.
- Breastfeeding and Human Lactation (Jones and Bartlett Series in Breastfeeding/Human Lactation) by Jan Riordan Publisher: Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 3rd Edition, 2004. Pages: 819.
- Marmet C., Breast assessment: a model for evaluating breast structure and function. Presented at: La Leche League International Annual Seminar for Physicians, Boston, July 11–13, 1990.
- Mohrbacher N., Stock J., La Leche League International, The Breastfeeding Answer Book, Third Revised Edition, 2008.
- O'Callaghan MA, Atypical discharge from the breast during pregnancy and/or lactation. Aust NZ J Obstet Gynaecol 21:214–16, 1981.
Alena Lukyanchuk Psychologist, lactation consultant, member of ILCA (The International Lactation Consultant Association)
Alena Korotkova, clinical psychologist, lactation consultant.
Causes of pathology
Breast thrush in a woman can develop due to various reasons, the main of which is an intense decrease in the body’s immune defense system and disruption of the microflora of the affected area. First of all, such disorders occur against the background of hormonal imbalance that develops during the period of bearing a child, as well as during the process of childbirth. In addition, there are other reasons that contribute to the development of mammary thrush during breastfeeding:
- long-term use of antibiotic drugs that disrupt intestinal microflora;
- use of glucocorticoids;
- progression of other chronic diseases, leading to a sharp decrease in immunity;
- increased level of skin moisture.
Cracked nipples
Keeping the whole body and its vulnerable areas clean and using ointments that heal wounds will help here. Such drugs prevent the growth of formed cracks and promote restoration (regenerate) the skin. Such treatment is necessary, since through cracks in the breast, an external infection can enter the outlet openings in the nipple, and through them gradually end up inside the mammary gland itself. All this will inevitably lead to quite serious and complex diseases. And many of them may be accompanied by various bloody discharges from the chest, including bloody ones.
When diagnosing diseases of this nature, the first question that arises and gives impetus to the search for the cause is why is there blood coming from the chest?
The reason for the occurrence of cracked nipples can be not only in wearing incorrectly selected underwear. There may be other reasons why the breasts crack and bleed. Here it is worth talking about improper care of the nipples while feeding the baby, and failure to take the necessary measures in case of excessive dry skin.
Possible complications
Progressive thrush on the breast can cause a decrease in the nutritional value of breast milk, as well as in the amount of its formation, which occurs against the background of a feeling of pain in the mother while feeding the baby. Moreover, if the newborn has the main symptoms of mammary thrush and a whitish coating has formed in his mouth, he may be reluctant to breastfeed or even lose his appetite.
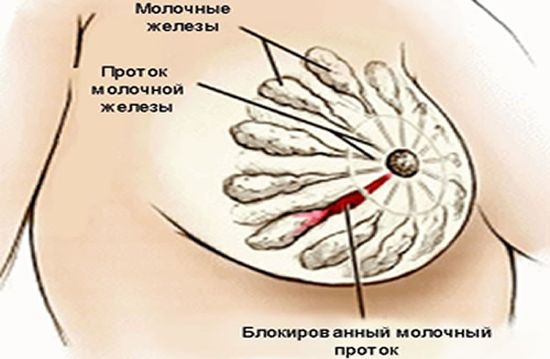
If nipple candidiasis is not eliminated in a timely manner, the progression of the pathology can cause the development of mastitis in a nursing mother, as well as lead to signs of blockage of the milk duct and the formation of lactostasis, which is considered one of the serious complications of mammary thrush.
In a child, thrush can provoke dysbiosis and progression of tonsillitis. Therefore, nipple thrush in a nursing mother should be promptly diagnosed and treated.
Possible risks and consequences
If a breast hematoma is small, it is usually not dangerous. However, it may take a couple of months to treat even a small hematoma if it is located on a woman’s chest. This is due to the structural features of this organ. There is little muscle tissue in the chest, but there are many mammary glands and alveoli, the regeneration of which occurs somewhat more slowly than in muscles.
If the bruise is very large and deep, then it can cause some problems that impair the function of the mammary gland. An old hematoma can lead to the development of nodular mastopathy, so any bruise should be treated immediately after it is identified. If a hematoma occurs in a woman with breast cancer, it can accelerate the growth of the tumor.
In cases where a bruise appears in a nursing woman, it can block the milk ducts, compress the alveoli, which will lead to lactostasis or even mastitis, therefore, if a hematoma is detected during breastfeeding, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible for consultation, examination and treatment .
Diagnostic methods
The initial diagnosis involves taking a history and examining the woman’s mammary glands. Then laboratory research methods are prescribed, for the purpose of which a scraping from the affected nipple and a sample of breast milk are taken from the woman. The taken biomaterials are subjected to microscopic examination, during which the type of causative agent of the developing infection is identified, after which the attending physician develops an individual treatment regimen.
To confirm the results obtained, a general blood test is prescribed, as well as blood to determine sugar levels. As an additional examination, the patient may be prescribed an immunogram.
Diagnostics
What needs to be examined?
The mammary gland of a man or woman is subject to examination. In addition, the patient will need to undergo a blood test to determine the level of white blood cells and measure hemoglobin levels.
Attention! A blood test cannot refute or confirm more serious diagnoses such as breast cancer, but it still gives a general picture of the processes occurring in the body.
A biochemical blood test is also used , which clearly shows the presence of tumor markers (proteins and antigens).
During the growth of a cancer cell, the process of their formation is most active. Using spectral analysis, the doctor can accurately determine the cause of the pathology.
Genetic blood analysis is also useful , which reveals a predisposition to breast cancer at the genetic level.

How to examine?
Examination of the mammary glands is carried out using instrumental methods.
The following diagnostic tests are used:
- Mammography . The patient is exposed to a small dose of radiation in the chest area. Using this method, developing pathologies can be detected already at the first stage of the disease. The method is very old, but widespread.
- Digital mammography . Some mammologists prefer to use a newer and improved diagnostic method in their practice, which uses semiconductor detectors. They ionize radiation and convert it into an electrical signal.
- Ultrasound . Fast, painless and safest way of examination. Ultrasound examination helps to detect breast lumps and cysts at the very initial stages of their formation. Ultrasound allows early detection of malignant tumors.
- Ductography . It is carried out by injecting a contrast liquid into the ducts of the mammary gland, which allows you to see any pathological processes in the mammary gland. A fast and modern method of ductography most accurately determines the location of a benign or malignant tumor, and also gives a specific idea of its size.
Methods for diagnosing breast cancer at an early stage are described in the video:
Basics of pathology therapy
In order to eliminate unpleasant symptoms as quickly as possible and restore lactation processes, a woman should know how to treat thrush on the nipples and what needs to be done for this.

In order to quickly and effectively cure nipple thrush, it is recommended to follow a number of the following rules:
- Balance your diet and strengthen the body's immune defense system. Do not consume confectionery products, foods containing gluten and yeast. It is recommended to diversify your diet with vegetable oils, fresh vegetables and fruits, seafood, and also take vitamin complexes.
- Before and after each feeding, be sure to wash your hands with soap.
- It is recommended to carry out feeding procedures somewhat more often, but with a duration of no more than 10-15 minutes, and it is better to put the baby first on the breast, which is less affected.
- If, when feeding, a woman is bothered by severe painful sensations from a prolonged form of thrush on the nipples, against the background of which the process of breastfeeding the baby becomes unbearable, the milk should be carefully expressed and fed to the baby from a bottle. If you use a breast pump to express milk, you should wash and boil it after each pumping procedure.
- After each feeding procedure, you should wash both breasts with warm water without household chemicals and dry them naturally, without wiping with a towel.
- Avoid the use of synthetic underwear; it is recommended to give preference to clothing made from cotton fabric.
- If there is a vaginal form of candidiasis, then you should definitely treat it.
- At the same time, treat the baby by treating its oral cavity with disinfectants prescribed by the attending physician.
It is important to know that during lactation, if a woman develops mammary thrush and the child has no symptoms of infection, both the mother and her baby should still undergo treatment.
Drug therapy
In order to cure nipple candidiasis, it is necessary to use drugs of the etiotropic therapy type. The selection of medications should be carried out with your doctor, since many medications for thrush are not recommended for use during breastfeeding.
Bloody discharge in nursing mothers
Mothers also often notice that colostrum or milk gradually changes in consistency
Young mothers who have recently (before 3 months) given birth to a baby pay attention to the nipples. The milk can be traditional white or yellow
This is not a reason to worry, since lactation is restored within 3 months from the date of birth of the child.
If you notice that there are black or blue dots in the milk that look like small strings, do not be alarmed. This is not a disease or pathology. The mammary gland touches the walls of the channels in the milk ducts.
More transparent milk is called “hind milk”; it appears after the baby expresses or sucks out the main portion (50-70 ml).
This type of milk is suitable for supplementary feeding of the baby after porridge, vegetables and fruits. The peculiarities of the mother’s body should also be taken into account, since blood clots may also appear during feeding.
The reasons for their occurrence are justified by unstable lactation, when a woman tries to independently express more milk with her hands or a breast pump, causing injury to the ducts. In this case, blood in breast milk can occur due to mechanical damage, as well as due to a viral and infectious disease. If you squeezed the nipple too much or grabbed too much of the areola while expressing, there is a chance that the skin has cracked. The resulting wound bleeds, causing blood to leak into the milk. If there is blood inside the breast, an ultrasound scan should be performed to identify hollow and dark areas in the fatty tissue area of the breast.
There are other reasons that lead to bleeding, and they are associated with the onset of the third trimester of pregnancy. Bloody spots can be excreted in milk, which is not dangerous for women.
ethnoscience
Thrush of the mammary glands can also be effectively treated with traditional methods, the most effective of which is considered to be treating the affected areas with a soda solution. To prepare a “healing” solution, you should dissolve a teaspoon of baking soda in one glass of warm boiled water.
The resulting product should be used to treat each breast after feeding, as well as the baby’s oral cavity using a cotton-gauze swab. After treating with a soda solution, it is not recommended to wipe your breasts with a towel; you should let it dry naturally, and then lubricate it with a moisturizer.
The development of thrush on the mammary glands is a rather unpleasant and dangerous pathology. Therefore, to prevent it, you should carefully monitor the body’s immune defense system, and also carry out prevention of vaginal candidiasis before conceiving a child.