There are a large number of women facing problems associated with breast diseases. Such problems are typical for any age.
Breastfeeding, this important period, causes many problems. About 25% of women have problems such as mastitis and lactostasis. What are they and why do they occur?
Characteristic features of mastitis and lactostasis
A woman is recommended to breastfeed for 6-9 months. But when faced with diseases of the mammary glands, many refuse to breastfeed due to certain manifestations of the disease: pain, discomfort and other unpleasant symptoms.
Many doctors believe that there are no clear differences between mastitis and lactostasis. After all, the appearance of one disease does not happen without the other; it turns out that they are interconnected. But still, these are two different diseases that should be distinguished.
In diagnosis, lactostasis is distinguished, which transforms into lactation mastitis. For this, one condition is necessary: an inflammatory process in the mammary gland. If it has joined lactostasis, there is a possibility that it will turn into mastitis in the near future.
Consequences of mastitis
With timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment, serious consequences can be avoided. An attempt at self-medication can aggravate the inflammatory process and lead to the development of purulent forms, or more precisely, to the formation of abscesses, phlegmon (spread purulent inflammation of the fiber, connective tissue) and the formation of fistulas in the mammary gland. Such conditions require surgical intervention. Rapid damage by microbes, low immune reactivity of the body of a nursing mother, late seeking specialized medical care and inadequate treatment of the disease become the causes of the development of sepsis against the background of lactation mastitis and can lead to death.
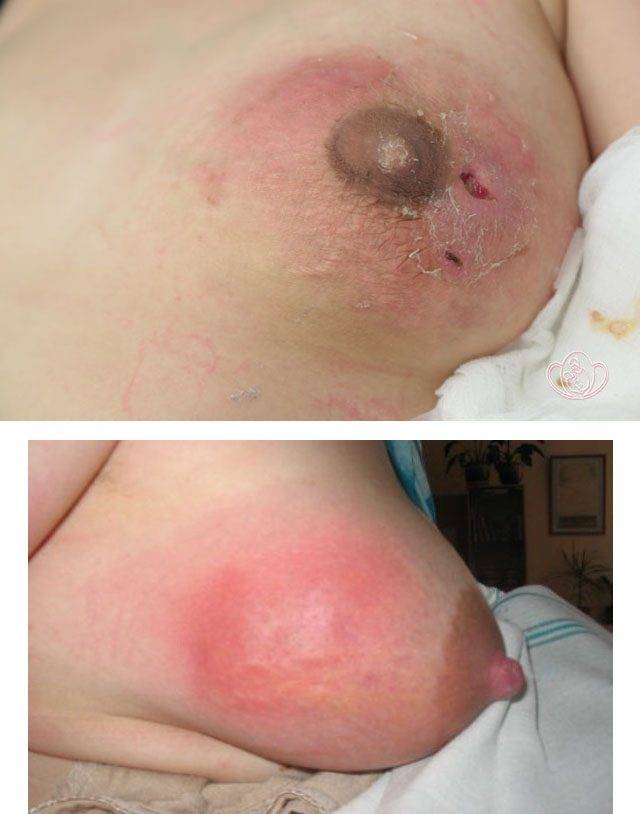
Lactation mastitis can cause sepsis and death
Main characteristics of lactostasis
This pathological process is characterized by blockage of one or more lobes of the milk ducts. In this case, the process of milk release becomes impossible or difficult. Discomfort appears, and with prolonged blockage, pain occurs, the gland turns red and swells. If you press on the gland, milk will flow from the unclogged ducts, but the affected ones will not secrete milk.
Such stagnation can occur in a woman during any period of breastfeeding, but is often typical for mothers who are just establishing breastfeeding.
Lactostasis develops when:
- Increased sweating - milk thickens, which becomes an obstacle to feeding the baby; Not all of the milk comes out; it remains in those lobes of the breast in which the blockage occurred.
- If the baby is not latched correctly, the outflow of milk is disrupted, as a result of which the breast does not empty and stagnation occurs.
- Lactostasis can occur when wearing tight underwear, so nursing women should choose loose underwear.
- Milk stagnation can occur due to blows and injuries to the breast. A woman needs to be careful not to injure the mammary gland. Impacts can lead to disastrous consequences and pathologies more serious than lactostasis.
The main difference between this pathology and other breast diseases is that, against the background of chest discomfort and elevated body temperature, the woman’s condition is satisfactory. But under no circumstances should we remain inactive. If measures are not taken to eliminate the disease, non-infectious mastitis may develop.

Comparison of signs of diseases
The symptoms of these two diseases are almost the same, blood tests are similar in both cases, how to recognize them?
Mastitis can be lactation or non-lactation, that is, a nursing mother is more likely to get it. Lactostasis occurs only during the lactation period, that is, when the baby is breastfeeding, and goes away with treatment after a couple of days.
Mastitis is a consequence of untreated lactostasis and begins with significantly pronounced symptoms of inflammation. There are three stages in the development of mastitis:
- Serous – signs of intoxication of the body appear.
- Infiltrative – prolonged fever and increased inflammation.
- Purulent – a purulent lesion is added.
Lactostasis differs from mastitis in the absence of inflammation, normal body temperature and the normal general condition of a nursing woman. With mastitis - a sharp rise in temperature, weakness, headache, chills or fever, the general condition is quite serious.
Since lactostasis imperceptibly flows into mastitis, it is very difficult to understand exactly when one disease ended and the second began. However, in the first case, conservative treatment is used, and in the second, most patients undergo more complex surgical treatment.
What to do if chest pain is caused by mastitis, watch the following video:
Women often confuse two diseases such as mastitis and lactostasis, however, there are certain differences between them. It is very important to know how to distinguish lactostasis from mastitis
, since unlike lactostasis, which nursing mothers can cope with on their own, antibiotics will be needed to treat mastitis.
Lactostasis
- This is stagnation of milk in the mammary glands.
It occurs only in women during breastfeeding. Mastitis
is inflammation of gland tissue. Mastitis can develop in both women and men.
Lactostasis develops due to blockage of the milk duct. At the same time, milk accumulates in it, bursting the lobule and causing inflammation. Inflammation and swelling of the tissues, in turn, further complicates the outflow of milk, so you should not expect that lactostasis will go away on its own. The main causes of lactostasis are:
- Rarely feeding the baby.
- Incorrect attachment to the breast.
- Holding a certain part of the breast while feeding.
- Tight, uncomfortable bra.
- Chest trauma, stress.
1
Mastitis
This is a more serious disease of the mammary glands than lactostasis. It should be borne in mind that the symptoms of the disease may indicate such a dangerous breast disease as mastopathy; their symptoms are similar. Therefore, only a doctor can determine the type of disease.
Breastfeeding, as this disease is also called, develops due to the same reasons as lactostasis. The main ones are: cracked nipples and stagnation of milk in the breast. The difference is the infection in the gland. Most often these are staphylococci and streptococci. When ingested, they cause inflammation of the mammary glands.
Penetration into the mammary gland can occur due to cracks in the nipple due to improper attachment of the baby. The source of infection is dirty hands or laundry.
Mastitis can also develop due to other reasons:
- chest injuries
- existing chronic diseases
- imbalance of hormones in women
Similarities between lactostasis and mastitis
These two diseases of the mammary glands are similar to each other not only in the symptoms of the disease, but also in the causes of occurrence:
- poor breast hygiene during feeding
- improper care of the glands
- frequent stagnation of milk, which remains unattended;
- improper attachment of the baby
- injuries and compression of the glands
- chest hypothermia
- viral infections
The manifestations of these diseases also have similarities:
- feeling of chest fullness
- discomfort turning into pain
- redness of the gland
- the mammary gland feels dense and hot to the touch
- there are knots or lumps due to stagnation of milk
- There is pain when feeding or pumping
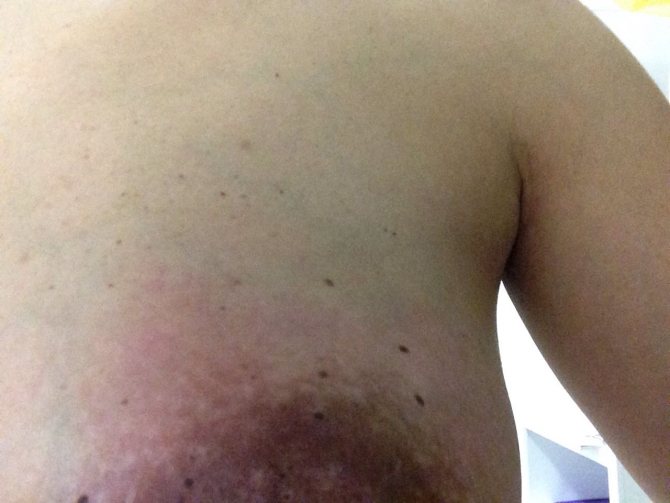
LACTOSTASIS
What is this?
Lactostasis is a blockage of the milk duct.
A woman's breast is divided into several lobes (15-25), each lobe emerges through a duct in the nipple. If one of these ducts is pinched, the release of milk becomes difficult and a kind of milk plug is formed, which does not allow milk to flow well out of this duct. The main causes
of lactostasis are poor emptying of the breast, often associated with improper latching of the nipple, limiting the baby’s stay at the breast, holding the breast while feeding with “scissors” (the nipple between the index and middle finger, the index finger pressed into the chest.) or with fingers, a tight bra, sleeping on the stomach, infrequent feedings, stressful situations.
Signs of lactostasis:
a lump the size of a nut or larger is felt, hard to the touch, often - redness of the skin over the tubercle and, possibly, painful when touched; looking in the mirror, you can notice a heterogeneous coloring of the chest, redness of any area; there is pain in one of the chest segments. The state of health may not change, but sometimes lactostasis is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and chills. Lactostasis can appear in a nursing mother at any feeding period
Fighting lactostasis.
If lactostasis begins to mature in the breast, you need to put the baby on it as often as possible. (if there is stagnation in certain lobes, suitable positions for feeding are selected, the child’s chin should be directed towards the place of stagnation). Sometimes it is necessary to express the breast BEFORE feeding and attach the baby to the breast... Sometimes it is necessary to massage the segment with lactostasis and express. The easiest way to warm up is to place a hot, wet napkin (towel) on the affected segment 5-10 minutes before feeding or pumping (or a warm shower).
Lactostasis in itself is not a dangerous thing; illiterate actions to overcome it are dangerous. You should not stop feeding the affected breast, even if you have a very high fever. The painful lump should not be left unattended during the night break. If there is no guarantee that the baby will wake up on his own in 2-3 hours, it is better for the mother to use an alarm clock to provoke the baby to suck every 2 hours. Alcohol compresses should not be used. You cannot “break stones” and massage your breasts with force. You can’t ask your husband to suck on his breasts; adults suckle very differently, and the flora in your hubby’s mouth is unlikely to add health. if you are not allergic to honey, you can spread a thin layer on the affected area and apply a cotton napkin (or cabbage leaf) over the top, keep it for up to 2 hours, if honey gets on the nipple area, wash it off before feeding; It is better not to give honey to a baby under one year old.
The difference between mastitis and lactostasis
It is generally accepted that mastitis does not occur without lactostasis, however, these two diseases will differ from each other. The main difference is their symptoms:
- the main sign of mastitis is the presence of elevated body temperature, which is an indicator of the inflammatory process in the gland
- general condition worsens: weakness, poor appetite, fever and chills, at high temperatures - headache
- severe pain and heat in the gland
- mastitis has an acute onset and pronounced symptoms at the very beginning
- pumping or feeding does not provide relief
- With mastitis, the nearby lymph nodes also become inflamed
- the duration of the disease is more than 3 days, whereas with lactostasis the duration of the disease is no more than 2 days

What to do at home after seeing a doctor

- You need to continue to put the baby to your breast. If the baby cannot cope with the compaction, you need to resort to additional pumping.
- You need to express milk as gently as possible so that there is no pain, which increases breast swelling.
- A very important measure is applying cold, which relieves swelling well. Often it is swelling that aggravates the situation, interfering with the release of milk. Take something cold from the freezer, wrap it in a towel and apply it to the painful area for 10 minutes.
- Often women apply a cabbage leaf to their breasts. But in fact, it simply replaces the cold with something. The cabbage leaf does not draw anything out, but simply cools until it heats up from the body.
- Warming compresses with honey and alcohol should never be used at fever.
- Some decongestant ointments can be used - consult your doctor.
- Do lymphatic drainage massage, which helps relieve swelling and improves milk flow. This is a soft stroking massage from the nipple to the periphery of the breast.
Lactostasis is a blockage of the milk duct. As a result, a lump appears in the chest, it becomes painful, the skin over the hardened area turns red, and the body temperature rises sharply (sometimes up to 40 degrees). The disease can occur due to mechanical compression of the breast, improper attachment of the baby to the breast, feeding according to a schedule and in a position that is uncomfortable for the mother.
In this case, you cannot stop breastfeeding. You should not apply compresses, especially alcohol-based ones, you should not pump for a long time, take medications that are aimed at reducing lactation, and it is not recommended to massage your breasts with a warm shower. It is advisable to ensure yourself eight hours of sleep, do not reduce the amount of fluid, and eat well.
During treatment, it is advisable to offer the baby the sore breast more often than the healthy one. During feeding, you can massage the lumps on your breasts using circular movements. After the procedure, you can apply an iodine mesh to the sore spot. If lactostasis has not gone away after three days, you should contact a mammologist and gynecologist.
Mastitis is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the mammary gland. It can appear as a result of untreated lactostasis or independently. In addition to the reasons that provoke the occurrence of lactostasis, mastitis can be due to trauma to the nipples, the severe psychological state of the mother, or infections against the background of reduced immunity. With mastitis, the body temperature remains at 38 degrees. Chest pain is sharp, the skin turns red. Until pus is released from the chest, it is necessary to apply the same measures as in the treatment of lactostasis. If fluid appears from the chest in the form of a thin green stream, you should call a doctor and start taking antibacterial drugs.
Lactostasis is most often the source of the development of mastitis. The disease without previous lactostasis occurs rarely. To prevent the appearance of mastitis in any of its manifestations, you need to follow the same preventive measures.
Unlike lactostasis with mastitis, expressing the lobule does not bring relief, although the degree of pain is quite comparable. This does not mean that expressing, especially with purulent mastitis, is impossible. On the contrary, it is this process that becomes the main therapeutic measure, because most of the pathogenic microorganisms are lost with milk. If pain after pumping with lactostasis goes away in one to two hours, then with mastitis they persist for a day, and with purulent forms - for a longer period of time.
Lactostasis is a stoppage of movement through the ducts (stagnation) of breast milk, usually occurring in the first weeks of feeding a newborn. Primiparas are more likely to suffer from this pathological condition. The disease usually occurs between the first three days and six weeks of breastfeeding. The consequences of lactostasis are the multiplication in an excellent nutrient medium of microbes that have entered through the cracks of the nipples into the gland, and the formation of purulent inflammation.
How to distinguish lactostasis from mastitis? The first is a non-inflammatory condition, with no signs of inflammation. When there is redness of the skin of the gland, its swelling, severe pain and induration, an increase in local temperature in the area of induration of the relatively healthy gland, deterioration in general well-being. Mastitis requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of diseases
As a rule, the diagnosis of “lactostasis” can be made by a woman herself during examination and palpation and no additional examinations are required. If you suspect mastitis, you should consult a doctor.
The mammologist will conduct a thorough examination: examination and palpation of the breast, collecting an anamnesis of the disease and prescribing additional diagnostics. It is necessary to take a general blood test to confirm the presence of an inflammatory process, as well as undergo an ultrasound of the mammary glands.

Methods for treating mastitis
It is very important to be able to recognize this disease as early as possible. The earlier this can be done, the faster and better treatment can begin.
It is necessary to empty the breasts either by pumping or feeding. Many women are afraid of infecting their baby and refuse to breastfeed. At first, you can and even need to feed. This does not pose any danger. The only contraindication will be the prescription of antibiotics for treatment.
No matter how painful it is, it is necessary to empty the sore chest, otherwise the situation will worsen. To do this, you should first place the baby on the inflamed breast to completely empty it. Then, if necessary, apply it to a healthy one.
After pumping, apply ice wrapped in cellophane and cloth to the breast for 10-15 minutes. Before feeding, a woman is recommended to take 4 drops of Oxytocin for better milk flow.
The high temperature must be brought down. To do this, you should take medications containing paracetamol or ibuprofen. If the causes of mastitis are cracks in the nipples, then they must be lubricated with ointments: Bepanten or Purelan-100.
If the body temperature is more than 38 degrees and it lasts for more than 3 days, the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics necessary in this situation. In some cases, anti-inflammatory drugs may be additionally prescribed. This is a significant difference in the treatment of lactostasis and mastitis.
In advanced cases of mastitis, when an abscess (ulcer) forms, surgery is necessary to open it. In this case, breastfeeding is stopped for the duration of treatment, but it is necessary to express. After recovery, you can resume feeding.
Pumping during mastitis is a must. There is no need to neglect them. If this manipulation is not carried out, milk may flow poorly and breastfeeding in general may be disrupted, not only in the sore breast.
If you have a fever, you need to drink plenty of fluids. Massaging the breasts with smooth movements, kneading the lumps, gives a good effect.
When to visit a doctor
If lactostasis, the symptoms of which are described above, makes itself felt only by minor thickening and soreness in the breasts, then you should carefully express the breasts, do a massage and apply a compress.
If a nursing mother has a fever and the lump does not decrease, she should immediately consult a gynecologist. In such situations, physical therapy is often performed.
If a woman shows signs of mastitis, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics. Drugs are always selected individually and may be compatible with breastfeeding. A nursing mother should not self-medicate if serious complications occur.
- Breast pain during breastfeeding: causes and methods of treatment.
- Lactation crisis.
- How to increase the fat content of breast milk?
Lactostasis therapy
There is a slight difference in the treatment of lactostasis and mastitis. Since there is no deterioration in well-being and the body temperature does not increase, the main actions should be directed towards emptying and breast massage.
Doctors advise doing compresses. Traumeel ointment has a positive effect.
Feeding should be frequent, many obstetricians and pediatricians agree with this, but the famous doctor Komarovsky thinks otherwise. In his opinion, a child should eat no more than once every two hours.
A woman should rest and get enough sleep. Sleeping on the stomach is not recommended, as the mammary glands are compressed, which contributes to the appearance of lumps in the breasts and stagnation of milk.
When the massage is carried out correctly, an effect is observed in the form of disintegration of nodes and improvement of the outflow of milk in the ducts. It is possible to perform a massage at home.

Massage for lactostasis
It is advisable to massage your breasts twice: before and after feeding. When rubbing, it is better to use cream or baby oil, to which you can add sage oil to enhance the effect. Sage reduces the amount of milk, so women who have little milk (hypogalactia) should not use it.
You need to take the sore breast with one hand and start massaging with the other. It is carried out from the edges to the nipple. Movements are light and smooth. It is necessary to identify and feel the nodes and pay more attention to them when rubbing. You can finish the massage with a pat, stand up and shake your chest a little.
If severe pain is observed, the massage should be stopped and seek help from a doctor. There is discomfort during this procedure, but it is small.
Reviews from women who regularly undergo massage for lactostasis indicate its effectiveness. It helps get rid of heaviness in the gland and the feeling of fullness.

Prevention
To prevent a woman from having problems with the mammary gland during breastfeeding, she needs to follow a few simple rules:
- wash your chest with cool water
- wash your hands before feeding
- do not overcool the glands
- avoid injury and shock
- Feed only when the baby requires it
- do not wear compressive garments
- examine the breast for cracks in the nipple
- master the technique of proper breastfeeding
During breastfeeding, a woman should take care of herself and clearly understand that complete and high-quality feeding and the health of her breasts will depend only on herself.
Reducing temperature during lactostasis in a nursing mother, first steps
Experts explain: as soon as the mother copes with the stagnation of milk, the temperature will decline and return to normal. Lactation consultants and doctors recommend using various methods to relieve the condition:
- frequent latching of the baby to the breast;
- pumping;
- cold compresses.
If there is no positive effect, the woman will become worse, only then can she resort to medication.
Putting the baby to the breast
Of course, the best assistant for blocked ducts is a baby. Frequent breastfeeding is a sure way to cope with stagnation of milk. But lactostasis leads to the fact that the mammary gland becomes very hard (stony), and the child is simply unable to latch onto the nipple. Therefore, before giving him the breast, it is recommended to express a little to make sucking easier for the baby.

The best way to cope with lactostasis is to put your baby to the breast more often
It is necessary to choose a feeding position so that the baby's chin is directed towards the seal. In this case, during sucking, the main emphasis will be on the lobe where the blockage occurred. The child will quickly resolve the problem area and relieve the mother of lactostasis.
Expressing breast milk
One of the main ways to combat lactostasis is to express breast milk. This procedure helps open the milk ducts and facilitates the movement of nutrient fluid. Experts advise doing it manually. This way, a young mother will achieve results much easier and faster.
Many women ask whether it is possible to use a breast pump to express? Experts explain that at the first stage, with this product, the mother will not achieve the same effect as with her own hands. The fact is that during the manipulation it is necessary to influence one specific area, but this cannot be done with a breast pump.

During the treatment of lactostasis, it is not prohibited to use a breast pump, but manually achieving a positive effect will be faster
The rules for pumping during fluid stagnation are as follows:
- Before starting the procedure, take a warm shower. This will help increase blood circulation and facilitate the outflow of fluid;
- choose a comfortable position so that you feel comfortable and nothing distracts you from pumping;
- clasp your chest so that your thumb is located on top of the mammary gland, and the other four are under it;
- Grab the areola with your thumb and index finger;
- By squeezing your fingers, you will express milk. With your second hand, it is advisable to lightly massage areas with compaction;
- after a while, change the position of your fingers to empty the other lobes. With such a uniform release of liquid, stagnation can be quickly drained.
If a woman pumps correctly, milk is released in strong streams.
Video: how to properly express milk during lactostasis
Using cold compresses
To alleviate the general condition and reduce the temperature, it is allowed to use special compresses.
- Cabbage leaves. This option is the most effective and also safe for the baby’s health, it perfectly relieves inflammation and helps with fluid stagnation:
- take a cabbage leaf and rinse it under running water;
- leave to cool in the refrigerator for about two hours;
- take out the leaf and beat it or press it with your hands so that the juice comes out;
- Apply a cabbage leaf to the area of compaction for three to four hours.
- Cool gauze. After feeding the baby and pumping, it is recommended to moisten a bandage or gauze in cold water and apply it to the area with the seal. This compress should be changed as soon as the fabric becomes warm;
- Cottage cheese. Some young mothers note that a cottage cheese compress helped them. To do this, you need to take a small amount of the product in your hands and make a cake, which is then applied to the chest. Place gauze or bandage on top.
It is worth noting that during breastfeeding it is forbidden to use compresses made from camphor, alcohol, or Vishnevsky ointment. They do not have the necessary effect in the fight against lactostasis, but can harm the health of the baby. The active ingredients quickly penetrate into breast milk and then into the baby’s body.










