Prevention of mastitis in nursing
| “Empty” breasts are the best way to prevent mastitis. To prevent mastitis, a nursing woman needs to express the remaining milk in the breast after each breastfeeding (if the baby has not sucked everything). And if even minor problems appear, start feeding the baby from the “problem” breast: while he is hungry, he sucks better and more actively. The remaining milk must be expressed using a vacuum aspirator, with your hands, with your husband - it doesn’t matter. |
Prevention of serous mastitis
Serous mastitis may either imply a refusal to breastfeed or a continuation of this process. A woman can breastfeed or express milk, which is necessary to avoid stagnation that does not contribute to recovery. The following antibiotics are used as prophylaxis:
- Cephalosporins of the first and second generations.
- Semi-synthetic penicillins: Amoxicillin, Sulbactam, Clavulanic acid, Lactamase inhibitors.
These drugs are sufficient at the initial stage of mastitis. Gram-positive bacteria are detected, which include Salmonella, Escherichia, Proteus, Shigella. Antibiotics are taken without causing side effects. In this case, concomitant medications are not needed, since antibiotics do not provoke dysbacteriosis and stomach upset.

Amoxicillin is prescribed to people of all ages because it causes virtually no side effects, is widely available (93%) and is easily tolerated. There are practically no contraindications or allergic reactions. Medicines that contain amoxicillin are:
- Hiconcil.
- Amoxicillin-ratiopharm.
- Ospamox.
- Grunamox.
- Flemoxin.
- Ranoxil.
- Amotid.
go to top
Symptoms of mastitis
When milk remains in the breast, it “burns out”: aseptic (without microbes) inflammation develops in the breast tissue, and a signal is sent to the central nervous system that so much milk is not needed. As a result, the lobule of the mammary gland (where stagnation occurred) stops milk synthesis, + milk synthesis in other lobes of the gland is inhibited - the total amount of milk decreases.
Milk stagnation is manifested by a temperature reaction of up to 38 degrees. Due to stagnation of milk, the lobule of the mammary gland becomes tense - with your hands, and on an ultrasound you can find a painful seal in the form of a triangle with the apex towards the nipple. Over time, redness of the skin appears over this area. Also, ultrasound can detect dilated ducts and “cellularity” of the gland due to its overflow with milk; ultrasound equipment can be viewed on this website: lkmed.ru .
Stagnation of milk and swelling due to inflammation lead to compression of the vessels of the mammary gland. Malnutrition of glandular tissue leads to its death - necrosis. Dead tissue rots. This is manifested by increased pain in the area of induration and redness, a temperature reaction of up to 38 or more, and local increased chest temperature.
When are antibiotics prescribed for mastitis for a nursing mother?
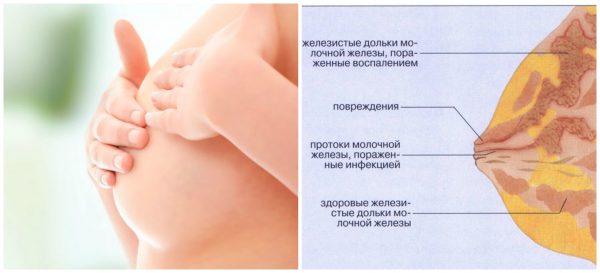
Mastitis
The main provoking factors for the development of the disease are penetration of a bacterial infection into the mammary glands or milk stasis. Milk stagnation creates a favorable microclimate for the development of pathological and pathogenic microorganisms, for example, intestinal and/or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcal and streptococcal bacilli, as well as Klebsiella.
The main danger posed by the inflammatory process is its rapid progression. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner and do not begin proper treatment, serous and purulent forms of mastitis will develop within 3-5 days. Suppuration of the infiltrate leads to the development of an abscess or phlegmon, the treatment of which requires surgical intervention.
If no action is taken when a purulent abscess develops, the young woman may die. Purulent masses can enter the bloodstream through soft tissue and cause sepsis.
At the initial stage of development, you can still do without taking medications, for example, regularly express milk after taking a warm shower, or perform lymphatic drainage massage. If there is no positive trend, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Ultrasound of mastitis
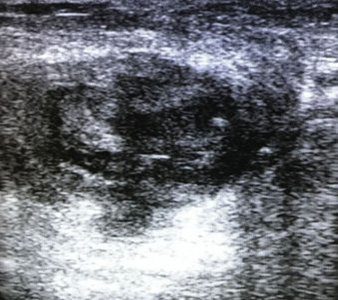
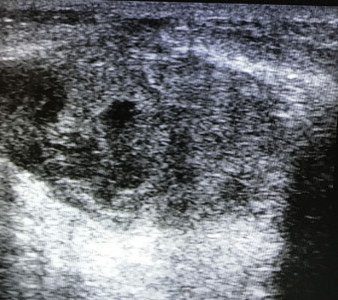
| An ultrasound scan for mastitis may reveal cavities with a vague, uneven contour against the background of swollen tissues with pus without blood flow; there may be enlarged lymph nodes due to inflammation. Pus is very viscous. It does not provide dorsal enhancement on ultrasound and only an experienced specialist can “see” it. We recommend that you be examined by trusted specialists: | |
|
|
Ultrasound signs of mastitis are very similar to breast cancer. But with cancer, the width of the “formation” is always equal to its height. Whereas with mastitis, the width will still be greater. In addition to the “vertical orientation”, with mastitis there will always be pain and redness over this place, whereas with cancer these signs are rare.
SEE more details about ultrasound for cancer
Treatment of mastitis and lactostasis
Physiotherapeutic procedures are widely used today and are absolutely harmless to mother and child. Such auxiliary methods are completely painless and help to establish lactation in the shortest possible time.
Among the physical procedures for lactostasis we list:
- ultrasound;
- vitaphone;
- darsonval;
- ultra high frequencies (UHF).
Thanks to these methods, milk stagnation is broken. For example, darsonval applies electric current to a painful area in a pulsed mode. Stagnant lumps gradually “break up”. Ultrasound for lactostasis is an active treatment method in which mechanical, thermal and physico-chemical action is directed to the affected area. The Vitafon device, thanks to the generated sound waves emitted at variable intervals, helps solve the problem of stagnation.
Before carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures, it is necessary to do a routine ultrasound
Attention: Vitafon and Darsonval devices can only be used after an ultrasound scan. It should be carried out to exclude tumor processes and mastopathy.
How does the treatment work?
The doctor uses an ultrasound sensor to diagnose lactostasis. Having seen the source of the problem and understanding the way to solve it, he chooses the most effective and painless treatment option. In more detail, the diagram looks like this:
- The mammologist conducts an examination, ultrasound, and then makes a diagnosis. Based on this, the doctor suggests treatment. It can vary depending on the complexity and neglect of the case: without drugs, with the help of medications, physical treatment, and also in severe cases - surgical intervention. The doctor’s extensive experience allows him to have a range of knowledge about the indications and contraindications of a particular procedure, which means he will be able to select an effective treatment specifically for your case.
- Today, numerous breastfeeding support services have become more widespread. Trained nurses make house calls and provide some assistance, mostly pumping. It is important to know that sometimes this is not enough, and in some cases such intervention is contraindicated. For example, the presence of mastitis in a woman requires the diagnosis of “purulent mastitis” to be made or refuted. Straining purulent areas will lead to extremely sad consequences. Purulent mastitis is also dangerous because even in the presence of purulent foci, the body temperature can be normal. The woman mistakenly believes that she is getting better, although in fact the disease is getting worse.
- A qualified doctor is able to help each patient by conducting a consultation on lactation and prescribing appropriate treatment.
If lactostasis has not progressed to mastitis, a lactation consultant can help establish feeding and pump the breasts
Diagnostics using ultrasound
The main purpose of ultrasound examination in mammology is the diagnosis of liquid and acoustic dense formations in the breast, as well as visible control of therapeutic and invasive procedures. Ultrasound diagnostics is an effective way to determine lactostasis. Scans show congestion in the form of overly dilated mammary ducts. The expansion of distant ducts and sinuses can be seen especially clearly. With lactostasis, unlike mastitis, there is preservation of the structure of the mammary gland in the absence of blood and lymph impurities in the tissues.
There is compensated and decompensated lactostasis (we recommend reading:). The presence of one of them can be determined using a pharmacosonographic test using pituitrin. To begin with, the woman is asked to express her breasts as much as possible, and then an ultrasound is performed. After determining the diameter of the milk ducts, 1 ml of pituitrin is injected into the body (intramuscularly). After 15-20 minutes, the ultrasound examination is repeated.
If the milk ducts have decreased compared to the first examination, a compensated form of the disease is diagnosed. If there is no effect, a diagnosis of “decompensated lactostasis” is made. This conclusion requires the selection of appropriate treatment with medications.
On an ultrasound, a specialist will see dilated ducts and be able to make an accurate diagnosis
Physiotherapy with ultrasound
Today, doctors successfully treat problems that arise in nursing mothers during lactation. Breast diseases are perfectly eliminated by ultrasound. In just 2-3 sessions, a young woman gets rid of her problem. An effective and painless method allows you to improve the functioning of the thoracic ducts, increase milk production and minimize the risk of inflammatory processes in the breast. This method should be combined with pumping, which should be done by an experienced specialist.
Ultrasound has a complex effect. Blood vessels dilate, milk ducts become easily passable, and pain disappears. In fact, ultrasound simulates massage movements that actively nourish breast tissue by increasing the diameter of blood vessels. An experienced functionalist doctor performs this procedure using an ultrasound probe. He treats the entire surface of the breast, except for the areola and nipple. Therapy time ranges from 15 to 20 minutes.
To achieve a positive effect, 4 to 8 physiotherapeutic procedures should be performed. The amount will depend on the severity of the disease.
As an alternative, the doctor may suggest the Vitafon device. Physiotherapy ends with mandatory pumping. It is not painful to perform it, because the mammary gland has received good softening. For complete pumping, you can seek help from an experienced specialist in this field.
When is ultrasound contraindicated?
Although ultrasound is very simple and harmless, there are still a number of contraindications to its use.
- The main prohibition will be diseases of the nervous system that a woman has. Active exposure to ultrasonic waves, especially in the chest and heart, can lead to various types of disturbances in the activity of the central nervous system.
- When a woman has breast tumors, the above method cannot be used. When exposed to heat, the number of cancer cells increases, as well as the transformation of benign tumors into malignant ones.
- Breast cysts and mastopathy can be the site of origin of the cancer process. It is also impossible to treat such areas with ultrasound.
- In the presence of purulent mastitis, an ultrasound procedure is excluded. The presence of inflammation due to milk stagnation implies immediate contact with a doctor who will offer a course of therapy and help avoid surgery.
Before you begin to treat the problem with ultrasound, you should consult with a specialist. Anything that interferes with physiology can have both positive and negative results. A young woman should be aware that self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
If the examination reveals a tumor of any kind, ultrasound is contraindicated for a woman.
Purulent mastitis
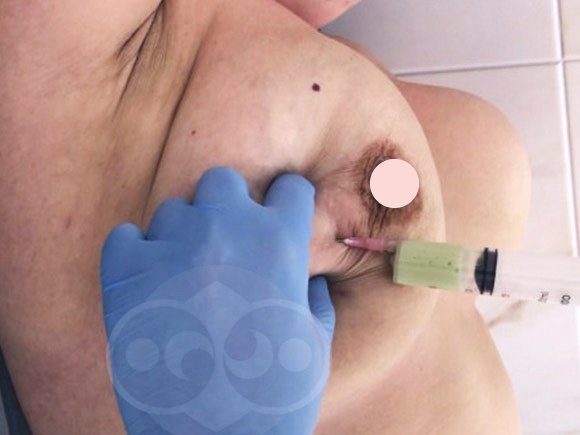
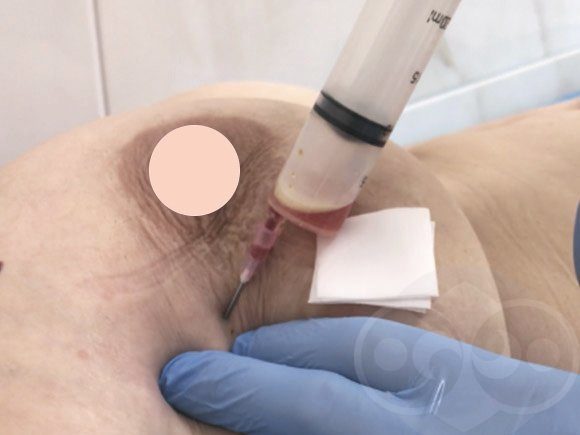
If the temperature reaction persists above 38 degrees for 3 days or more, there are no signs of relief of the situation (reduction of pain, disappearance of a lump in the chest), or an abscess cavity in the chest is detected by ultrasound, removal of pus and prescription of antibiotics is indicated.
Removal of pus can be done classically - through an incision (opening mastitis) and through a series of punctures. In the first case, the wound heals with a rough scar. In the second, there is no scar, but punctures are performed for several days in a row until, instead of the dead breast tissue, a cavity (cyst) with milk without pus is formed.
The decision to breastfeed is made individually: either milk is expressed during treatment (taking medications), or lactation is suppressed with the drug Dostinex.
How dangerous is the disease?
Mastitis is a concern due to the acute course of the disease
and rapid change of its phases. Thus, serous uninfected mastitis, characterized by moderate symptoms of intoxication, in the absence of proper treatment, already in 2-3 days passes into the next stage - infiltrative. It is characterized by severe chills and an increase in the size of painful lumps, which gradually merge with each other.
Literally after 3-4 days, the stage of abscess formation begins: the patient loses sleep and appetite, chest pain intensifies, and due to the admixture of pus, it is difficult to express milk. Ultimately, an abscess forms, represented by extensive purulent cavities (abscess form), which is replaced by necrosis of the mammary gland involving subcutaneous tissue and skin.
Important!
There is a real threat to a woman’s life as a result of blood poisoning and septic shock.
In addition, the consequences of mastitis can be:
- Disorders of the heart muscle.
- Meningitis.
- DIC syndrome (deterioration of blood clotting and blood clots).
Only a timely visit to a specialist is the key to successful and most gentle treatment
infectious process in the chest.
It is necessary to seek help if:
- Body temperature does not fall within 24 hours.
- Redness of the skin on the chest increases.
- Induration and swelling do not decrease after pumping.
Non-lactation mastitis
It occurs more often in women who smoke. If they do not quit smoking, it often occurs again and again. Non-lactation mastitis also occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus.
It occurs due to a decrease in immunity (more often during menstruation - due to hormonal changes), when against this background the microflora that normally lives in the ducts is activated and, with strong immunity, is restrained by your immune system.
Mastitis is more common with nipple piercings.
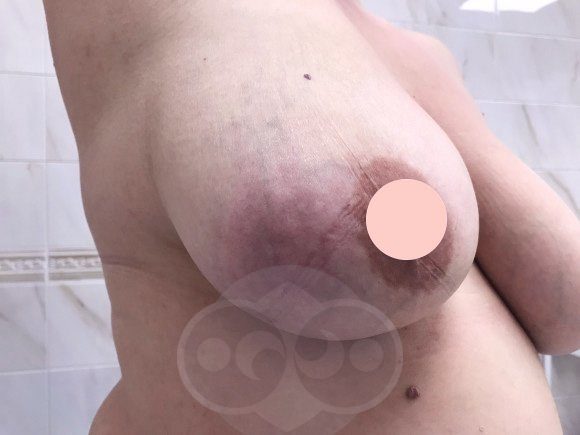
It manifests itself as pain, redness and local increased temperature in the redness area. General fever up to 38 or more occurs with severe inflammation. The signs on ultrasound are similar, only dilated ducts with milk are not found.
|
|
|
|
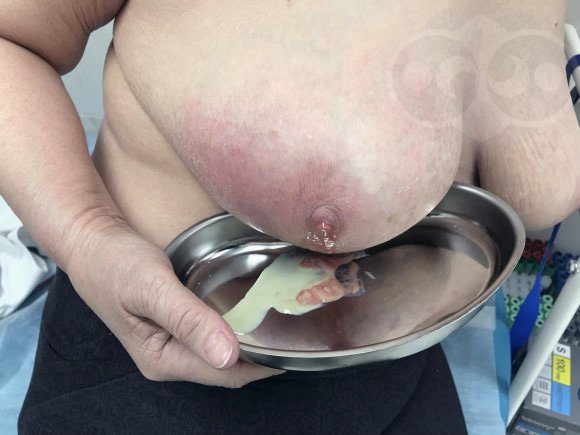
Mastitis photoSometimes the abscess itself breaks into the ducts and then the pus flows out through the nipple. If this does not happen, it is necessary to either make an incision or puncture to remove the pus. | |
The principle of making an incision to remove pus was introduced in the era without antibiotics.
Today (under the guise of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs) it is possible to remove pus through punctures. During the first puncture, the pus into which the dead breast tissue has turned is removed. But at the same time, only what is dead and rotten is removed. What did not rot but died remained on the walls of the cavity. It will turn into pus and will be removed during the next puncture(s). When the cavity is cleared, during puncture we will get a scanty blood discharge (light, transparent).
Physiotherapy for mastitis
Treatment of initial and infiltrative mastitis can also be carried out using physiotherapeutic methods. Ultrasound and UHF therapy bring the greatest effect. Ultrasound therapy helps relax the milk ducts and releases stagnant milk. The main advantage is that during the procedure the patient does not experience any pain or discomfort, while normal pumping is always accompanied by pain. Ultrasound also promotes the resorption of infiltrate and, unlike antibiotics, is applicable during breastfeeding.
Along with ultrasound, antibacterial therapy is also used using a set of antibiotics, which must be selected by the doctor. In the infiltrative stage, novocaine and penicillin are injected under the seal.

How to treat lactostasis
To eliminate lactostasis, milk must be expressed; a breast pump can be used for this.
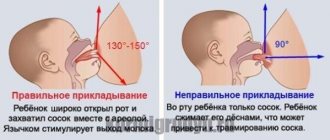
First of all, it is worth saying that in most cases of milk stagnation, especially at an early stage of the process, a woman can easily cope with it on her own, or more precisely, with the help of a child. The main method in the treatment of milk stagnation is frequent (at the slightest opportunity, at least every 10 minutes) application of the child to the affected breast. Attachments must be correct, and they will be more effective if the baby is positioned so as to direct his chin towards the seal (then during sucking there will be an additional massage of the seal with the baby’s chin). If stagnation occurs in one of the upper segments, the child should be placed “upside down” (the child lies and the mother hangs over him) - that is, the mother and baby will have to twist a lot, but the result will not be long in coming.
Before feeding, the mother needs to take a warm (but not hot!) shower, directing the shower head jets to the seal area and the interscapular area. Warm jets massage, resulting in relaxation of spasmed muscles and ducts. Instead of a shower, you can use a warm compress, which is applied to the affected area 15-20 minutes before feeding.
Some experts recommend using compresses with camphor alcohol. Mom should know that this drug helps reduce lactation in the area of its use, which can later be quite difficult to restore. This method is justified and should be used only in cases where lactostasis occurs due to hyperlactation - camphor will reduce the amount of milk secreted by the gland, the process of its secretion will be normalized.
Also, before and after feeding (and sometimes during the process), the mother should undergo a gentle breast massage. I want to focus specifically on the word “gently”... Previously it was believed that with lactostasis, stagnation of milk should be “broken”. They did it quite roughly, causing my mother excruciating pain and leaving a lot of bruises after such a “massage”. Under no circumstances should you do this! Rough mechanical impacts, even if they help restore the flow of milk today, tomorrow will cause swelling of the delicate glandular tissue, which will provoke a whole series of new lactostases. Yes, massage is necessary and very important in the fight against congestion, but the movements of the massager should be soft, not traumatic to the breast tissue, and they should be carried out in the direction from the periphery to the center. It is worth noting that the most correct person to perform such a massage and teach it to a young mother is a specially trained midwife.
You should express milk at the same time as the massage. But it is important not to express it “to the last drop,” but to stimulate the lobule with stagnation as much as possible in order to release it. The mother should learn the pumping technique while still in the maternity hospital, and if this does not happen, you can also contact a midwife or use an effective breast pump.
It happens that after feeding, standing in the bathroom under a warm shower, massaging the area of compaction and expressing, a woman practically does not observe milk, but suddenly the stream intensifies sharply, and the milk has a rich white-yellowish color, it is relatively thick and quite warm. This just means that mother’s actions were crowned with success and lactostasis was defeated.
Often, after the milk flow has been restored, a woman immediately notices an improvement in her condition, whether this happens while feeding the baby or during a breast massage. The feeling of pressure and fullness in the affected area decreases, the pain becomes less intense, and for many, body temperature returns to normal very quickly. Residual effects of lactostasis may bother the young mother for several more days - until the swelling goes away.
To reduce swelling, you can treat the skin over the area of compaction with Traumeel ointment or use folk remedies such as cabbage leaves. It should first be scalded with boiling water, then beaten a little with a kitchen hammer (to release the juice) and applied to the chest, covered with a cloth or polyethylene. Keep it until you get tired of it, because as you probably guessed, there are no side effects from this remedy.
You have probably heard about this method of treating lactostasis, when instead of the child, the mother puts the father to the breast so that he resolves the stagnation. This is unreasonable, ineffective, and sometimes harmful for both mother and baby. Firstly, the child suckles at the breast using his own unique method - he does not suck, but as if squeezes milk out of the gaps located under the areola. An adult cannot do this physiologically. Secondly, dad’s oral cavity contains a lot of microorganisms, even opportunistic ones. If there are even microcracks on the mother's nipple, the infection can easily penetrate from the father's mouth through them into the area of the ducts, infecting the milk. This can lead to mastitis in the mother and infectious diseases in the baby.
If the temperature is high, a nursing woman can take a paracetamol tablet or, if the baby is over 6 months old, ibuprofen.
Even if a mother consults a doctor on the first day of illness, but he assesses her condition as not severe, she may be advised to fight lactostasis on her own for 2-3 days. If during this time the woman’s condition does not return to normal, the doctor will prescribe her an antibiotic (there is a high risk of infection at this stage) that is compatible with breastfeeding (there are actually quite a lot of them, so don’t worry that you will have to temporarily stop breastfeeding - you won’t have to ), straining and physiotherapeutic treatment methods. Sometimes, based on the woman’s condition, an antibiotic, pumping and physiotherapy can be prescribed earlier - this is decided by the doctor (usually a gynecologist) in each specific case.