Medicines allowed during breastfeeding
When choosing painkillers that you can take while breastfeeding, pay attention to the following factors:
- How toxic is the medicine;
- How quickly it is eliminated from the body;
- What percentage of the components contained in the drug are absorbed into the blood;
- How fast-acting is the medicine;
- What happens if you take more dose than the doctor prescribed;
- The effect of painkillers on mother's milk.
A nursing woman needs to read the instructions very carefully. The drugs may contain harmless components, which, however, cause allergies in infants. A mother should know what her child may have an allergic reaction to.
For headaches
There are many causes of headaches in breastfeeding women. Young mothers are in constant stress, worry about the baby, worry that he will have enough milk. Sleepless nights, lack of proper rest, and poor nutrition contribute to the fact that a nursing mother often develops migraines. Also, after childbirth and during lactation, many women experience hormonal imbalance, which provokes migraines.
Headaches cannot be tolerated, and sometimes it is simply impossible, you can feel so bad. While breastfeeding, you can take the following medications to help relieve headaches:
- Products with the active ingredient Paracetamol: Strimol, Panadol, children's syrup with paracetamol. It is advisable to take a Paracetamol tablet with warm green tea to enhance the effect of the drug;
- Medicines based on ibuprofen: Ibufen, Nurofen.
For toothache
What painkillers can you take during breastfeeding if you have a toothache:
- Ketanov tablets will reduce toothache, but will not eliminate the cause. Ketanov is usually prescribed after tooth extraction. For acute toothache, treat the pain with medication, but go to the dentist as soon as possible.
- Lidocaine. Dentists use Ultracaine, an analogue of lidocaine in injections, to numb the oral cavity in order to carry out subsequent treatment.
You can use products designed to reduce pain in babies during teething:
- Kalgel with Lidocaine in the composition;
- Kamistat Baby in gel. Contains not only Lidocaine, but also chamomile extract;
- Dentol Baby. The gel cools, anesthetizes, and disinfects.
All approved medications for toothache only provide temporary pain relief, so if you feel pain in your tooth, do not delay your visit to the dentist.
Almost every woman in labor after a CS feels severe pain that is impossible to endure. What painkillers can you use when breastfeeding after a cesarean section?
- One-time injection of no-shpa;
- Ultracaine injections. Maternity hospitals often give injections of this drug, which is safe for babies and relieves pain for a long time.
If the pain does not go away after taking painkillers and the condition worsens, you should seek medical help.
To determine whether this product can be taken while breastfeeding, carefully read the instructions and pay attention to the following factors:
- Toxicity;
- How much of the drug gets into the blood and breast milk;
- How quickly the drug is eliminated from the body. The drug, which is completely eliminated in less than four hours, is optimal for a nursing mother. Taking it after breastfeeding will protect the baby as much as possible;
- How quickly does the medicine take effect?
- Side effects and contraindications;
- Consequences of overdose;
- Compatibility with lactation, effect on breast milk;
- The composition of the drug, often the mother already knows which components the baby is allergic to. Choose medications with one active ingredient, this will reduce the risk of allergies;
- Method of taking the drug;
- Duration of admission and course of treatment.
Be sure to consult your doctor before using medications while breastfeeding. Even if the drug can be taken while breastfeeding, only the doctor will select the correct dosage depending on the individual developmental characteristics of the baby. In addition, pain and cramping may indicate serious problems in the mother's health that will require other treatment.
Some mothers think that when the dose is reduced, the painkiller does not affect lactation or the baby. For example, if you take only half of a tablet, it will not cause harm. This is wrong! In any case, if the drug is absorbed into the blood, it will pass into breast milk. In addition, a small dosage may not have the desired effect and may not relieve pain.
The baby receives nutritional compounds from the mother's milk. Nursing mothers need to carefully select their diet, avoid consuming alcohol-containing products and smoking. The use of medications during lactation is especially alarming.
Painkillers for nursing mothers are chosen based on the drugs allowed for the newborn. Therefore, it is permissible for women to take Ibuprofen and Cefekon, which are used in the treatment of small children.
Toothache during pregnancy and lactation is relieved with Ketorolac and Dexalgin tablets.
These products can be used, if necessary, after consulting a medical professional.
Pain relieving ointments
In addition to tablet forms, pain-relieving ointments are widely used during lactation. Medicines provide safety and effectiveness. Convenient due to the possibility of local application. Harm to the baby is excluded as much as possible. We list the effective means:
- Biopin;
- FinIce;
- Traumeel-S;
- Menovazin;
- Arthrolight.
Health suffers noticeably after childbirth. New mothers are often affected by hemorrhoids. You have to use pain-relieving suppositories during lactation. The active substance of the drug can be absorbed into the blood, spread through the bloodstream, and accumulate in milk. It is necessary to obtain a doctor's advice before using the medicine. Medical professionals recommend using to solve a delicate problem:
- Relief;
- Belladonna extract;
- Hexicon;
- Natalsid.
These drugs contain minimal concentrations of harmful substances that can harm the baby.
The effect of painkillers on the body
Many modern women are of the opinion that while breastfeeding they should not take any medications without consulting a doctor. Painkillers are no exception, the vast majority of which, when they enter the body, have a negative effect on hematopoiesis in the baby’s body, liver cells, and the nervous system. It is in this regard that there are often cases when, due to the use of analgesics, especially combined drugs, mothers are faced with the occurrence of toxic reactions in the child - the appearance of jaundice, excessive drowsiness, and impaired sucking are possible.
Basically, the clinical effects that occur are similar in adults and children, and the accumulation of drugs occurs in the same tissues and organs. But in adulthood, it is possible to create a drug depot due to a larger amount of adipose tissue, and in babies in the first months of life, all chemical substances, after they enter the body, are included in the course of metabolic processes. It is in this regard that the advice to take a very small dose of any painkiller during breastfeeding is completely meaningless. For the mother, such a dose may be completely insufficient to relieve pain, and such an amount of medicine will pass into her milk, which will be enough for the child to experience a side effect.
Medicines allowed during breastfeeding
Even if you take legal pain medications, you should still follow certain rules, the main one of which is not to self-prescribe medications. The initiative can result in negative consequences for you, allergies and bowel problems in your baby.
Most mothers try to endure pain as long as possible. But often the pain becomes simply unbearable. In order to be able to care for the child calmly, the mother needs to take painkillers. Doctors say that many types of pain cannot be tolerated, so you need to act immediately.
How to take painkillers correctly during lactation:
- Some women prescribe painkillers for themselves after reading reviews on the Internet or listening to friends. The drug can harm the baby, so do not self-medicate, because the consequences can be disastrous.
- Before taking the medicine, even if it was prescribed by a doctor, you should carefully read the instructions.
- Pay attention to the expiration dates of painkillers. Many pharmacies practice such promotions: 1-2 months before the expiration date of drugs, they are offered at a reduced price. You should not buy such drugs, because you do not use the whole package at once.
We suggest you read: When can you drink coffee after brushing your teeth?
How to relieve pain?
Lidocaine is far from the only remedy that can be used to relieve pain.
Doctors recommend that if severe pain occurs, take those pharmaceutical drugs that do not contain steroids. Such medications include Ketoprofen and Naproxen. Of course, you shouldn’t get too carried away with them, but if absolutely necessary, you can drink them. You should be aware that these drugs have not been adequately studied in this population and should be taken with extreme caution.
If the mother suddenly develops a severe headache, then she can take no-shpu, paracetamol or ketorol.
In dentistry, lidocaine ultracaine is often used to relieve pain, which is safe for nursing mothers when used once. After the drug has expired, the mother can feed her baby again.
Drugs prohibited during lactation
Painkillers that are prohibited during breastfeeding (the medicine can be available in the form of powder, syrups, pills, etc.):
Citramon;- Aspirin;
- Baralgin;
- Pentalgin;
- Analgin;
- Codeine;
- Andipal;
- Spasmalgon;
- Spazgan;
- Nimesulide.
Aspirin, Citramon, Analgin and its analogues are considered the most dangerous. Citramon and Aspirin have a negative effect on the baby’s internal organs. Analgin and drugs with names that end in -gin can cause a severe allergic attack.

You should not take combined medications, since they also affect the development of the child’s internal organs, and many diseases may appear in the future.
Anyone who says you JUST take a pill is wrong. No drug can be treated irresponsibly, because there are certain rules for taking it.
Rule one: visit a doctor to identify the cause of discomfort, since pain is a protective reaction of the body, which indicates various problems in the body.
Rule two: carefully study the annotation for drugs; special attention is required to the section that indicates the degree of safety of the drug for pregnant and lactating women, and possible adverse reactions.
Rule three: any medicine can be taken once. Long-term treatment is unsafe for the baby, so you will have to stop breastfeeding for a while.
Rule four: follow the dosage; do not reduce the dose of the drug so as not to harm the child. The medicine will not work, and the baby will still receive its portion of the drug from breast milk. You should also not increase the dose - this will not help you cope with the pain faster, but the negative consequences of such treatment are guaranteed for you and your baby.
Rule five: study the absorption and half-life of the drug in the instructions. Most analgesics act quickly, within 30-40 minutes, during which time the active substances also enter breast milk. It takes 2-3 hours to remove them from the body.
Rule six: try to use products that are absorbed into the blood in minimal doses - pain-relieving suppositories after childbirth and ointments help a lot. Their action will not be as fast as after taking pills, but as safe as possible.
And now - THE MAIN RULE: you should clearly memorize the list of drugs that cannot be taken during lactation.
Analgin and drugs that contain it - Baralgin, Spazmalgon, Tempalgin - are included in the first risk group during breastfeeding.
Nimesulide, Nise, Nimid - their safety for nursing women has not been proven.
Aspirin, Citramon, Askofen, tablets that contain codeine, phenobarbital - contain components dangerous to the health of the baby.
Side effects of the substance Lidocaine
be advised to exercise caution in case of liver and kidney diseases, hypovolemia, severe heart failure with impaired contractility, genetic predisposition to malignant hyperthermia. In children, debilitated patients, and elderly patients, dose adjustment is necessary in accordance with age and physical status. When injecting into vascularized tissues, an aspiration test is recommended.

When applied topically, use with caution in case of infection or injury at the site of application.
If during the period of use of the plate a burning sensation or redness of the skin appears, it must be removed and not used until the redness disappears. Used plates should not be accessible to children or pets. Immediately after use, the plate should be wiped off the face of the earth.
depression or stimulation of the central nervous system. nervousness, euphoria, flashing of flies before the eyes, photophobia, drowsiness, headache, dizziness, tinnitus, diplopia, impaired consciousness, depression or cessation of breathing, muscle twitching, tremor, disorientation, convulsions (the risk of their development increases against the background of hypercapnia and acidosis ).
sinus bradycardia, cardiac conduction disturbance, transverse heart block, decreased or increased Hell. collapse.
nausea, vomiting.
generalized exfoliative dermatitis, anaphylactic shock, angioedema, contact dermatitis (hyperemia at the site of application, skin rash, urticaria, itching), a short burning sensation in the area of action of the aerosol or at the site of application of the plate.
feeling of heat, cold or numbness of the extremities, malignant hyperthermia, suppression of the immune system.
It is worth noting that the drug Lidocaine is most common in dentistry. It is the safest. This is because lidocaine:
- is a short-acting local anesthetic,
- has antiepileptic and antiarrhythmic effects,
- characterized by almost zero absorption,
- enters mother's milk in negligibly small quantities, which will not harm the baby in any way,
- in dentistry it is used in low concentration,
- very rarely has side effects.
, injection method (infiltration method), , conduction method, terminal or application method for fear of injection.
The well-known children's doctor of the highest category, E. Komarovsky, believes that it is advisable for a nursing woman to abstain from any medications, including painkillers. During lactation, the painkiller is directly transported into the milk, and then immediately into the baby’s body, which is not yet fully formed. But no one is immune from situations when the pain becomes unbearable. In this case, you should discuss taking pain medications with your doctor.
Any medications, even conditionally approved for breastfeeding, have an impact on the health of the baby. The small body does not yet know how to remove toxic substances, which means that any drug can poison the baby.
In addition, even an approved painkiller in the wrong doses can cause milk loss. This happens when a large dose of the drug was taken, or the medicine was chosen incorrectly. Before taking a painkiller, think about how necessary it is? After all, many mothers, even with the slightest headache, immediately resort to pills, although you can get by with warm tea and a half-hour rest.
During the process of bearing a child, almost all calcium is spent on the growth and development of the baby, which is why many mothers experience dental problems after childbirth.
Of course, you know that with caries and other dental diseases you need to immediately contact a specialist. But if the toothache started at night, or it is not possible to get to the clinic, you can take a painkiller tablet, you just need to know which one so as not to harm the baby’s health.
We invite you to read: What is the difference between the drugs Miramistin and Chlorhexidine - compare the composition and properties
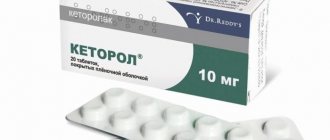
Remedy No. 1. Ketanov, Ketonal is a drug of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory group, has an antipyretic, analgesic effect, and is fully compatible with breastfeeding.
A very small dose of active substances enters the milk and does not affect the child’s condition. The maximum concentration of the drug in plasma occurs within 45-55 minutes, and is eliminated from the body in 4.5-6 hours. They are also produced in the form of rectal suppositories.
Remedy No. 2. Lidocaine, Ultracaine - safe products for topical use.
Remedy No. 3. Pain-relieving ointments and gels that are used for teething in infants - Kalgel, Dentol Baby, Kamistad Baby, Traumeel.
In addition to painkillers, you can use local antibacterial agents - Furacilin, Chlorhexidine.
Before drinking the medicine, rinse your mouth with a warm decoction of sage, chamomile, a solution of salt and soda, and brush your teeth. Such simple manipulations will help to slightly reduce the discomfort.
What drugs are compatible with breastfeeding?
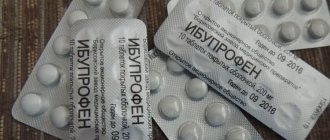
Women know what to give their child when his temperature rises and pain of various types appears: Panadol or Nurofen. Accordingly, if the baby is allowed to use these drugs, then they are not prohibited for mothers while breastfeeding. Medicines intended for children are produced in the form of syrups and suppositories; analogues for adults are produced in the form of tablets or injections.
What painkiller can you take while breastfeeding:
- Paracetamol (analogs - Panadol, Efferalgan);
- Ibuprofen (analogs - Ivalgin, Ibuprex, Nurofen).
To minimize the effect of the drug on the baby and at the same time get rid of pain, it is better to take a form of painkillers that will neutralize the local site of pain. For example, Ketanov can be used in the form of a gel: it is applied to the affected area and acts in a specific place, practically without penetrating into mother’s milk.
Allowed painkillers during breastfeeding, except Paracetamol and Ibuprofen:
- Ketanov. The drug is quite strong, so doctors prohibit taking it in the first month after birth.
- Diclofenac. If a woman has problems with the gastrointestinal tract, it is better not to use this drug.
- No-shpa. Among the medications that relieve painful spasms, no-spa is considered the safest. However, doctors recommend no-shpa in the form of a one-time dose for severe spasmodic pain.
- Ultracaine and Lidocaine are quickly eliminated from the body, so they are quite safe.
If you experience pain, you should discuss with your doctor what pain medications you can take while breastfeeding. In most cases, these medications are approved for use in infants, so they are quite safe. The release form can be varied - tablets, syrups, ointments, gels, suppositories, injection solutions.
When breastfeeding, one-time use of painkillers is allowed:
- Paracetamol (analogous to Panadol);
- Ibuprofen (Nurofen, Ivalgin, Ibuprex);
- Naproxen (Pronaxen, Apranax).
How can a nursing mother save herself from pain?

The range of modern analgesic drugs includes those that are officially approved for lactation. But even if such a medicine was prescribed by a doctor, it would still be a good idea to carefully study the instructions, which describe possible adverse reactions and contraindications.
A nursing mother can draw a conclusion about which painkillers she can take on her own. To do this, you should be guided by the following rule: if the drug cannot be given to small children, then it is not suitable for a new mother, because it will inevitably end up in the milk.
Here are some painkillers that can definitely be used while breastfeeding:
- Paracetamol. Other names for this drug are Panadol, Efferalgan, Acetaminophen. WHO recommended them for use by pregnant and lactating women. As a result of many studies, it has been proven that they are fully compatible with hepatitis B. Only 20% of the medicine taken by a woman penetrates into milk - this is much less than the dose prescribed to an infant to relieve pain in the ear, throat and teething. The drug leaves the body after 2 hours, so it is better to drink it immediately after feeding. The dose for nursing women is 650 mg. You can take the next tablet after 6 hours;
- drugs from the non-steroidal group - Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Naproxen. They produce a double effect - they relieve pain and inflammation. Although they can be combined with feeding, it is better to take them once, at a dose of 200 mg with an interval of 6-8 hours. If the pain does not subside, then you are allowed to drink 400 mg of this drug at a time. Only 0.7% of the accepted volume will be in the milk.
These drugs are considered completely harmless, but the problem is that they are not very strong, so with their help it is not always possible to overcome pain.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
Here are some painkillers that can be taken while breastfeeding, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the E-LACTANCIA electronic directory, but are prohibited from taking according to the medication annotation:
- in case of intense pain, you are allowed to drink Ketanov (Ketorol). Since these medications are acceptable for children over 15 years of age, it is still better to be on the safe side - express milk once or twice. It can be placed in the freezer and reheated before feeding. These medications have a fairly short half-life (6-12 hours) so their plasma concentrations will soon drop to a safe level without you having to stop feeding. Standard dosage is 10-20 mg with a break of 4-6 hours;
- if it is necessary to provide anesthesia when performing dental procedures, then use Lidocaine or Ultracaine. They are considered safe for the baby, as they enter the blood in minute quantities. But the opinions of doctors regarding Lidocaine are still ambiguous, so we advise you to do pumping according to the scheme described above;
- Diclofenac. It reaches its highest concentration in breast milk within an hour after administration. Safe dosage – 25-20 mg three times a day (limited period of time);
- if the pain is spastic in nature, then No-shpa is suitable (unless it is prescribed for a long period). Drotaverine has a cumulative effect, that is, it can accumulate in the baby’s body, and after some time this will make itself felt.
Decide for yourself what to trust more - the pharmacological instructions, an electronic resource, the reference book of the American children's doctor Hale, or the medical experience of your local pediatrician.
How to get rid of pain faster?
Any drug must be prescribed by a doctor. There are situations when it is impossible to do without potent analgesics and anesthesia. When taking prohibited painkillers once during breastfeeding, it is advisable to replace 1-2 feedings with an adapted formula or pre-expressed milk. You can also choose a form of the drug that acts locally, for example, ointments and gels. Suppositories provide longer lasting pain relief. Injections work faster than tablets.
When a potent drug is prescribed by a doctor for a course of treatment, you will have to temporarily stop breastfeeding. After treatment, it can be improved if you pump your breasts regularly. There is no need to be afraid of taking medications; milk containing toxic substances produced in the body during illness can cause much more harm.

If severe pain occurs, you should see a doctor as soon as possible so that he can prescribe suitable painkillers. Prescribed medications should not contain even the minimum amount of substances prohibited during breastfeeding.
First of all, you should have Ibuprofen in your medicine cabinet. Choose any form: candles, gel, suspension. It is advisable to use ketanol for young mothers in the form of a gel. Novocaine and Ultracaine are best purchased in the form of injections. But it is worth paying attention to the fact that after injections, continued breastfeeding is sometimes prohibited.
If you need a long-term analgesic effect, the optimal form of the drug is rectal suppositories. Tablets and pills are taken as a one-time remedy, after which doctors recommend not breastfeeding for a day.
During lactation, some painkillers from analgesics are used for local anesthesia.
Symptoms and types of headaches in a nursing mother
There are many reasons for such symptoms in breastfeeding women. But you can’t rush to the first aid kit. After all, everything that the mother takes goes to the newborn through breast milk. Dizziness appears during hepatitis B, which often happens against the background of epidural anesthesia.
Tension headaches
Women, creating comfortable conditions for the child, close the windows and create greenhouse conditions. This is another mistake that causes similar symptoms in a nursing mother.
The normal rest regime has been disrupted. Sleepless nights, endless awakenings. This does not give the brain the opportunity to rest properly. After such nights, characteristic symptoms appear in the morning.
Interesting: Dizzy during pregnancy in the second trimester: causes and treatment
Migraine
Pathology occurs not only in women who are breastfeeding. Pregnant women complain of headaches. Poor nutrition, lack of sleep, lack of oxygen, stress are just some of the factors that provoke migraine attacks.
A severe headache appears suddenly and may not go away for several days. It increases in bright light, the baby's cry, sudden movements, and during breastfeeding. This aggravates the physical and emotional state of the young mother. The hand habitually reaches for the first aid kit for emergency help. We must not forget that a pill that is safe for the mother is harmful to the child.
Headache due to high blood pressure
Sudden changes in blood pressure are a symptom that appears after an overload of the body associated with the birth of a child. When breastfeeding, if your blood pressure rises, this can be accompanied not only by headaches. The condition is accompanied by shortness of breath, tachycardia, and nausea.
Osteochondrosis can provoke hypertension. A nursing woman is forced to remain in one position for a long time, carrying the baby in her arms without transferring him to the crib so that the baby does not wake up. This places a static load on the spine, provoking the appearance of this disease, which is accompanied by frequent, severe headaches.
Pain reliever during breastfeeding for different types of pain
Toothache
During pregnancy and while feeding the baby, there is a lot of stress on the mother’s body and teeth. The main cause of dental disease is a lack of calcium, changes in hormonal balance, and loss of beneficial components. For hepatitis B there is also a list of approved drugs. The onset of pain can be tolerated and you can use folk remedies, but if you cannot visit the dentist in the near future, and the pain becomes unbearable, a nursing mother is allowed to use the following medications:
- Lidocaine or similar Ultracaine: its use involves local use in the form of injections for sanitation procedures and for medical procedures;
- Kenatov: the pill will temporarily relieve severe pain. It will not eliminate the origin of pain; the action is aimed at reducing pain. Use no more than twice, no longer than three days.
Ointments can be used as pain relievers for toothache. These methods of alleviating pain are allowed for a baby when teething, which means that a mother can also use them for toothache:
- Kalgel, based on Lidocaine.
- Traumeel.
- Kamistat Baby in the form of a gel: in addition to Lidocaine, it contains chamomile.
- Dentol Baby - has a cooling, analgesic effect, relieves inflammation.
Headache
Headache is a common symptom. Fatigue, lack of sleep, worry about the baby, milk, etc. are the main reasons. Changes in hormonal balance also become a frequent cause. It often goes away without taking medications; it is enough to use folk remedies or a head massage.
A nursing mother is allowed the following painkillers to relieve pain:
- preparations with Paracetamol (Strimol, Efferalgan, Panadol);
- Nurofen, Avil, Ibufen with Ibuprofen in the composition.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Drugs for trigeminal neuralgia
Pain relief during feeding is a necessary measure. First, it is recommended to use gentler methods: relax, take a walk in the fresh air.
Pain syndromes in the groin area are a companion to the first months of a woman who gave birth by cesarean section. What pain reliever can nursing mothers use in such situations? Allowed:
- No-spa: as pills and injections, taken after childbirth, non-systemically;
- Ultracaine is effectively used by gynecologists and is not dangerous for nursing mothers;
- Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen.
Why is Pentalgin not recommended for breastfeeding?
The combined drug has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, antipyretic effects. Caffeine causes dilation of blood vessels in skeletal muscles, heart, and kidneys; increases mental and physical performance, helps eliminate fatigue and drowsiness; increases the permeability of histohematic barriers and increases the bioavailability of non-narcotic analgesics, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effect. It has a tonic effect on the blood vessels of the brain. Drotaverine has a myotropic antispasmodic effect due to inhibition of PDE-4, acts on smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract, genitourinary and vascular systems. It has an antispasmodic and mild sedative effect, reduces exudation, and also enhances the analgesic effect of paracetamol and naproxen. With caution: cerebrovascular diseases; diabetes; peripheral arterial disease; history of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract; renal and liver failure of mild or moderate severity; viral hepatitis; alcoholic liver damage; benign hyperbilirubinemia Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndrome; epilepsy and tendency to seizures; glucose phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; elderly age.
In the first year after childbirth, a woman’s immunity decreases, and postpartum pain can bother her almost every day. Medicines will help eliminate the discomfort.
Natalia Belyaeva.
The minimum period for lactation is 1 year; rarely does anyone manage to avoid getting sick during this period. And this is not surprising, because the immunity of a nursing mother is weakened after childbirth. Headache, toothache or earache, groin pain after a caesarean section - this is not the entire list of unpleasant symptoms that new mothers experience. Medicines will help eliminate pain. Pentalgin is a combination drug from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The analgesic is used to relieve pain of various origins; it eliminates inflammation and swelling. VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: 153. Anesthesia for hepatitis B. Is it possible or not? Natedent
How to take analgesics during lactation
Dr. Komarovsky, for example, recommends avoiding the use of painkillers while breastfeeding or pregnant, as some drugs simply have not undergone proper clinical studies. However, if a woman cannot tolerate severe pain, there is no point in waiting for it to go away on its own or using dubious traditional methods. Here are a few rules that will help you quickly deal with the problem and avoid harming yourself and your child:
- It is important to understand: painkillers only relieve the symptom, but do not cure the disease itself. Therefore, in case of painful discomfort, it is recommended to consult a doctor, find the cause of the discomfort and eliminate it. So, if you have a toothache, visit the dentist; if you have pain in your ear, visit an ENT doctor. If the root cause is not eliminated, the pain will occur again and again, requiring another dose of medication.
- Even for a drug prescribed by a doctor, check the instructions, or rather the section “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.” There are no prohibitions - take it, and in the recommended dosage. But! The quantitative transfer of drugs into mother's milk has been studied only for a few drugs. Therefore, in most cases, you will see that the drug has not been studied during pregnancy and lactation, or pregnancy and lactation are contraindications for use (precisely due to the lack of studies on this group). Some mothers try to reduce the harm of drugs by reducing the dose. It is not recommended to do this; the expected effect will not happen (especially if we are talking about products that are acceptable during breastfeeding!).
- Look in the instructions for an indicator that is important for us - the drug elimination period. As a rule, it is the same for blood plasma and breast milk. This way you can calculate the period when the drug leaves your body. Analgesics penetrate into the blood and into mother's milk at the same time: this requires only half an hour, the maximum concentration occurs after 1–1.5 hours. And they appear longer – up to 2–7. The half-life of paracetamol, for example, is about 3, and acetylsalicylic acid - up to 7.
Thus, the ideal time to take the product is after evening feeding. Babies, even newborns, sleep for 3–4 hours at this time; during this period, the medicine will not only have time to eliminate the mother’s pain, but will also be eliminated from her body, including from milk.
Of course, there are cases when pain relief is needed urgently, but it is impossible to get to a doctor. For example, a nursing mother had a toothache at night. In this case, from the list of approved painkillers, the drug that contains the least amount of toxic substances is selected. Toxins immediately penetrate into breast milk, and the child’s body has not yet learned to eliminate all toxic substances.

After taking painkillers and feeding the baby, the mother should constantly monitor the condition of the baby. If he develops increased drowsiness, lethargy, apathy, lack of appetite, and especially nausea with vomiting, you should immediately call an ambulance.
In the case when the drug is taken as a course, it is necessary to exclude breastfeeding at the very peak of activity of the active substances. If a nursing mother is prescribed a medicine that is incompatible with lactation, she should stop breastfeeding and resume it after treatment. Under no circumstances should you reduce the dose of the drug in order to continue feeding your baby milk. This is dangerous for his health, development, and sometimes life.
Pediatricians strongly recommend that when taking painkillers for a long time, you constantly express milk so that the active substances do not enter the baby’s body.
If the pain is temporary and does not occur often, it is quite acceptable for a woman to take an approved painkiller while breastfeeding. When the pain does not stop, occurs regularly, and causes severe discomfort, this signals that the woman needs to undergo an examination to identify the true causes of the pain.
Chronic lack of sleep, fatigue, nervous tension, changes in blood pressure, hormonal changes, PMS - all this leads to severe headaches in nursing women. There is no need to endure pain; there are safe medications that can help cope with migraines.
What can nursing mothers take for headaches?
Remedy No. 1. Paracetamol and drugs based on it - Panadol, Strimol, Efferalgan. No more than 20% of the active substances will get into the milk; it is better to take the medicine immediately after feeding - its maximum concentration in the blood is observed within 30 minutes, and it is almost completely eliminated within 2-3 hours.
Remedy No. 2. Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Ibufen, Ibuprom - do not affect the child’s well-being. There are Ibuprofen suppositories that act gently and effectively.
Remedy No. 3. Sumamigraine - helps to quickly get rid of even very severe migraines, but has strong side effects.
All of these drugs have antipyretic properties, so you can take them for colds and flu.
At the initial stage of a migraine, when the pain is not expressed, a contrast shower will help cope with the unpleasant sensations - direct alternate streams of cold and hot water directly to the top of the head. The duration of the procedure is 7-10 minutes, after which you can massage and comb your hair.
Strong black sweet tea helps cope with headaches well - this drink cannot be called the safest for a child, but a single dose will not harm the baby; drink it immediately after feeding.
Often headaches occur with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region; in such cases it is better to use painkillers and warming ointments. The safest medications during lactation are Menovazin, Nurofen and Ibuprofen in gel form, Finice, Chondroxide, Biopin.
Consequences of using painkillers during lactation
Doctors don’t just forbid you to take certain medications on your own. Many drugs pass into breast milk and then enter the baby's gastrointestinal tract. Through the bloodstream, dangerous substances are carried throughout the body, leading to serious disorders.
Useful: 9 reasons why watery blisters appear on a child’s skin
Here is just a small list of problems that painkillers can cause in a child:
- changes in behavior, anxiety, tearfulness;
- sleep disturbance;
- drowsiness, lethargy;
- regurgitation;
- toxic liver damage;
- disruption of the nervous system;
- damage to blood cells.
Advice
Do not take painkillers without a doctor's prescription!
The consequences of using analgesics can be completely unpredictable. That is why many nursing mothers have the opinion that during lactation they should not take any of the existing drugs at all. Actually this is not true. A young mother does not need to endure pain, because her condition will inevitably affect the child. Babies perfectly feel the mother’s condition and begin to worry with her. Breastfeeding women can take analgesics to relieve pain. It is only important to choose the right medications that will not negatively affect the baby’s condition and will not lead to a decrease in breast milk production.