Causes of migraine
Migraine during breastfeeding is caused by the following number of reasons:
- Hypertension and a constant decrease in blood pressure;
- Chronic or acute diseases of the nose and sinuses, ears, nasopharynx;
- The development of pathogenic pathogens and infectious complications affecting the central nervous system;
- Diseases that initially affect the brain;
- Violation of the structure and functioning of the spine, namely the cervical spine (osteochondrosis);
- Constant nervous and physical tension.
The condition worsens sharply with poor diet and non-compliance with a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms and types of headaches in a nursing mother
There are many reasons for such symptoms in breastfeeding women. But you can’t rush to the first aid kit. After all, everything that the mother takes goes to the newborn through breast milk. Dizziness appears during hepatitis B, which often happens against the background of epidural anesthesia.
Women, creating comfortable conditions for the child, close the windows and create greenhouse conditions. This is another mistake that causes similar symptoms in a nursing mother.
The normal rest regime has been disrupted. Sleepless nights, endless awakenings. This does not give the brain the opportunity to rest properly. After such nights, characteristic symptoms appear in the morning.
Migraine
Pathology occurs not only in women who are breastfeeding. Pregnant women complain of headaches. Poor nutrition, lack of sleep, lack of oxygen, stress are just some of the factors that provoke migraine attacks.
A severe headache appears suddenly and may not go away for several days. It increases in bright light, the baby's cry, sudden movements, and during breastfeeding. This aggravates the physical and emotional state of the young mother. The hand habitually reaches for the first aid kit for emergency help. We must not forget that a pill that is safe for the mother is harmful to the child.
Sudden changes in blood pressure are a symptom that appears after an overload of the body associated with the birth of a child. When breastfeeding, if your blood pressure rises, this can be accompanied not only by headaches. The condition is accompanied by shortness of breath, tachycardia, and nausea.
Osteochondrosis can provoke hypertension. A nursing woman is forced to remain in one position for a long time, carrying the baby in her arms without transferring him to the crib so that the baby does not wake up. This places a static load on the spine, provoking the appearance of this disease, which is accompanied by frequent, severe headaches.
Clinical picture
Headaches can take on a different character, be aching, dull, sharp, paroxysmal, and so on. Discomfort either becomes focal, that is, it disturbs in a certain area, or diffuse, when the patient cannot point to a specific point of pain.
Migraine is often accompanied by intoxication (with an infectious lesion) - weakness, chills, fever, fatigue and decreased ability to work. In case of disturbances in the structure of the nervous tissue, nausea and vomiting are observed, which do not bring relief. Possible mental disorders, hallucinations, sudden changes in mood.
Headache pills allowed while breastfeeding
For headaches, a nursing mother can use Paracetamol, Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Drotaverine.
These medications are used for various types of pain and are relatively safe for a breastfed baby.
Paracetamol
One of the most popular and safest medications for a mother who is breastfeeding is Paracetamol. This is a drug from the group of analgesics-antipyretics. The mechanism of action is based on suppressing the synthesis of special substances - prostaglandins, which are responsible for the development of the inflammatory reaction. Paracetamol for hepatitis B exhibits analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activity. Used for various types of headaches. The drug is prescribed orally, the maximum single dosage is 1 g.
Paracetamol passes into milk: approximately 0.04% of the dosage taken by a nursing woman. The medicine does not exhibit a toxic effect, but in some cases it can cause allergic reactions or digestive upset in a child. Such symptoms will require discontinuation of the medication.
Ibuprofen [1]
A medicine from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ibuprofen has an active analgesic effect during breastfeeding and can be used as an emergency treatment for pain.
Nurofen, Ibusal, Ibufen, MIG - these are all different trade names for the same active ingredient - ibuprofen. It is available in the form of capsules, syrups, effervescent tablets, drops and dragees. The mechanism of action is based on inhibition of the synthesis of an enzyme that activates prostaglandins (inflammatory cells). The drug relieves pain, relieves inflammation, and reduces temperature.
A good medicine for headaches that is not toxic to a child. Does not cause adverse reactions.
The analgesic effect is especially pronounced for headaches associated with inflammation. For neurological or vascular problems, it may not be effective. In rare situations, it can cause allergies or disorders of the digestive tract.
Prohibited drugs
All other drugs are undesirable during breastfeeding, but there are separate groups of analgesic drugs that should not be used under any circumstances. These include:
- Analgin. A rather toxic drug even for adults, it negatively affects absolutely all organ systems;
- Nimesulide. No negative effect on a small child has been experimentally proven, but due to the lack of objective data, the medication is treated with caution;
- Citramon. Contraindicated in women with a tendency to arterial hypertension, as it contains caffeine. Another active ingredient, aspirin, negatively affects the cellular composition of the blood and reduces its clotting.
It is important to remember that any medicine can become toxic to mother and child if the specialist’s recommendations and dosage are not followed.
Migraine and breastfeeding
As a rule, if a woman suffered from migraine before pregnancy, then with its onset and during breastfeeding, the condition improves significantly - it’s all about altered hormonal levels, but there are exceptions.
Migraine is characterized by throbbing, one-sided pain of moderate or high intensity, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and increased sensitivity to light and sounds. Such an attack lasts from several hours to several days and completely deprives a woman of her ability to work and the ability to look after her child. Therefore, stopping a migraine attack with medication is mandatory even for nursing mothers.
Modern pharmacology offers a large number of drugs, both to eliminate an attack that has already begun and to prevent the next one, but almost all of them are potent medications that have many contraindications even for non-lactating women.
The only anti-migraine drug that can be used while breastfeeding is Sumatriptan from the group of serotonin receptor agonists.
The medicine is available under the names Sumamigren, Sumatriptan, Imigran in the form of tablets of 50 and 100 mg, as well as in the form of a nasal spray. To stop an attack, it is enough to take 1 tablet of 100 mg (50 mg helps some people). The instructions for the drug say that it should be used with caution when breastfeeding. This means that use is possible, but with some nuances: the period during which a safe concentration of the drug for a child is achieved in breast milk is 12 hours. Thus, during this period of time, the baby must be transferred to artificial feeding or fed with breast milk expressed before taking the pill.
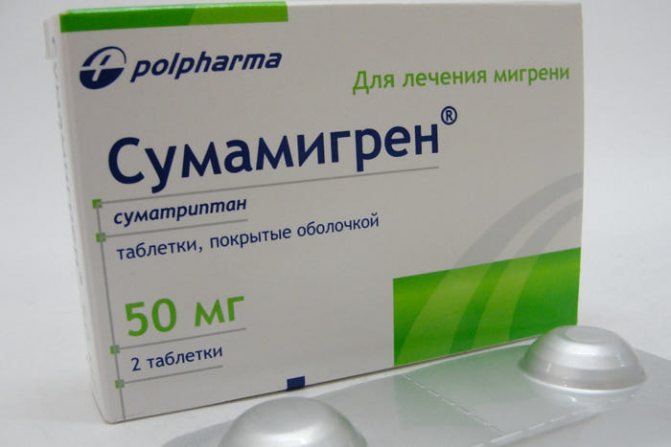
Sumamigren is approved for use in nursing mothers for migraines
ethnoscience
Many people in practice resort to alternative medicine recipes, which, on the one hand, is correct, since infusions and decoctions are made exclusively from natural raw materials, and on the other hand, patients forget about the sense of proportion and the rules for taking such medicines. They also do not consider it necessary to consult specialists.

Doctors categorically prohibit the use of sedative medications from valerian, hawthorn, and motherwort for two reasons. Firstly, sedatives have a bad effect on the baby’s brain function, and secondly, some mothers prefer alcohol tinctures, and, as is known, ethanol is toxic to cells and tissues.
In moderation, chocolate is beneficial in cases of constant stress. When consumed, endorphins are released into the blood, relaxing the nervous system and relieving headaches. For the same purpose, in the absence of contraindications, herbal aromatic teas with lavender, raspberries, chamomile, rose hips and viburnum are recommended.
Prohibited drugs while breastfeeding
There are practically no medications that, after being taken by a woman, do not pass into breast milk. The instructions for the drug must indicate this in a separate paragraph or in the “special situations” section.
If there is no such indication, this does not mean that the drug does not pass into milk - perhaps, research on this matter has simply not been conducted, and taking such a medicine is strictly prohibited without consulting a doctor.
But there are times when it is impossible to get medical advice, for example, a headache took you by surprise, and there is no way to go to the clinic. It is for such emergency situations that all mothers should know which headache medications they should absolutely not take.
The most important thing is to forget about analgin! This medicine is prohibited for use in most developed countries of the world due to its danger and toxicity not only for the mother, but also for her child. Also dangerous are combined analgesics, which contain similar molecules - tempalgin, sedalgin, pentalgin and the like (they can be identified by the ending “gin”).
You should also not take painkillers that contain derivatives of barbituric acid (can lead to inhibition of all processes in the central nervous system), codiene (a narcotic analgesic that can cause respiratory depression in the baby), caffeine (can cause agitation in the child and poor sleep).
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is also contraindicated for nursing mothers, as it has a negative effect on the baby’s hematopoiesis and brain, and in addition, it often causes the formation of ulcers in the mother’s stomach. In view of the above, it becomes clear why nursing mothers should not take the “favorite” and effective citramon for headaches - in addition to paracetamol, it contains caffeine and aspirin.
Video about taking medications during breastfeeding and pregnancy:
Headache medications prohibited during lactation
There are painkillers that are safe for adults, but contraindicated for children. This is due to the fact that the active substances pass into milk and can cause serious adverse reactions in infants.
Aspirin®
Acetylsalicylic acid or aspirin is a popular remedy for eliminating headaches and fever. For children under 15-16 years of age, this medicine is contraindicated in any dosage due to the risk of Reye's syndrome.
Reye's syndrome is a rare dangerous complication that develops during viral infections in children while taking medications with acetylsalicylic acid.
In addition, aspirin in breast milk can cause bronchospasm or other severe allergic reactions (Quincke's edema, urticaria).
Citramon P
A combined product that includes three active ingredients: caffeine, paracetamol and acetylsalicylic acid. Citramon is not prescribed to a nursing mother due to the content of acetylsalicylic acid in it. In addition, caffeine can have a negative effect on the child and cause symptoms of overexcitation of the nervous system.
Analgin
A good pain reliever for adults, the metabolites of which pass into breast milk in high dosages. In young children it can cause complications related to the functioning of the nervous system, allergies and other toxic effects.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
A wide list of drugs (Diclofenac, Nimesulide, etc.) that have a powerful analgesic effect. Drugs in this group are not recommended for use during lactation, since there is no proven clinical data on their use during this period. The only exception is Ibuprofen, described above. This remedy has been well studied; along with Paracetamol, it is one of the safest for nursing mothers.