All mothers strive to feed their baby with their milk. And almost everyone thinks that the baby is malnourished, something is being done wrong. Mothers begin to get nervous, their mood is transmitted to the baby and all family members. How can you make sure everyone is happy and calm?
Baby as the best “medicine”
After delivery, either naturally or after a cesarean section, the mother’s body releases a specific hormone from the anterior pituitary gland -. This is the so-called lactogenic hormone, which is responsible for stimulating the secretion of breast milk. A woman who has just given birth produces very little colostrum, the prototype of milk. There is very little of it, literally a teaspoon (about 5 ml), but this is quite enough for a newborn.
The baby has just experienced the great stress of his own birth, and his digestive tract and kidneys are not yet able to process a larger volume of food. Colostrum contains special substances (globulins and albumins) that do not need to be digested; they are absorbed immediately in the intestines.
Doctors believe that the optimal intake for the first months of life should be at least 500 grams per month. You don’t have to wait for such a period of time; weigh the baby once a week; if the number on the scales does not show a weight gain of more than 120 grams, it means that the mother actually has little milk. There is also the so-called “diaper test”, or “wet diaper test”. The baby should urinate at least 8 times a day, and only well-wet diapers are taken into account.
Most often, nursing mothers experience “”, that is, a condition when, under the influence of hormones, milk production decreases slightly. This is a natural phenomenon. Typically, crises occur in the second or third week after birth, 30-40 days after birth, and the last crisis dates back to 3-3.5 months after birth. Of course, the dates may vary somewhat, because the endocrine system of each woman works differently. You need to take this calmly, because in 3-9 days this condition will pass, but on average, it lasts 3-5 days. Don’t be upset, because “lactation crises” are easy to correct. As we already wrote above, we should try to breastfeed the baby at his first request, even 15 minutes after the previous feeding. Also try to feed your baby at night, because it is at this time that more prolactin is produced, which means there will be more milk. If you feel that there is still milk left in the breast, and the baby is already full, then...
To have more milk
Mothers, when it seems to them that the baby is malnourished, strive to supplement him with formula. You shouldn’t do this, since the baby will willingly follow your lead (after all, it’s easier and easier to suck from a bottle), and the mixture is always sweeter than mother’s milk, and therefore seems tastier. Early introduction of complementary foods will not have the best effect on the baby's immature intestines; colic, constipation and allergies will not take long to appear. Modern pediatricians advise only after 6 months.
It is better to establish your own drinking regime: drink as much as you want, doctors recommend still mineral water. The old recipe of our grandmothers - to drink more - has already been refuted, but, nevertheless, it helps many, it’s more about the placebo effect, but it’s worth a try. Increasing lactation is indirectly helped by quality sleep (so try to sleep in every free minute, even during the day), walks in the fresh air, gymnastics (by the way, with its help you can maintain an attractive breast shape), and the opportunity for proper rest. You can do a light massage of the mammary glands: lubricate your palm with castor oil and with light circular movements (without pressure) massage the gland without touching the area of the nipple and areola.
Carrots have lactogenic properties, but you can use this recipe only if the baby does not have allergies. The easiest way is to grate the carrots, add hot boiled water, wait a little and eat, after adding a little milk or cream for better digestion and improved taste. You can squeeze it out and drink it, after adding 1 teaspoon of cream.
They also help increase milk supply, but they must be used carefully and only as directed by a doctor. If mom has digestive problems, dill, anise and fennel will help her. These herbs will not only help increase lactation, but will also solve digestive problems for a nursing mother. It happens that mom is nervous and doesn’t sleep well, then her choice is mint, oregano and lemon balm. And nettle will help if there is a persistent feeling of physical fatigue. All herbs should be brewed according to the same scheme: 1 tsp per 1 glass of very hot water. Take a quarter glass before each feeding.
In such an important matter as feeding a baby, there are no trifles. But there are important rules: the mother should listen to the doctor’s recommendations, eat right, and not be nervous. A newly born baby is very uncomfortable in our world, and it is necessary that he be in close contact with his mother for as long as possible. Remember the advice of grandmothers: talk kindly to your baby, look him in the eyes, stroke him, give him breastfeeding as often as possible. If the baby is ready to “hang on his chest” for hours, this is a sign that there is some kind of psychological instability in the family and the mother is forced to worry a lot. And if sometimes you are unable to change the mood of all family members, then you can try to devote as much time as possible to your baby.
Tatyana Timofeeva
Nowadays, there are more and more cases when a young mother, upon discharge from the maternity hospital, is faced with the problem that the newborn does not have enough breast milk or the baby himself begins to refuse the breast. Most doctors, instead of finding the root of the problem and establishing lactation, simply transfer the child to artificial feeding. Although, first, we need to figure out what happened. After all, nature created that after birth, a baby does not need any other nutrition other than mother’s milk.
It is possible that there is not enough milk if the first attachment to the breast did not occur immediately after birth or the baby is rarely applied. As you know, the more often you breastfeed, the more colostrum there will be, and soon milk.
Another important factor influencing the level of lactation is the stress or experiences of the mother. After all, after giving birth, a woman experiences great changes in her body, both physical and moral. The woman becomes more vulnerable and receptive. Postpartum depression is common. And even a rude or incorrect attitude of the maternity hospital medical staff can affect the mother’s mental experience, which will lead to a decrease in lactation.
It happens that after giving birth, a woman is prescribed treatment with medications, after the use of which feeding is contraindicated for some time, as a result of which breast milk may disappear completely. In this case, it is quite difficult to establish lactation, but it is also possible. There are cases when a woman, after a break in feeding for one reason or another for 1 or even 2 months, then managed to resume breastfeeding.
Therefore, even before the moment of birth itself, a woman must prepare herself for the above-mentioned points and try to prevent anything from affecting the process of natural feeding of the newborn. After all, breast milk is the most valuable nutrition for a little person. No artificial mixture contains so many useful substances and does not strengthen the immune system. Natural feeding is also more economical in terms of money and is very convenient - there is no need to get up in the middle of the night to prepare the formula.
However, if the problem of normalizing lactation still arises, do not despair! Under no circumstances stop putting your baby to your breast, even if you then need to supplement him with formula. If the baby stops taking the breast on his own, try to give it anyway, help him with this, if you can’t do it yourself, ask the medical staff or your mother (sister, friend, roommate, husband) for help. The child may not be able to grasp the nipple, then it is worth buying special silicone pads at the pharmacy. There are breast pumps on sale; they can be used to express milk into a bottle and even pull out the nipple (this will make it more comfortable for the baby).
Control your diet, eat foods approved by your doctor in moderation, but often. Drink more fluids (tea with milk helps). Special herbal teas to increase breast milk will help improve lactation. Spend more time outdoors. Rest. And, under no circumstances, do not be nervous! After all, now there are more of you in the family! Be happy! And more delicious mother’s milk for the little one!
| Increase lactation folk methods |
The lactation period is a very important moment in the life of every woman who gives birth to a child. Mature lactation is the most important phase of this process. The entire period of milk production is divided into different stages - mamogenesis, lactogenesis and lactopoiesis. The first stage is characterized by the maturation of the mammary gland, during the second stage milk is formed after childbirth, the third is aimed at maintaining milk secretion with the development.
The very concept of “lactation” means the release of milk into the mammary gland, and lactogenesis is directly proportional to the hormones prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin, being a key maternal hormone, determines the behavior of a woman during the lactation period. It is he who helps the child come to the fore. Oxytocin is responsible for boundless love for your child. It is formed in the depths of the brain. In addition, its main purpose is to secrete milk.
How is lactation established?
How and when is lactation established? The secretion of milk in the mammary gland is divided into three stages:
Stage No. 1 - initial. It begins during pregnancy. About 13-14 weeks before giving birth, a woman’s body begins to produce colostrum. During this period, women's breasts change their shape and become sensitive to touch. All this happens thanks to estrogen and prolactin, which affect it.
Stage No. 2 - formation of active lactation. When the baby is born and the placenta is separated, the main stage of lactation begins. As a rule, when a baby is put to the breast for the first time (usually immediately after birth), the above-mentioned hormones send a signal to the brain, which in turn gives the command to the active phase of lactation. As a result, the baby receives the required portion of colostrum.
Stage No. 3 is transitional. During this time, colostrum is gradually replaced by breast milk. The duration of the transition stage is approximately 4 to 8 days. From the first to the third day, the breast secretes colostrum, which is replaced by early milk. After 7 days, the body begins to produce mature milk. But here everything is quite individual, and to a greater extent the period of establishing lactation depends on the mother’s body.
Thus, the complete process of establishing the lactation period after childbirth occurs according to the scheme below:
- from days 1 to 8, colostrum is produced;
- from 8 to 21/40 days - transitional milk;
- from 22 or 40 days to 2 years - mature milk.
Throughout the entire lactation period, milk is produced under the influence of hormones, even regardless of whether the baby is feeding or not.
From the 1st day to the 4th week, you should feed your baby frequently so that prolactic receptors increase. This ensures that the mammary glands best adapt to the synthesis with prolactin, the participation of which is very important. The presented interaction represents the most important step in the formation of all subsequent stages of lactogenesis.
It should be remembered that during this period there is no need to feed the child according to the planned regimen. The optimal and useful option is to feed the baby on demand, approximately once every one and a half or two hours. Don't forget about night feeding. It is also not recommended to use pacifiers (they can only be used in rare cases) if you want to feed your baby healthy breast milk for a long time.
Return to contents
What is mature lactation
The formation of the lactation process occurs long before the baby is born and is put to the mother’s breast for the first time - milk production begins in the third trimester of pregnancy under the influence of hormonal changes.
In the first days of life, a newborn receives the most valuable nutrient - colostrum. After 3-5 days, milk appears, but this does not mean that the time has come to establish mature lactation.
Physiologically, the process of breastfeeding is so complex that it will take a lot of time for both participants to get used to it.
At this stage, the woman begins to experience unpleasant sensations:
- body temperature rises;
- there is a feeling of fullness in the chest, it becomes heavy;
- tingling in the mammary glands;
- often throws you either hot or cold.
During this period, it is very important to put the baby to the breast at his first request, so that painful lumps do not form in it due to excess milk.
After 3-4 weeks (for some it happens later - up to 2 months), the woman discovers that the tides in the chest are not felt at all and they are soft. And if the baby continues to eat enough and gains the required weight, then this period is marked by the establishment of mature, full lactation.
Active lactation and oxytocin reflex
Many nursing mothers are bothered by tingling and pain in the mammary glands. How to understand what causes pain in the chest area? The answer is simple: it is the hormone oxytocin that performs its function. Signs of the oxytocin reflex are:
- burning sensation in the chest during feeding;
- pain and feeling of fullness in the chest;
- milk leaking from one breast when the baby suckles on the other;
- breast leakage before feeding;
- release of milk after the baby has interrupted feeding.
Surprisingly, it is oxytocin that affects the female body during the sucking process. He directs the collected milk to one breast or another. This process is an active reflex of the release of breast milk.
It is often influenced by the general mood, existing or imagined thoughts and various emotions of the mother. Tender feelings and love for your baby have a beneficial effect on oxytocin, while fear, doubt and resentment have a negative impact and periodically dull the functioning of the hormone. In any case, in all stages of feeding, smile more often, do not pay attention to the negative aspects of life, avoid scandals, concentrate on the positive.
The lactation period is a hormonal process that is strongly influenced by the mother's various emotions, which directly control the hormones themselves responsible for milk production. Therefore, try to create the most favorable atmosphere around you. If you have a conflict situation with your husband, then you don’t need to immediately attack him or take all his advice with hostility, but sit down in the evening and talk in a calm atmosphere and draw constructive conclusions. By the way, in the first 3 months, direct and adequate assistance from your mother is strongly recommended.
Return to contents
Features of mature lactation
As mentioned above, mature lactation is established in different ways and depends on certain factors.
Mature milk can begin to be released both from the 22nd day and from the 40th. But, as practice shows, this often happens immediately after 3 weeks. Features of the formation of lactation and the release of mature milk:
- breast softness;
- feeling of unfilled gland before feeding;
- there is no pain in the breast during the arrival of milk;
- Milk production occurs during feeding.
The difference between the mature phase is that from now on milk is produced not according to the amount of hormones in the blood (in other words, not under the influence of prolactin and oxytocin), but directly depends on the degree of emptying of the breast.
Now the scheme is already in effect: “it’s empty, so it needs to be filled.” The mother feeds her baby, the breasts are freed, therefore, milk will continue to be produced. If there is demand, supply is born. The mature lactation period is a measured flow of milk, without any surges. In addition, a self-regulatory process is now activated, where the supply of milk depends on the child’s desire. What is the appetite, so will the amount of milk. How do you know if the baby is getting enough? There is a very original way to check whether there is enough milk for the baby. Choose any day without using a diaper and check how many times your baby pees. If the total number of urinations per day is approximately 10 times, then your baby has enough milk. Well, if it’s less than 10, then there are some flaws in the development of your lactation that need to be corrected.
The lactation process is characterized by the production and secretion of breast milk in the mammary glands. This important physiological process begins its formation in the late stages of pregnancy, preparing a woman for future motherhood.
The stage of mature lactation is characterized by stable production of breast milk in the same volume without significant hot flashes. In order for this to happen, hormonal changes occur in the young mother’s body.
Signs of mature lactation
The active phase of lactation occurs differently for everyone. For some mothers it begins at 3 weeks of age, for others a month and a half after birth. How can a woman understand that lactation has established, what signs will indicate this? Among them:
- No hot flashes or swelling of the mammary gland.
- There are no tingling or painful sensations before breastfeeding.
- The feeling of fullness and the desire to express milk disappear.
- The breasts are soft before feeding, and there is often a feeling of lack of milk.
- The child's behavior was calm: he ate, then fell asleep.
- Equal time intervals between feedings are established, that is, the baby’s daily routine is formed.
Lactation in multiparous mothers is no different from the process of feeding first-time mothers. The woman just becomes more experienced. Don't panic if your chest feels empty. She latches on to the baby more often to quickly establish breastfeeding.
Stages of lactation formation
The mechanism of lactogenesis is very complex, and in order for the mammary glands to begin producing breast milk, the female body goes through several successive stages.
Preparatory stage
During pregnancy, a functional restructuring of the mammary glands occurs in a woman’s body under the influence of hormonal factors. During this period, the ducts of the mammary glands grow and branch, and the alveoli and lobes of the mammary glands develop. There is also a rapid growth of lactocyte cells responsible for the production of mother's milk. 11-12 weeks before the onset of labor, these cells produce colostrum in small quantities.
Stage of formation of the lactation process
This stage of lactogenesis includes such successive stages as:
- Start of lactation. The start date for this stage is the moment the baby is born and the placenta is separated. A delay in the start of lactation may be due to incomplete separation of placental tissue.
- Milk production. The first flow of breast milk is observed 35-40 hours after the birth of the baby. During this period, the amount of colostrum produced decreases, and the amount of milk increases. At this stage, the woman’s endocrine system is responsible for the production of milk, so lactation increases regardless of whether the newborn is attached to the breast or not.
- Stage of transition to mature breast milk. This stage is characterized by the complete replacement of colostrum with full-fledged breast milk.
- Stage of adaptation of the female body. During this period, the nursing woman’s body gets used to its new function, and also adapts to feeding a particular child. The duration of the adaptation period is 4-6 weeks. Another important feature of this period is that from this moment control over the level of maternal milk production is carried out in an autocrine way. This means that the more milk the baby eats, the more milk will be produced in the mammary glands.
Stage of mature lactation
The duration of this period is the first 3 months of the child’s life until the complete end of lactation. The level of milk production depends on the needs of the newborn baby. During this period, so-called lactation crises often occur, characterized by a temporary decrease in maternal milk production. If such a situation arises, then there is no need to rush to feed the baby with an artificial formula.
A lactation crisis is a physiological process that occurs due to a mismatch between the age-related needs of the child and the level of milk production in the mammary glands. The crisis goes away on its own after 5-7 days without outside intervention.
Stage of lactation suppression (involution)
The timing of involution is individual for each nursing mother. This usually happens when the child is between 2.5 and 4 years old. The entire stage of cessation of lactation is divided into the following stages:
- The active stage, which is characterized by a sharp decrease in the production of maternal milk and a reduction in the number of cells responsible for this process. At this stage, breast milk is similar to colostrum, which is so necessary for a baby at this age. A characteristic sign of the onset of involution is the absence of milk flow during long breaks between feedings. When a woman stops lactation, her mammary glands are not at risk of congestion and mastitis.
- Stage of immediate involution. The characteristics of this stage are based on the complete destruction of the mammary alveoli, which are responsible for the production and accumulation of mother's milk. The duration of the stage is 2-3 days, after which the ducts of the mammary glands narrow and the outlet openings completely close. 35-40 days after the start of the process, the mammary glands cease to be lactating, and the glandular tissue turns into adipose tissue.
Stages of lactation formation
The milk production process has several stages. It begins during pregnancy and ends with the involution stage. Only 1.5–3 months after the birth of the child does mature lactation begin. Moreover, in primiparous women this process takes longer than in women who have given birth.
This stage of preparing the mother's breast for feeding begins during the period of gestation before birth. A number of hormones are involved in this process, each of which performs its own function.
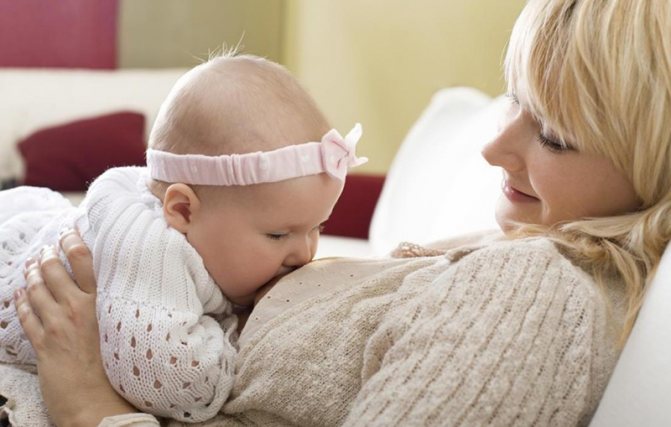

Changes in the mammary gland occur under the influence of estrogen, prolactin and progesterone. Hormones provoke the growth of milk ducts and their branching. Thanks to the influence of prolactin, the lobes and alveoli of the gland develop. Lactocytes (milk-producing cells) increase. Colostrum appears around the 28th week of pregnancy. Milk production begins immediately after birth.
During this period, a woman may notice external changes in her breasts. It may increase in size and the nipple areola may darken. The nipple itself becomes more elastic, sometimes more sensitive.
The process of establishing lactation begins after the birth of the child. Strong hormonal changes provoke the onset of milk production. The process of separation of the placenta takes place, and the baby is placed on the breast. This is accompanied by a significant decrease in progesterone levels and the release of oxytocin.
We suggest you read: Mifepristone for inducing labor
After 2–3 days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk, its amount is several times greater. The woman notes the fullness of her breasts, sometimes density and heaviness. In some cases, fever and redness may occur.
At this time, the process of breastfeeding is controlled by the endocrine system. Therefore, milk production occurs even if the mother does not breastfeed. At this stage, it is important to put your newborn to the breast frequently. This promotes the formation of a large number of receptors for the hormone prolactin. They affect the production of sufficient milk volume. The number of receptors remains constant throughout all stages of lactation.
2–3 weeks after birth, the final transition to mature milk is observed. The amount of prolactin decreases. This occurs as the process of establishing lactation completes. Milk production is no longer carried out under the influence of hormones, but under autocrine control. This means that the volume of milk produced depends on the amount of milk the baby drinks.
Mature lactation
This period lasts from 3 months after birth until the end of lactation. Milk production is completely under autocrine control. Milk is produced as much as the baby needs. The amount of prolactin stops at a level almost equivalent to what it was before pregnancy.
This property is especially important during lactation crises. They appear as a result of an increase in the need for milk in a growing baby. At this time, it is important to give the baby the opportunity to breastfeed for as long as he sees fit. This way it signals the breasts to produce more milk. After 3–7 days, the body adapts to the increased needs of the baby and milk becomes sufficient.
Involution
A physiologically justified cessation of natural feeding is called involution. Milk continues to be produced even after the baby stops breastfeeding. According to WHO, the period of involution in the female body lasts for 40 days. At this time, it is possible to restore breastfeeding if the baby is often put to the breast.
We suggest you read: Freezing and storing breast milk using bags
The main signs of involution are:
- The chest stops filling.
- Prolactin levels decrease, and milk-producing cells are destroyed.
- The milk becomes similar in appearance to colostrum. It has a translucent appearance and a more liquid consistency.
- The glandular tissue of the breast is replaced by fatty tissue.
- Closing of the gland ducts is observed, the breast returns to its pre-pregnancy size.
Even if the break between feedings is a day, no noticeable breast enlargement is observed. During this period, stopping the baby's feeding is painless for the mother's body. There is no excess milk or breast fullness in the absence of feeding.
The timing of lactation is individual for each organism. There are no recommendations for accelerating its formation, but there are general rules, adhering to which, it is easier to ensure that the process of establishing natural feeding is as comfortable as possible for both mother and child.
Firstly, feeding on demand is the key to providing the baby with a sufficient amount of milk and producing milk in proportion to the infant’s needs. You should avoid supplementary feeding and resort to pumping only if necessary. Secondly, it is necessary to maintain a normal drinking regime. Thirdly, the mother’s good psychological state and the absence of stress will ensure normal lactation and sufficient milk production.
Characteristics of mature lactation
The so-called mature lactation is characterized by a stable flow of mother's milk into the mammary glands, without the risk of spontaneous hot flashes. The characteristics of this period are individual for each woman. For some mothers, mature lactation is accompanied by crises, and for some it proceeds smoothly and uninterruptedly.
Another characteristic sign of the onset of this period is the softness of the mammary glands when palpated. The formation of such lactation takes from 1 to 3 months from the moment the baby is born. Changes also occur in a woman’s feelings. If earlier she felt heaviness and slight discomfort in the mammary glands, then during this period she experiences absolute lightness. Some women confuse this feeling with a lack of milk.
When lactation is established, the mother's body adapts to the needs of the newborn and produces as much milk as the baby needs.
The process of mature lactation develops gradually and has 3 stages:
- Initial stage. The potential for mature lactation is revealed even during pregnancy. 2 weeks before giving birth, the female body begins to synthesize colostrum. The sensitivity of the mammary glands increases and the shape changes.
- Formation of active lactation. At this stage, under the influence of hormones, the process of active production of colostrum is activated.
- Transitional stage. Replacing colostrum with full milk takes from 4 to 9 days from the moment the baby is born. A week after the start of the synthesis of the first milk, mature lactation begins.
Feeding a newborn should be done on demand, avoiding an hourly schedule.
The onset of mature lactation can be recognized by the following signs:
- the mammary glands become soft to the touch and cease to be heavy;
- the young mother ceases to feel pain during the flow of breast milk;
- before feeding there is a feeling of incomplete filling of the mammary glands;
- any discomfort that previously accompanied lactation disappears.
Important! A distinctive feature of mature lactation is that the amount of milk produced does not depend on the concentration of hormones in the blood, but on the degree of emptying of the mammary glands during feeding.
Causes of lactation disorders
Nature gives every woman the opportunity to breastfeed her baby. However, for successful lactation, a woman needs certain conditions - quality nutrition, proper rest, and the ability to feed the baby on demand. If problems occur during breastfeeding, it is necessary to first find their root causes.
Most often these become:
- improper attachment of the baby to the breast;
- irregular feeding and its absence at night;
- difficult childbirth, stress, postpartum depression;
- infectious diseases;
- overwork.
Thus, in order to eliminate lactation disorders
it is necessary to timely understand the cause of its occurrence. A woman cannot always figure this out on her own, especially if she has become a mother for the first time. In this case, it is important to promptly seek help from a specialist - a mammologist, because if they are ignored, the child may lose breast milk, and the woman may develop serious inflammatory processes in her breasts.
How to speed up the onset of mature lactation
The timing of this process is individual for each young mother. For some women, the formation of mature lactation takes a long time, and therefore, they wonder about accelerating this process.
- The young mother is advised to eat healthy foods, avoiding overeating and hunger. It is recommended to eat rationally and balanced. Eating fresh vegetables and fruits is beneficial.
- During breastfeeding, it is recommended to avoid increased emotional tension and stress;
- Heavy lifting and physical activity that can cause fatigue are strictly prohibited;
- The young mother is recommended to visit her doctor and agree with him on the use of decoctions based on anise, fennel and dill. It is also recommended to consume dried fruit compote, fermented milk products and foods rich in animal protein.
- The flow of milk depends on the individual needs of the newborn, so the mother should not go to extremes if, in her opinion, there is not enough milk being produced.
It is recommended to discuss taking medications that stimulate lactation, as well as expressing breast milk, with your doctor to avoid serious mistakes.
In matters of developing proper feeding, it is recommended to rely on the opinion of experts in this field. Even “valuable” advice from close relatives causes significant damage to the health of the newborn and mother.
Dear girls, today I will tell you about how lactation is formed. After reading this article, you will be able to understand well the condition of your breasts while breastfeeding your baby.
The lactation process can be divided into several stages:
- Mammogenesis
is the development of the mammary gland. - Lactogenesis
is the formation of milk in the secretory cells of the mammary gland after childbirth. - Lactopoiesis
is the development and maintenance of milk secretion.
We will talk about what lactogenesis
, we will learn all the stages of milk production in a mother’s body after the birth of a child.
Lactogenesis ( lacto-
+ Greek genesis origin) is the process of milk formation in the cells of the mammary gland, that is, it is the process of the formation of lactation - milk synthesis.
Signs of mature lactation
Often mothers, especially those who have given birth to their first child and who do not have sufficient experience, believe that since the breasts are soft, it means the child is not getting enough to eat.
This is the most common complaint at a regular pediatrician appointment. Medical negligence is considered if he immediately decides to supplement the baby with milk formula. A competent specialist must find out the reasons why the woman determined that the child is hungry and, based on this, give a conclusion whether she is right or wrong.
The absence of milk in the breast may indicate the onset of mature lactation, which has the following signs:
- Soft breasts, no hot flashes.
The body begins to produce exactly as much milk as the baby needs to satiate it; it simply does not accumulate in the breast.
- No breast leakage.
The explanation is the same - the baby’s needs are met during feeding.
- It is impossible to express milk from the breast.
During mature lactation, neither manually nor new-fangled breast pumps can empty the breast as effectively as a child does.
If a newborn cries after feeding, first of all you need to rule out colic (they can bother you for up to 6 months), a full diaper, overheating or hypothermia, and not immediately decide to stop breastfeeding.
Frequent demand for the breast is also not a sign of hunger; for newborn children, the mother's breast is not only food, but also a means of communication with the mother, reassurance, it gives a feeling of comfort and security.
Some women conduct an experiment - after feeding, they offer the baby a bottle of formula - if he takes it, it means he is not satisfied with breast milk. This is a common misconception that does not have any logical relationship - in the first few months the sucking reflex is developed so strongly that the baby will not be able to refuse the bottle, even if he is not hungry.
Lactation (lactatio; lat. lac, lactis milk) is the secretion of milk by the mammary gland.
Lactogenesis goes hand in hand with the hormones Prolactin and Oxytocin. I'll tell you a little about them:
Prolactin
Known as the motherhood hormone, prolactin plays a critical role in breastfeeding. It is believed that it is he who is responsible for the behavior of the mother during lactation. During breastfeeding, the presence of prolactin forms a pattern of behavior in the mother, when caring for the baby and his needs is placed above all else.
It is released by the pituitary gland under the influence of a signal from the hypothalamus. Prolactin acts on the alveoli, which, upon its signal, begin to produce milk.
Oxytocin
Oxytocin produces feelings of altruistic love. Oxytocin is produced in one of the deepest parts of the brain - the hypothalamus and accumulates in the neurohypophysis, from where it is injected into the body in doses.
This hormone plays a decisive role in the reproductive cycle, it triggers what we call eruption reflexes. In breastfeeding, it is responsible for the secretion (eruption) of milk from the mammary glands.
- (more information about hormones)
Now that it has become clear what the hormones prolactin and oxytocin are responsible for during breastfeeding, we will return to lactogenesis.
Lactogenesis. All stages.
Lactogenesis can be divided into several stages:
This stage begins during pregnancy.
12 weeks before giving birth, a woman's breast cells begin to produce colostrum. During pregnancy, the breasts, under the influence of the hormones estrogen, progesterone and prolactin, begin to change and become more sensitive.
The hormone prolactin during this stage directly controls the development of the lobules and alveoli of the mammary gland.
The second stage of lactogenesis “Formation of lactation”
It begins to work actively after the birth of the child and separation of the placenta. The immediate beginning of lactation is considered to be the first time the baby is put to the breast. Normally, this occurs in the first minutes after birth, the baby begins to suckle at the breast and receive the colostrum
.
3.Transition stage
The next stage is called transitional, during which colostrum is replaced by milk. The transition process lasts from 3-7 days. The first 1-3 days the breast produces colostrum
which gives way to
early transitional milk
, which changes to
late transitional milk
, after which
mature milk
.
Let's summarize how lactation is established at the lactogenesis stage:
- colostrum ->
- early transitional milk ->
- late transitional milk ->
- mature milk.
The transition from colostrum to early and late transitional milk lasts 3-7 days. The transition to mature milk lasts from 3 weeks to 2-3 months.
During the entire stage of lactation development until mature milk, milk production occurs under the influence of hormones, so milk is produced in the breast regardless of whether the mother feeds the baby or not (!)
- It is important to feed the baby frequently at this stage of lactation to increase the number of prolactin receptors in the breast. This is necessary so that the mammary glands become more adapted to interact with the hormone prolactin, which is directly involved in the process of milk production. And this interaction is an important step in the formation of lactation at the next stage of lactogenesis.
- It is important at this stage of lactation not to artificially regulate the amount of milk: do not feed the baby according to a schedule, on demand. Feed at least every 2 hours, including 2-3 night feedings. Do not pump and do not use nipples or pacifiers.
Why can breasts hurt when feeding in the second stage of lactation?
Due to the work of the hormone oxytocin. This phenomenon is called the "oxytocin reflex"
. Signs of the oxytocin reflex:
- tingling, burning sensation in the chest before and during feeding,
- pain and feeling of fullness in the chest,
- release of milk from the breast while the baby is suckling on the other,
- breast leakage before feeding,
- release of milk from the breast if the baby interrupts feeding.
Oxytocin, like prolactin, is produced when the baby sucks the breast due to stimulation of the sensory nerves of the nipple, is secreted by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland and enters the mammary gland through the blood.
Oxytocin is activated when the baby sucks at the breast and causes milk to be released specifically for this feeding. This process is the milk ejection reflex or oxytocin reflex.
Helping and hindering the oxytocin reflex
The oxytocin reflex can be influenced by the mother's mood, thoughts and emotions. Feelings of tenderness and love for your child improve the effect of oxytocin. Fears, doubts, and grievances interfere with the functioning of the hormone.
Milk release using oxytocin:
A mother looks at her child with love, thinks about the child, hears the child. At this moment, the hormone oxytocin begins to be produced in her pituitary gland, which instructs the mammary glands to secrete milk.
Oxytocin prevents milk release if:
- The mother is in pain and does not want to feed the child.
- Mom is upset or very offended.
- Mom is worried about something, worried.
- Mom doubts her abilities.
Lactation is a hormonal process, and emotions are also controlled by hormones. Accordingly, these processes are seriously interconnected. Any anxiety, fear, tension interferes with normal milk secretion, thereby only aggravating the problem.
The third stage of lactogenesis “Milk formation”.
At this stage, lactation is established and “mature milk”
. The transition to the production of mature milk can last from 1-3 months. In multiparous women, the transition to mature milk occurs faster, from 3 weeks to 1.5 months.
Signs of the formation of lactation and the arrival of mature milk:
- The breast becomes soft.
- Breasts do not fill before feeding.
- Painful milk flows no longer bother you.
- Milk is now produced during feeding.
What is the difference between the stage of “formation of lactation” and “milk formation”?
The difference is that now milk will not be produced due to how many hormones are in the blood, that is, not under the influence of the hormone prolactin and oxytocin, but will be produced at the moment the baby sucks. And its quantity will depend on how empty the chest is.
Now the “empty vessel” principle works: the mother feeds the child, the breast is emptied, which means milk will continue to be produced. Demand creates supply. The main rule of feeding with mature milk: longer, more often, do not skip night feedings!
Mature lactation is characterized by a stable supply of milk without significant “hot flashes” and a soft state of the breast. The processes of self-regulation are also activated, milk comes in the process of sucking the child and the child himself regulates its quantity.
How do you know if there is enough milk for your baby?
Wet diaper test.
You need to not use diapers for 24 hours and count the number of urinations that the child will make. There should be at least 12 of them per day, this number means that the mother has enough milk.
On average, urination can be from 12-18 times. If there are less than 12 urinations, then you can already think about what mistakes you made in the formation of lactation. And work on these mistakes.
Calendar for Today
Birthdays: Freckle (38) Angik (40) s0lnyshk0 (37) Tinfea (38) mamamira (35) Cosmeya (38) marmishka (38) insa (40) aniaetko (34) Natashapivovar (34) balek (39) Tomiko (39 ) Larsan (48) Kachtanka (46) semich (38) space (37) katuha. (35) Selestia (38) zhmenya (42) emiliya55 (37) Katerina-it will be good (31) na-ta (40) MAMAARTEMA (39) supertangel (38) Tonicav (34) [email protected] (41) Brigadier_Gerard (47 ) [email protected] _Juli (35) p.olya (38) drakohka (37) Nafanka (40) Iriska_r (35) Ta-Nyusha (38) Winstyle (39) Tata-10 mila_xx (44) ashka.best (34) Un_Ghost (34) Marisha 506 (42) Annushka 85 (35) _arina_ (45) Lizavetka (34) data_masha (36) Memslolla (44) RioKlant (46) HritininSsor (40) Seigphide (42) smotretSoks (44) immadsPiz (47) KrisToodiA (45) Oregremy (42) rastFruth (44) unemponeymnab (43) Santdrind (43) _Marina_Ko (34) kronowols (32) kitirima (48) grabaza (41) mrkngeoralo ) MOOMBPYPE (42) scoordroarp (32) tbuslik ( 38) alaaf (32) dadyRargorm (43) Arsuta (46) louplidlitiex (41) RAKOXICEHOICE (39) Olenka10.09 (41) dessisopLic (43) allexbarobin (41) dymnElderry 38) ivansegytokeev (44) Involomma (38) NorwromsSom ( 45) beildinnobind (41) DimitraD (41) OblisCibe (39) dilsswacids (41) woovaScop (40) LanaYasn ( AbapleloHeili (40) Thullieri (42) sendCeRyise (41) Brarlenefoode (40) IMMEREBOALA (33) belyjmavr (40) reillitle (39) HerbWrevy (43) tewvessyjex (34) Bupexepay (44) drymnorarm (40) Kekssteemecer (32) Reensekix (40) Holoreite (42) Babarromb (41) KayamyBalBamy (38) Stermobbeme (40) calfSedycle (36) Swesaulseds ( 43) puntaiptunsen (41) thychoabaph (42) KemKneepe (32) insactflics (38) icogestodiemi (42) hodyKayanna (35) ErEmbaryEpima (36) syncswory (43) CoimamonOmisp (41) YliaKovach (34) TaseInfassy (45) Orepterly (37) BrekTrerE (43) BankFauntee (41) wekundurn (41) Gello4ka (34) vedlyFall (38) Toogdiose (44) psycle (43) Foxnic (43) Sniniaskabs (43 illillhop (35) peldfrels (40) budolga (44) NuffVoini ( 40) Attacuuts (41) KisaBroossy (32) Divedribe (42) Simpompulka (27) Kneessytace (38) noiccattizDiz (40) AgusSt (41) Solomonshef (38) sefdydrisyGex ) beteTotsSmate (38) akulhut (35) tewephessjelm (42) veslowa (40) Lalsunfinia (41) MibEsoto (39) Letcereinfele (38) SerjHice (40) BrerCypetip (32) antabewex (44) Larfwaroton (43) Dexmebypele ) SilkGoowelali (33) Erroguesedsef (39) danyengacle (41) abenonsommofs ( 43) shalva (39) coestyseaxema (40) Bellaccwc (42) preoreitike (40) Leoncold (41) JesseBD (41) AAbsobbycype (38) AnnuarkUnsals (45) Dickdegc 40) ATofincom (41) Ecotteamage (44) Chainelie (40) SnagmaPreem (40) nemTriersefus (43) infonoMougs (40) TatDemTanty (41) Liverlax (39) TesKefarret (40) Boatamrop (44) Beattydrete (39) Aftectgek (39) Inandilleme (45) Marlagen (41) Arissefocrisy (42) Anya. Yar (33) uniocopusiapy (36) Floumousa (42) cicrebyreaf (45) Roultuntolo (41) Ramygrammal (43) PetPlaype (42) engergyreurdy 42) SeefTufF (41) Fuokilo (40) vseracokpa (42) oscimiCrodo (39) sconiawoomo ( 41) Irratarfunota (32) NurfPlug (40) attifisuspili (37) pornoizlehd (36) Boris_nam (42) alenspavarp (42) Verunka (33) WristeHiese (44) Ranfagefs (45) TravisTymn (39) InvelveDenkix (34) esserdoky (35) AintuitHak (35) kiraplasti (40) Drarmartothef (41) Sheertize (42) Vol_Ta_Va (34) Chitlerie (40) Morrisnome (35) StettyKasy 35) wobbyibucoult (42) Loosyloky (39) Inosezex (42) WilliCag (38) CharlesSa ( 35) Bruscut (34) banfasteroijes (36) AliusJar (41) Anneway (35) DonaldKALE (44) Adrianveby Michaelpn ( 43) Unwittigo (43) Richardused (44) Fuhfluild (38) Luuchkiino (32) Brendalymn (38) WilliamTal (43) Anthonycem (37) MichealKese (39) CharlesOr (41) Evelynvemi (37) FeliciaCeks (38) Jeromypn ( 39) Jeromeor (33) wrathorma (44) Dmitrijous DanielSl ( 36) maritta (34) MarinFaip ( 41) Charlesjarf (37) portalichA (37) RonaldWotA (44) EdwardEr (40) Sercourne (33) ABornKnows (43) AlalFrehile (38) JamEruttmor ( Anarfsmab (43) Denireweip (39) Williamgaw (44) teodormama (48) Ronaldcild (37) Rolandpi (45) magnitMAGN (33) MiguelOr (34) Evgenylab (44) Lamontset (43) MarceneCOW (34) Ernestnoum ) EdwardFror (34) Zsaqiray (43) Michaelfani (39) voskn (34) AyntsiaFum ( 36) Solevina (39) strimswrit (33) awessay (34) RichardBets (39) VinDaf 34) Asiakamn (35) Brendaot (32) vseluzgawqi (38) JosephFef (41) Aliesa (31) LeslieCed (38) Vimersck (40) FreddyKn (36) Smartinz (41) Joannesn (33) Carlosgag (40) kreeddjaxeel (38) Livaskaon Superfek (35 ) Angelatift (40) samsaalex (42) Gudorianopn (33) RichardSoro (43) XERobert (38) VXGerald ( 38) Westonma (39) Robertjeft (37) Douglaspiz (33) Kiqdabas (41) Jeremypa (40) Johnnyland (45) Viktor30pn (38) annaiy4 (45) AlyaZatravina (31) CharlesTiep (38) morgmashlab (35) vireus (37) EcoclubNits (41) broiDaf (40) Ricardoniz (34) AlbertOl (38) Marrywam (38) Jonecank ( 33) Homeinterriorjes Afrikandox (43) natkamuwa (35) List Teresa (6) sicuroexpert (34) micdoSof (38) Kochuralkalf (34) Angio1rusa (42) Robertolomi (41) tocertMt (45) ezovUsex (37) RichasVom (44) ArmandoKek (36) Fedorrew (39) DavidNE (35) JosephGaw (37) StroiCity (38) rasilLOK (42) yukyol (37 ) Sergeylaw (39) Irishkina (38) Gabrielcot (35) Careydrift (43) [show all]
Forum statistics
1644504 Messages in 24914 Topics from 272537 Users. Last user: 20News20Tuh Last message: “Re: December 2020” ( 09:09:2020, 19:32 ) Latest messages on the forum. [Detailed statistics]
Online users
Currently online on the site: 330 Guests and 2 Users. Maximum online today: 1026 . All-time maximum: 21257 (08/14/2020 at 11:50).