Severe weakness, headache, high temperature...I feel so bad! The baby immediately began to cry - it’s time to feed... is it possible, what if it’s dangerous?
No matter how wonderfully breastfeeding is organized, no matter how well it turns out, many are faced with such a problem as illness of the nursing mother. It is no secret that just 20 years ago, the recommendations of our doctors in these cases were unambiguous - you should not breastfeed if you are ill! However, since the mid-80s, attitudes towards breastfeeding have undergone dramatic changes. The composition of breast milk and its protective properties were practically re-examined. At the same time, all methodological omissions of previous years were taken into account. By 1989, modern views on feeding children, including those for various maternal diseases, were set out in the WHO Bulletin “Feeding children in the first year of life: physiological basis.” For more than 10 years, doctors around the world have been guided by these principles. Our mothers are sometimes not always familiar with these principles and find themselves captive to outdated ideas. What should a modern woman know about breastfeeding when her mother is ill?
First, let's try to identify different situations in which a nursing woman can get sick. This could be an exacerbation of a chronic disease that the woman has been suffering from for a long time, it could be an accident or injury, and finally, the woman could become infected with some kind of viral or bacterial infection.
Main signs of influenza
Flu presents with the usual symptoms. In a nursing mother, clinical manifestations increase acutely and quickly.
They consist of the following symptoms:
- Hyperthermia, intoxication. With the flu, the temperature rises to 38-40 degrees. Weakness develops, headache, chills, and body aches appear.
- Pain and sore throat.
- Dry cough.
- Nasal congestion, runny nose.
A nursing mother is primarily concerned about the condition of her newborn baby. Previously, it was believed that breastfeeding (BF) should be stopped. But, according to the latest recommendations from the World Health Organization, feeding the child should continue in the same mode as before the flu.
After the mother becomes infected with the influenza virus, and before the first symptoms of the disease appear, time passes during which the baby can already get sick. And according to scientific research, continued feeding during the flu is not only possible, but also necessary to continue to strengthen the child’s immunity.
In what cases should lactation be stopped?
Is it possible to feed a child with the flu if the mother’s health is very bad? There are cases in which you should stop breastfeeding:
- at a temperature of more than 40 degrees;
- if a complication occurs;
- when the body is dehydrated;
- if the disease does not subside within a week.
Be sure to consult your doctor . Some forms of influenza require hospital treatment. In such a situation, feeding a child is quite dangerous, since lactation creates additional stress on the female body.
What does therapy consist of?
Treatment of influenza in a nursing mother consists of the following components:
- bed rest;
- diet and drinking plenty of fluids;
- medications;
- gargling, nose.
Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor. Selecting medications on your own is dangerous for the baby’s health, since many medications can pass into breast milk and reach the baby.
If during lactation the mother gets sick with the flu, it is necessary to provide her with rest. Bed rest is a mandatory part of treatment. The body of a nursing woman spends all its reserves on producing full-fledged milk. When you have the flu, you need proper nutrition.
You need:
- vegetables;
- lean chicken, turkey;
- porridge;
- dairy products.
To relieve intoxication and ensure the required volume of milk, you need to drink plenty of liquid.
Can you drink at high temperatures?
:
- sweet tea;
- compotes;
- mineral water.
You can't drink:
- sour;
- cold;
- hot drinks.
This viral disease during breastfeeding cannot be treated with all medications. All medications must be approved by the attending physician.
If possible, treatment should not involve the use of medications. But in severe cases they are necessary.
The table below shows medications that can be used to treat influenza during lactation:
Gargling and gargling for the flu are effective and safe treatments for breastfeeding. Thanks to them, a sore throat is relieved, the mucous membranes are cleared of the virus and the products of inflammatory reactions.
You can gargle:
- salt solution;
- soda;
- chamomile decoction;
- St. John's wort.
You can rinse your nose with saline solution, which is sold at the pharmacy. You can pour it into a bottle of used nasal drops and spray it into your nostrils.
Please note that when using any medical product, you must not only consult a doctor, but also carefully study the instructions. It should state the safety of the medication during breastfeeding.
You should drink herbal teas, fruit drinks with viburnum and raspberries, and compotes with caution, as they can be allergenic for a child. Monitor his reaction and check him daily for rashes.
Due to the high risk of infection, regularly monitor the baby’s body temperature, and if it increases, call a pediatrician at home.
Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Breastfeeding may not be interrupted, since the baby could already be infected before the first symptoms appear.
Most of the drugs that we are used to using in the treatment of influenza are contraindicated during lactation, so the possibility of taking any medications should be discussed with a doctor.
The period of breastfeeding is as important as the period of pregnancy (bearing a child). The stage of development and formation of the child’s physical health continues, which completely depends on the state of health and lifestyle of the mother herself. If during this period a woman falls ill with the flu, then she needs to know about ways to heal herself so as not to harm the child and restore her health. Many medications become prohibited for a woman who is treating the flu and breastfeeding her baby.
The website indicates that already at the stage of the incubation period, the woman transmits the virus to the child, which will also begin to develop in his body. However, you should not stop breastfeeding when a woman becomes ill. Along with mother's milk, the child is given antibodies that are produced by her body, which fights on its own. The baby's body needs the mother's antibodies, which are stronger than his own immunity. And since the mother infected the child with the virus, it should also help in recovery.
If you deny a child breast milk, then this will follow:
- Decreased immunity.
- Nervousness.
- Worried state.
- Exacerbation of the disease.
- Temperature increase.
- Increased chills, runny nose and watery eyes.
- Increased inflammation.
- Strengthening and head.
- Increased aches in muscles and joints.
The baby should be given mother's milk in the form in which it is produced by the body. There is no need to boil it, because in this case it will lose all its beneficial and medicinal properties. This will be similar to the baby switching to artificial feeding.
Doctors see the reason for the development of influenza in the mother's body as an additional burden on the respiratory system, which occurs both during pregnancy and during breastfeeding. It takes a lot of energy to produce milk, so a woman may feel short of breath.
Is it possible to breastfeed
If a seasonal flu epidemic is coming, young parents are advised to take care of disease prevention. If infection has occurred, the primary task for the mother is to select safe treatment methods.
Some medical specialists are inclined to believe that it is necessary to temporarily interrupt lactation until the nursing woman fully recovers. The reason for this is the high probability of infection of a newborn from a sick mother. The need to suspend lactation can be debated, since by the time the first symptoms of the disease appear, the child manages to receive a dose of the virus from the mother.
During this period, breast milk is more important than ever, since it contains valuable antibodies that provide support in the fight against infectious pathogens. If a woman could not avoid catching the flu, it is recommended to continue breastfeeding. To reduce the likelihood of infection of a newborn baby, a woman must wear a gauze or cellulose bandage before each feeding.
The danger of influenza lies in its consequences, therefore, if a characteristic clinical picture appears, a nursing mother should consult a medical specialist for advice.
Drug treatment
Flu should not be left untreated, as complications always develop after it. However, the treatment process is complicated by the fact that a nursing woman cannot take absolutely any medications that will help her in recovery, which is associated with the penetration of components into mother’s milk and further into the baby’s body. Drug treatment is permissible. However, you should carefully read the instructions for use or consult a gynecologist or pediatrician.
You can use drugs of the interferon group, since they have a gentle effect. As for antibiotics, aspirin and paracetamol, these drugs should not be taken. These drugs are harmful not only to the virus, but also to the antibodies that are transferred to the baby. Antibiotics also have a detrimental effect on the intestinal microflora, which is why they are recommended to be taken with yogurt or kefir to restore health.
- Strengthening property, in which the walls of blood vessels stop inflaming and swelling.
- Activation of carbohydrate metabolism.
- Redox processes.
- Cell regeneration.
- Formation of steroid hormones.
- Synthesis of connective tissue cells.
However, even this drug should be taken strictly according to dosage and course of treatment.
In principle, every woman should first study information about a particular medicine before taking it. It is advisable to first consult with a doctor who will prescribe exactly those medications that are permissible during breastfeeding. Then you should study the package insert for the drug, especially the “Contraindications” column.
It would not hurt to read any information regarding the drug on the Internet. Remember that many drugs are not tested for compatibility with lactation. These studies are quite expensive, and their implementation is not necessary to release a medicine. Therefore, every woman should understand that the package insert may say “Do not take during lactation,” but in fact, the developers do not know for sure about the effect of the medicine on the woman and her baby.
On the Internet you can read reviews from ordinary people, especially nursing women, who have already used medications during lactation when they had the flu.
Establishing a diagnosis
Doctors such as a gynecologist or mammologist can diagnose mastitis. Every woman who experiences symptoms of this condition must be examined by appropriate specialists and receive professional advice.
If a nursing mother has a cold in her breasts and has signs of lactostasis, she undergoes an ultrasound examination of her breasts. She must also take a general blood test, which will help determine whether there is an inflammatory process in the body. If the color of breast milk has changed, then in addition to the above procedures, its bacteriological examination is added, as a result of which infectious agents are identified (see also: how and with what can you restore breasts after breastfeeding?). The prescription of therapeutic therapy depends on the results of ultrasound and laboratory examinations.
If mastitis is suspected, consultation with a mammologist and gynecologist is necessary.
Home treatment
Flu does not need to be treated in a hospital. You can even resort to traditional medicine, which is also effective and quite safe for a nursing mother:
- Drink more water, juices, fruit drinks and compotes. This will ensure the normalization of water-salt balance, the removal of toxins and the quality of milk.
- Make a chest mixture to eliminate cough: thyme, anise, ivy, licorice root, thyme, plantain, radish juice mixed with honey.
- Dress warmly and do not heat the room with appliances that dry out the air.
- Stick to bed rest to make your body stronger.
- Ventilate the room.
- Eat a balanced diet, without overeating or starving.
- Put your baby to your breast more often, which will increase the circulation of fluids in the body.
- Humidify the air and clean the room.
- Saturate the air with oxygen.
- If you have a runny nose, you can put a solution of sea salt, propolis and onion juice in your nose.
You should check the temperature under your arms to make sure it is not too high. Otherwise, you need to consult a doctor.
It is forbidden to take hot baths for the feet, since the woman is already burning from the high temperature, and the addition of additional heat will lead to an influx of milk in the breasts, which can cause stagnation. In this case, you need to apply a cold compress to the breast, express the milk or give it to the baby.
Fighting germs
Germs can be completely eliminated only through the use of medications. The effect can be achieved even with the help of herbal ingredients. If you have a runny nose, breast milk will remain of high quality if you instill Pinosol in your nose. Its ingredients are completely natural, so use is allowed even immediately after childbirth. Breastfeeding still leaves a risk of developing allergies, so the baby's reaction should be constantly monitored.
It is not allowed to use essential oils of tea tree, anise or cumin for treatment. Children often develop allergies to these ingredients. Complications arise even after inhalation.
Inhalation with onions and garlic should also be avoided. These components are too aggressive and can lead to irritation of the nasal mucosa. Their effect minimizes mucus production. As a result, the healing process is delayed.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to deworm a pregnant woman?
It's important to understand
If a woman gets sick, then it is important for her to understand that her lifestyle is not conducive to health. She can not only get sick herself, but also lead to illnesses in the baby. If she does not want to face difficulties, then all the measures she takes during cold weather and flu epidemics should be reconsidered.
The following preventive measures will be taken:
- Walks in the open air.
- Taking vitamins.
- Protecting yourself and your baby from crowded places.
- Being in a good mood.
Forecast
Flu is dangerous not so much for the mother as for her child, who is less protected. A woman should protect herself for a time until her child reaches one year of age and gets stronger. If the disease has developed, then you need to be treated, which will certainly improve the prognosis for further developments. It is better to do this together with a pediatrician, who will primarily care about the baby’s health.
If the flu has already made itself felt in a nursing mother, then it is not only not necessary for her to stop breastfeeding, but, on the contrary, it is highly not recommended.
The fact is that infection of the body occurs before the first symptoms of the disease appear. So, even before a woman develops a fever, a runny nose and a sore throat, her baby will receive the virus itself, antibodies to it, and immune protection against the virus through milk. Therefore, by the time the flu finally shows up in a mother, her baby will either already be sick along with her or protected by breast milk.
Milk is a natural flu vaccine for breastfeeding babies. By depriving the child of this milk, the mother takes away from him an effective, “individually developed” medicine. Another mistake is boiling breast milk - this will destroy all its protective properties. A gauze bandage is also an unnecessary measure, since the causative agent of the disease is already present in breast milk.
Neither a sick nor a healthy child should be weaned!
By stopping feeding, the mother only exposes the child to the risk of illness or complicates its course. Flu in a nursing mother poses less danger to the child when he receives all the protective and antimicrobial substances he needs with milk. For the same reason, formula-fed babies are more susceptible to the influenza virus and get sick more often and for longer.
How to treat flu in a nursing mother?
Breastfeeding is dangerous due to its complications, which are completely unnecessary for a nursing mother, but, unfortunately, not all medications can be compatible with lactation. Therefore, only home remedies remain.
So, as symptomatic remedies, for example, for the treatment of cough, breast milk, licorice root, radish juice with honey, etc. can be used. Antiviral drugs based on interferon are allowed during lactation. A nursing mother who has the flu should drink a lot - herbal teas, fruit drinks, water. To reduce the temperature, use paracetamol or Nurofen (never aspirin). All medications must be prescribed by a doctor.
An indication for stopping breastfeeding is the incompatibility of any drug with lactation, but there is the following aspect. Clinical trials of the safety of the drug for pregnant women, nursing mothers and infants are not required for registration of the drug on the market. Since this procedure is expensive, it is easier for pharmaceutical companies to indicate that the medicine is contraindicated in such cases. But don’t rush to stop feeding! Always check medicines prescribed by your doctor against WHO references before you stop breastfeeding on the advice of your doctor, acting in accordance with the instructions for the medicine.
In any case, even if it turns out that the drug is dangerous during lactation, perhaps there is a safer analogue. Flu in a nursing mother does not eliminate the possibility of drug treatment.
Flu while breastfeeding is not a reason to neglect the mother’s health by refusing treatment, and also not a reason to deprive the child of adequate nutrition. If the mother is already sick, she should rest as often as possible, be treated as thoroughly as possible and feed the baby as often as possible, protecting him from the virus.
The question of how to treat during lactation was asked by every nursing mother who has either already fallen ill with this acute respiratory disease or is afraid of its occurrence. After all, many medications are contraindicated during this period due to the harm they can cause to the baby through milk.
A nursing mother should not panic when she gets pregnant. After all, our body has evolved over many millions of years and has become resistant to various viruses. As for kids, there is no need to worry about them either, because usually such an infection is defeated by the protective forces of the immune system in a matter of days.
The disease begins to develop according to the following principle: first it enters a healthy body and begins its active reproduction, and as a result, the cells of the mucous membrane are damaged. An inflammatory process appears, which manifests itself in skin hyperemia, increased blood circulation and swelling. Development begins, and... In response to acute respiratory infections, the body's defenses are immediately activated.
The immune system produces specific antibodies that destroy this infection. There is no need to be afraid of complications from a cold if a nursing woman has good body resistance. You should not panic and take the appearance of such a disease calmly.
You need to make every effort to support your body in the fight against the emerging viral infection.
A cold during lactation has the following symptoms:
- Dryness and itching appear in the sinuses, which causes frequent sneezing.
- The voice becomes hoarse, irritated and sore.
- It begins.
- Aches joints and muscles.
- A nursing mother experiences severe weakness and fatigue, accompanied by drowsiness.
- begins to increase from very insignificant numbers on the thermometer to very large ones.
- There is discharge from the nasal sinuses with a transparent tint and a thick liquid structure, which can thicken and turn into crusts.
- There is severe discomfort in the throat, which is associated with pain when swallowing.
- Profuse lacrimation begins, accompanied by a fear of light and pain in the eyes.
May present with varying combinations of symptoms. They can be either pronounced or completely insignificant. But all these signs bring severe discomfort to a nursing woman.
Breastfeeding when you have a cold
Some people mistakenly believe that breastfeeding during ARVI is dangerous. But this is absolutely not true. On the contrary, it can help the child. As mentioned earlier, along with mother’s milk, the baby receives a number of antibodies that resist such a virus. With a high degree of probability, it can be said that an infant will not get a cold while breastfeeding.
It is best not to deprive the baby of mother's milk when such a viral infection occurs, trying to protect him from the disease.
But there are situations when feeding a child is contraindicated.
These are cases when the mother has a very serious condition, and her state of health does not allow her to properly care for the baby. This disease can lead to complications such as pneumonia and acute bronchitis. If they occur, then it is better for the woman to stop breastfeeding and transfer the child to formula feeding.
Most medications are contraindicated during lactation. This is due to the fact that medications can harm the baby’s health if they enter his body through mother’s milk. It is for this reason that a nursing mother needs to choose only safe drugs that will not harm her newborn baby.
How to treat a nursing mother
Antiviral drugs such as Ribavirin, Remantadine and Arbidol are effective only in the first hours of the disease or as a preventive measure. But their use by the mother can cause side effects in the child in the form of abdominal pain, loose stools, allergic rash and increased excitability. When using Immunal, allergic reactions in the baby are also possible. Therefore, the listed drugs should not be used.
When treating acute respiratory infections or preventing colds, you can instill Grippferon into the nose, which contains interferon produced in the human body and increases its resistance to viruses. Viferon suppositories can also be used in the treatment of a nursing woman without harm to her baby.
Since antibiotics are not used in the treatment of viral diseases, due to their uselessness, treatment consists of symptomatic therapy, reducing intoxication and increasing the patient’s body’s resistance. But there are times when the attending physician may suspect the development of a bacterial complication (sore throat or pneumonia). Then there may be a need to use an antibiotic combined with breastfeeding. If the doctor is forced to prescribe an antibiotic that is not compatible with breastfeeding, then the woman will have to stop feeding the baby and express and discard breast milk during her treatment.
Drinking plenty of warm fluids throughout the entire period of illness is very important, as it prevents the mucous membranes of the nose and throat from drying out, promotes sweating, thins sputum and reduces intoxication in the body.
You should not take antipyretic drugs at your own discretion. After all, an increase in temperature is a manifestation of the patient’s body’s defense mechanism. You can lower the temperature only when the thermometer marks 38.5 degrees or higher.
The safest antipyretic drug is Paracetamol. Theraflu, Coldrex, Fervex should not be used for this purpose, due to the fact that their effect on a certain group of people has not yet been studied.
To treat cough, Ambroxol and Lazolvan can be used as expectorants and sputum thinners. Herbal preparations based on anise, licorice root, thyme, ivy, thyme, and plantain will also help. Can also be used
Breastfeeding women are more susceptible to colds than others. This is due to the fact that the mother’s body is weakened by pregnancy, childbirth, worry about the child, frequent stress and lack of sleep. If a woman develops a cold while breastfeeding, she begins to be overcome by painful thoughts - is it worth continuing to breastfeed the baby, what is the likelihood of the baby becoming infected, and many others. Let's try to sort out the issues that worry many nursing mothers.
Most often, a cold is called an acute respiratory viral infection, or ARVI. The infection is usually transmitted by airborne droplets through the upper respiratory tract.
A woman is especially susceptible to ARVI when breastfeeding as a result of the fact that her respiratory organs work under increased load. This is because breast milk requires a lot of oxygen to produce.
From the moment the virus enters the mother’s body until the development of the disease, about two to three days pass. This means that even before the first symptoms of the disease appear in the mother, the baby has already received the pathogen along with breast milk. But besides this, he received antibodies to the pathogen, special enzymes of this pathogen to produce its antibodies, and complete immune protection against complications. Therefore, by the time the mother shows signs of acute respiratory viral infection, the baby will already be sick or actively immunized while breastfeeding.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a cold are the following:
- elevated temperature;
- general weakness;
- nasal congestion or runny nose;
- cough, sneezing;
- sore throat;
- There may often be congestion or tinnitus.
Usually, a cold with proper treatment goes away within ten days.
What to feed your baby
Just a few decades ago, treating a cold while breastfeeding meant completely isolating the mother from the baby and stopping breastfeeding. But modern doctors completely reject this method.
Under no circumstances should you wean your baby off the breast if the mother has a cold. It doesn’t matter whether the child is healthy or sick. In any case, weaning will instantly lead to a decrease in the baby’s immunity. In a sick child, the disease will be more severe and longer.
When treating a cold while breastfeeding, there is no need to feed your baby expressed milk or boil breast milk. During this period, mother’s milk contains all the substances necessary for the nutrition and treatment of the child. In addition, he will also receive medications through his mother's breast milk.
Of great importance in the formation of a baby’s immunity is his infection with microorganisms that pass along with the breast milk of a sick mother. This will help him in the future either not to get sick, or to endure the disease much easier.
Treatment
The main principle for treating colds while breastfeeding for a woman should be the safety of her baby. During lactation, the mother can use medications or folk remedies.
The safest antipyretic for a nursing mother is paracetamol. Of course, you don’t need to abuse it, but you shouldn’t endure high temperatures for a long time either.
Often a woman with ARVI while breastfeeding is accompanied by a runny nose, cough, and sore throat. To relieve these symptoms, special drugs or methods are used.
Cough is best treated by inhalation with decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula. These procedures are carried out for 15-20 minutes three to four times a day.
Medicinal treatment of cough during breastfeeding is best done with the expectorant Lazolvan or Ambroxol. Herbal preparations containing anise, plantain, licorice root (Doctor MOM, Gedelix, Bronchicum) are also excellent for this.
Drugs containing bromhexine are absolutely contraindicated for the treatment of cough during breastfeeding. The antiviral drug Grippferon is compatible with lactation. It has no harmful effects on the child and does not cause side effects.
Drug treatment
Colds during lactation should be treated with medications that do not contain any harmful components:
- To eliminate strong symptoms, you should take medications with an expectorant effect. During lactation, a good choice would be to take medications or Ambroxol. To make breathing easier, products such as Chest Elixir or, that is, those syrups that contain medicinal herbs are recommended.
- Severe congestion in the nasal sinuses is eliminated using the type Tizin, Farmazolin or. Abuse of such drugs can lead to complications in the form of atrophic rhinitis, so you should not get carried away with these drugs. They can be used for no more than seven days.
- During this time, you should use products that have a local effect and are antimicrobial in nature. These include Hexoral and Strepsils. As for the mucous membrane, it can be spread.
- Herbal oil drops have an excellent anti-inflammatory effect on the sinus area.
- Acute respiratory infections caused by infections of viral origin can be eliminated with the help of Grippferon. This drug has no contraindications to treatment during lactation. In addition, the body tolerates it well.
- During a cold, the nasal mucosa must be additionally moisturized. This can be achieved using sea salt drops and sprays.
It should be remembered that during lactation it is strictly forbidden to use drugs containing bromhexine.
Traditional methods of treatment
Since ancient times, treatment of acute respiratory infections using traditional medicine recipes has been not only safe, but also had a fairly good effect:
- Application is as safe as possible for the mother’s body. They can be made using herbs (for example, steaming eucalyptus leaves). Using steam from boiled potatoes gives excellent results. To facilitate the process, you can purchase a special drug -. It will also be useful to the mother when the child grows up for treatment. Inhalations with its help are done using Borjomi, Ambrobene (solution) or saline. The doctor must decide which remedy will be most effective for acute respiratory infections. By doing inhalations three to four times a day, after just two days you can see how your health has improved.
- With the help of raspberry tea, you can easily soften the general condition during such a disease.
- To help a sore throat, use a solution that contains water (1 glass) and apple cider vinegar (1 tablespoon). Procedures with its help should be carried out at least once every hour.
- To make breathing through the nose easier, use the following recipe: heat a quarter cup of sunflower oil in a water bath and mix with garlic and onion, previously crushed into fine crumbs. This mixture is infused for an hour to two, and the resulting composition is lubricated inside the nasal sinuses.
- Linden tea with the addition of honey has an excellent effect. The concentration of such a drink should not be too strong; it should be slightly darker than water. You should not be overzealous with the use of linden; its excessive use is fraught with the appearance of pain in the heart area.
- For acute respiratory infections, the use of onions and garlic is very useful. They can be pre-chopped and mixed with honey. To get rid of colds, one or two teaspoons of this composition are eaten after each meal. However, we should not forget that these odorous products can provoke diarrhea in an infant. Therefore, before using such a drug, you should consult your doctor.
Useful video - Colds during lactation.
Many nursing mothers are concerned about the question: is it possible to steam their feet if they have a cold during lactation? Yes, such procedures are indicated during acute respiratory infections. It is very important to follow one rule: the water temperature should not be more than 40 degrees, and the process itself should last approximately 8-12 minutes. This method is quite effective. And to make its effect even better, you can add a small amount of mustard to the water. Immediately after the procedure, you must put on cotton socks.
Actions at temperature
If during lactation the temperature rises to 38.5 degrees, the nursing mother can take paracetamol (one tablet) or drugs based on it. This medicine is the safest for reducing high fever. This drug perfectly eliminates pain in the head and muscles that accompany acute respiratory infections.
But before doing this, you should consult your doctor to avoid unwanted effects. As for drugs like Theraflu, Fervex or Coldrex, it is better not to take them on your own, since it has not yet been established how they can affect the baby’s body.
At temperatures below 38 degrees, you can use a wipe based on a weak vinegar solution. Vodka in equal proportions with water is also suitable for this purpose. After the whole body has been rubbed, you need to cover yourself with a light sheet. These steps should be repeated every 15-25 minutes. If the thermometer shows a temperature of 37.5, then there is no need to bring it down.
But when the temperature is very high (more than 38 - 38.5 degrees), the milk may well “burn out” and lactation will stop.
One important rule during acute respiratory infections is that if a prolonged increase in body temperature occurs, you should never self-medicate. You should immediately seek the help of a general practitioner, and do not forget to mention breastfeeding at your appointment. A specialist can prescribe antibiotics and other drugs against this viral infection that will not harm the baby’s health.
There are situations when it is not possible to cure this type of infectious disease without simultaneously interrupting lactation. This can occur in diseases that are bacterial in nature. There are also cases when surgical treatment is required for a nursing mother. If such a situation occurs, the woman needs to consult a doctor and warn him that she is breastfeeding.
If there are acute respiratory infections that are in no way compatible with breastfeeding the baby, the doctor will prescribe a switch to artificial feeding. In this situation, the child may need additional therapy if he has already become infected. This is a necessity, since having lost his mother’s milk, the baby needs a natural increase in the immune forces of his body.
If doctors’ forecasts are not so disappointing, and complications from acute respiratory infections in the mother can be combined with breastfeeding, then there is no need to stop it. To do this, a woman must express her milk so that the lactation function remains normal. This needs to be done several times a day.
Before you begin to treat a cold and its complications with medications, you should carefully read the instructions included with them in advance.
These actions are necessary because any, even the safest drug, may contain chemical components that can harm the health of a nursing mother and her baby. It is strictly forbidden to exceed the amount of the specified dose prescribed in the instructions for the medicinal product. By following all the above rules, you can easily survive the unpleasant period of a cold during lactation and not be afraid that the child will be left without breastfeeding.
The causes of influenza in a nursing mother are the same as for everyone else: contact with the virus and its entry into the body. The disease is transmitted:
- by airborne droplets;
- through everyday objects.
After childbirth, the female body is most vulnerable to viral infections. During lactation, the body weakens. Milk production places an additional burden on the respiratory system, since this process requires a large amount of oxygen. In addition, the immunity of a nursing mother is weakened due to lack of sleep and stress that accompany the first months of motherhood.
Last consultation
Gulnaz asks:
Good afternoon Can Nol Flu tablets be taken by a nursing mother?
Answers:
Hello, Gulnaz! Breastfeeding is a contraindication to taking Nollgipp. This is written in the instructions for the drug. Take care of your health!
Olga asks:
What medications can you take while breastfeeding for ARVI?
Anna Stepanovna Abrosova answers:
Good afternoon, Olga! For the treatment of lactating women, Viferon suppositories, which are a complex of recombinant alpha-2b human interferon in combination with tocopherol acetate (vitamin E) and ascorbic acid, or Nazoferon drops, can be used. The safest way to reduce high fever in nursing mothers is paracetamol or ibuprofen. Complex cold medications such as Tetraflu, Coldrex, etc. are not recommended for use by nursing women. Drugs whose main active ingredient is bromhexine (ambroxol) are contraindicated for nursing and pregnant women. For coughs, you can use herbal preparations based on licorice root, anise, ivy, thyme, thyme, plantain and other herbal ingredients. For a runny nose, vasoconstrictor drops and oil drops can be useful. They can be used no longer than 3-5 days. For a sore throat, it is possible to use local antiseptic (antimicrobial) drugs, lozenges “Sebidin”, “Strepsils”. Ibuprofen, paracetamol, mefenamic acid can be used as an antipyretic drug. They enter milk in small quantities and are quickly eliminated from the body. It is advisable not to use several drugs at the same time. With a long course of treatment, the drug should be taken in the evening, after the last feeding.
Anna asks:
My youngest daughter is 1.5 years old and still breastfeeding. But a month ago I started menstruating. My milk is slowly disappearing. And Lerochka really loves her mother’s milk. What should I do to do everything to increase lactation or should I wean her off the breast little by little?
Albina Anatolyevna Shevchenko answers:
Hello. In any case, you will have to wean your baby sooner or later. Modern recommendations are based on the idea that the child himself knows when to stop breastfeeding. But, if at 1.5 years the amount of milk is already gradually decreasing, then you should not worry too much about this, but start transferring the child first to mixed, and then to completely “adult” food. To wean the baby from the breast, mutual consent of both mother and child is required. You will decide when you need to completely wean your baby off the breast. As your baby gets older, breastfeeding occurs less frequently. This is a natural process. You also need to watch yourself: if at the end of the day your breasts are still filled with milk, then it is too early for you to stop feeding. So the final advice would be this: listen to yourself and your child. Unlike the average book recommendations, you feel your child better. If your daughter needs breast milk, and you have it, you should not deprive your child of this healthy joy. Good luck.
Oksana asks:
Is it possible to breastfeed at a fever?
The medical consultant of the portal “health-ua.org” answers:
Hello, Oksana! A fever in a nursing mother itself is not a contraindication to breastfeeding; rather, it is important what exactly caused the fever and what treatment the mother receives. If the mother is sick with an acute respiratory viral infection, it is necessary to wear a mask and ventilate the apartment in order to prevent the child from becoming infected as much as possible. It is very important to try not to stop feeding the child in such a situation, because ready-made antibodies against infection enter the child’s body with milk. This is a natural immunoprophylaxis for the disease in a child. In addition, it is necessary to remember the dangers of self-medication when breastfeeding. After all, what is familiar and “safe” for you can be very harmful for a child. All the best!
Bondarenko asks I.A. :
Please tell me, is it possible to breastfeed a baby with a fever and flu? And what is the most effective and safe way to undergo treatment without consequences for the child?
Drannik Georgy Nikolaevich answers:
The influenza virus is not transmitted through mother's milk. Protective antibodies will be transferred to the baby with the mother's milk (this is not bad). The main danger is infecting the baby. In this situation, there are two options - breastfeeding and communicating with the baby while wearing a mask, or expressing milk and bottle feeding. Unfortunately, specific drugs aimed at destroying the pathogen are quite toxic chemical agents and are not used during lactation, since they all pass into breast milk to a greater or lesser extent. Among the drugs that are safe for infants, we can recommend antipyretics containing paracetamol, as well as vitamins such as ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and rutin (vitamin P).
Tatiana asks:
Hello! I had a sore throat, a headache and a runny nose. Apparently this is ARVI. Please tell me how to protect a 2-month-old child from a cold and how to speed up my recovery process?
Parshin Sergey Alexandrovich answers:
First of all, the tactics depend on whether you are breastfeeding. If not, then you need to isolate yourself from the child and carry out full treatment. If you are breastfeeding, then: 1. Constantly ventilate the room (naturally, the baby should be in another room). 2. Treat the child’s nasal passages with oxolinic ointment and rinse with Aqua Maris. Personally, you need therapy. It is possible to use homeopathic antiviral drugs. If the severity of the condition does not allow you to limit yourself to them, then when using synthetic antiviral drugs it is always necessary to use the principle of balancing the risk for your child and the benefit for your health.
Anna asks:
My son is 4 months old. He has been on breastfeeding with one breast (the other without milk) since birth, and does not take a bottle or pacifier. The doctor thinks that one breast is no longer enough for his age, and he doesn’t want to eat formula. What should we do, please tell me how to increase the volume of milk? Or do you need complementary feeding?
Burlaka Evgenia Anatolyevna answers:
Dear Anna, you definitely won’t increase the amount of milk. But your child already needs complementary feeding and supplementary feeding (these are different things). Supplementary feeding is supplementary feeding of the child with the amount of milk (formula) that is not enough. The baby is simply not used to the pacifier, try with a different size pacifier or supplement the baby with formula from a spoon. Complementary feeding is the introduction of foods other than milk (vegetable puree, milk porridge) into a child’s diet. They are introduced during breastfeeding from 5 months. Your pediatrician will tell you how and what to administer. In addition, at 3.5 months you must introduce corrective supplements (fruit juice, fruit puree, yolk).
Svetlana Cheskidova asks:
What nasal drops can I put in my nose? I am breastfeeding my baby. The baby is 3 months old.
Vera Alexandrovna Strizh answers:
Good afternoon Vasoconstrictor drugs should not be used to treat rhinitis. In solving this issue, it is necessary to use only methods and means that are absolutely safe for mother and child, and are also quite effective. On your own, you can use drops based on sterile sea water, instill an isotonic solution, use folk remedies (breast milk, diluted onion juice, etc.). It would not hurt to contact an ENT specialist to determine the cause of the runny nose and, if necessary, select stronger medications that are approved for breastfeeding. Be healthy!
Dinara asks:
Good evening!!! I have a flu or a cold, I don’t know, the third day I have an ache in my bones, a scratchy throat and a dry, irritating cough, but no temperature in the evening, sometimes 36.9 or 36.8. I smear oxalin on my son and spray IRS 19, I started drinking beseptol, I disdain inhalipt, I drink a lot of tea with lemon and honey and insti tea. Tell me if I'm doing it right. I give you the blog in advance
The medical consultant of the portal “health-ua.org” answers:
Good afternoon, Dinara! It is impossible to establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment during a correspondence consultation. Although the complaints you listed do most often accompany an acute viral infection. And if we consider the existing disease as ARVI, then the treatment should look like this: antiviral drugs (especially effective in the first three days of the disease: arbidol, anaferon, vifiron, lafirobion, etc.), antihistamines (laratodine, erespal, etc. .), immunomodulators, multivitamins, drink plenty of fluids. In addition, symptomatic treatment is prescribed depending on the prevalence of one or another symptom of the disease: for a runny nose - vasoconstrictors, for a sore throat - antiseptics, for a cough - expectorants, for fever - antipyretics, etc. Biseptol, as well as antibiotics, are prescribed only by a doctor in cases of high risk of developing bacterial complications. And lastly, on the issue of preventing the disease in the child and other family members: reduce contact to a minimum, use protective equipment (gauze bandage, for example), give antiviral drugs in a prophylactic dosage, and IRS is not appropriate here. All the best!
Anna asks:
Hello! Please tell me! My daughter started getting sick on Saturday and started coughing with snot. At first they drank sumomed, it didn’t help. Then they started giving her cefozaline injections, and she hasn’t had a fever for like three days. Today is the third day of her injections. Yesterday I felt bad, my throat hurt and I started coughing, my temperature was 37-5. Please tell me if I can infect her again, because we are on breastfeeding. I gargle with sage and want to insert Genferon suppositories. Is this correct? Thanks in advance!
The medical consultant of the portal “health-ua.org” answers:
Good afternoon, Anna! If you have a viral infection, then the possibility of infecting your child is really high (not through milk, but through airborne droplets). But here I have the following question: wasn’t it your daughter who infected you? In general, in order to understand the nature of the pathological process and prescribe adequate treatment, an in-person examination by a specialist is necessary - be sure to call your family doctor at home. Regarding treatment, in this situation Vifiron or Nazoferon, for example, are more indicated (Genferon primarily has a pronounced local antimicrobial effect and is more effective in the treatment of gynecological diseases and sexually transmitted infections). The same drugs can be used for prevention in a child, but only after prior consultation with a doctor. Do not forget also about the simple rules of anti-epidemic measures - wear a mask, wash your hands and minimize contact with the baby. And, most importantly, do not stop feeding your baby, because breast milk contains so many useful substances, including antibodies to the infection that you have now. All the best!
Galina asks:
Hello! The doctor diagnosed me with tonsillitis. He prescribed Chlorophyllipt (but the instructions say that it is not recommended for breastfeeding women) and Septefril, Ascorutin and drops of calendula tincture into the ears. Can I take these medications? The child is 7.5 months old. I'm breastfeeding. And now an incomprehensible, corrosive cough has begun. What can you advise me? Thank you!
Ekaterina Mikhailovna Kovbasko answers:
Good afternoon, sore throat - plaque on the tonsils, fever, enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Just a sore throat and fever - not a sore throat. So, if you have a sore throat, be sure to take antibiotics (for example, Augmentin) + rinse locally with furacillin, Givalex, tinctures of calendula, chamomile, etc., + dissolve Lisobact, + Nurofen for a course of 3 days, regardless of temperature. If the mother is taking medications that pass into milk, it is recommended to express the milk and temporarily switch the baby to formula. After recovery, breastfeeding should be resumed.
Evgeniya asks:
Hello! Please tell me, can a nursing mother take Ascorutin if the baby is 2.5 months old?
Natalia Alekseevna Kundina answers:
Hello, Evgeniya. 1.Ascorutin is a drug that reduces the permeability and fragility of capillaries, strengthens the vascular wall, reduces its swelling and inflammation, has antioxidant and radioprotective properties, is involved in redox processes, carbohydrate metabolism, the formation of steroid hormones, tissue regeneration, and the synthesis of connective tissue elements . But... when using the drug during pregnancy and lactation, as well as for children, strictly follow the dosage and duration of the course prescribed by the doctor.
During the period of aggravation of the epidemiological situation, no one is immune from influenza. This is especially true for nursing women, whose immunity is not fully restored after pregnancy. If a young mother breastfeeds, then she is responsible not only for her body, but also for the body of the newborn baby.
If infection with influenza cannot be avoided, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with methods of treating the disease and new conditions for feeding the child.
Symptoms
Influenza is characterized by an acute course. Symptoms in typical forms of the disease are pronounced. They appear on the second or third day after the virus penetrates. Typical signs of influenza include:
- high temperature (from 37.5 to 40 degrees);
- lethargy;
- headaches (in the temples, forehead, eyeballs) and muscle pain;
- runny nose;
- dry cough.
The most dangerous form of influenza is severe. It is accompanied by a sudden sharp temperature jump (40 degrees), pronounced intoxication. Sometimes hallucinations appear and meningeal syndrome develops. A characteristic sign of a severe form of the disease is capillarotoxicosis syndrome - a cough with blood streaks, a petechial rash.
In the atypical course of the disease, one of the main either catarrhal or intoxication symptoms is absent. For example, the temperature may not rise or the respiratory system remains unaffected.
Diagnosis of influenza in a nursing mother
Diagnosis of influenza in a nursing mother is based on the clinical picture. Diagnostic measures include:
- drawing up a picture based on the patient’s complaints;
- inspection;
- differential diagnosis (the symptoms of influenza are similar to the symptoms of other diseases, especially if not all signs of a viral disease appear).
In some cases, a nasal and throat swab may be needed. But laboratory diagnostics are usually resorted to only in the case of an atypical form of a viral disease: the clinical picture of the typical course of the disease allows a diagnosis to be made without the use of laboratory methods.
Complications
Flu can cause a number of complications in breastfeeding mothers. Problems arise in several cases:
- have chronic diseases;
- treatment was performed untimely or incorrectly;
- bed rest was not observed (the most common cause of complications in young mothers).
Complications of influenza include pneumonia, otitis media, meningitis, bronchitis, and diseases of the cardiovascular system. Influenza can affect lactation, especially if the disease occurs with complications and requires taking medications that are incompatible with breastfeeding. Early weaning of a child from the breast risks the fact that his immune system will be weak, since the child’s body will not receive enough important substances from mother’s milk.
Causes of mastitis during breastfeeding
Lactostasis combined with a cold or other infection can lead to mastitis
Due to spasm of the milk ducts caused by cold, milk begins to flow poorly and with disturbances, and this leads to its stagnation. Against the background of an infection or inflammatory process, lactostasis develops into mastitis. A common cause of mastitis is also a combination of lactostasis and a bacterial infection, for example, staphylococcal. Cracks in the nipple halos are a direct path to the milk ducts, through which bacteria penetrate, so it is very important for nursing women to maintain personal hygiene and correct breast care. After each feeding, it is necessary to lubricate the breast area with special creams that provide a softening and healing effect.
There are cases when stagnation of milk without any other additional factors other than the presence of an infectious disease in the mother’s body develops into mastitis. Such a source may be endometritis, pyelonephritis, and sometimes simple caries.
If the baby does not eat all the milk from the breast, and the mother does not make efforts to soften and express congestion, then there is a high probability of mastitis.
Other causes leading to mastitis include:
- milk stagnation caused by incomplete emptying of the mammary gland after each feeding;
- the appearance of cracks in the nipples as a result of the child’s incorrect attachment to the breast or the eruption of baby teeth;
- tight, too tight underwear;
- getting a chest injury;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- low body resistance.
Treatment
Treatment of influenza during lactation is complicated by the fact that many effective medications are prohibited for use by nursing mothers. At the first symptoms of the flu, you should call a doctor. When treating a disease after childbirth, it is important to pay attention to the following issues:
- how to relieve symptoms;
- how not to infect a child;
- how to maintain lactation and milk quality.
Treatment in most cases is carried out at home. However, influenza is not an indication to stop feeding. The hospital is indicated only in case of serious complications that require constant medical supervision.
What can you do
A nursing mother who has the flu should not take any medications until she consults a doctor. It is important to find out in advance from your therapist what first aid for high temperatures is possible during lactation, because with the flu it is often necessary to urgently bring down the fever. Even safe antipyretics are used only in consultation with a doctor. It is strictly forbidden to take medications that are incompatible with breastfeeding and to exceed the dosage of safe medications. Simple measures will help speed up your recovery:
- wet cleaning in the house;
- frequent ventilation in the room;
- drinking plenty of water;
- bed rest;
- full sleep.
Uncontrolled use of traditional medicine during lactation is not recommended: each measure should be discussed with a doctor. The safest advice from traditional medicine that applies during lactation is to rinse the nose with saline solution to get rid of a runny nose.
What does a doctor do
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment that is compatible with lactation. Treatment usually comes down to symptomatic therapy: safe drugs are prescribed that can alleviate the influenza condition. The doctor may prescribe:
- interferon-based antivirals;
- antipyretic drugs;
- topical agents - aerosols and nasal drops.
Antibiotics are extremely rarely prescribed for influenza during the postpartum period. They may be used if a viral disease is complicated by a bacterial infection. Taking antibiotics usually involves temporarily stopping the baby from breastfeeding. This often leads to further disruption of lactation.
Taking medications approved for breastfeeding
Pharmacies offer a wide selection of medications whose action is aimed at combating the influenza pathogen. But another question arises: how to treat flu while breastfeeding. You will need to consult a doctor who will draw up a treatment regimen and select safe medications.
During the flu, a nursing mother is prescribed the following medications:
- Immunomodulatory and antiviral medications . This group of drugs affects the cause and actively fights the pathogen. Immunomodulatory drugs increase the body's defenses.
- Antipyretics . Breastfeeding women are allowed to take paracetamol-based medications.
- For nasal congestion, use saline solutions .
It is important to correctly draw up a treatment regimen that will be completely safe for the child.
Antiviral and immunostimulating drugs
The list of medications that breastfeeding women are allowed to take is small. Let's consider how a nursing mother can be treated for the flu:
- Grippferon . The drug is available in the form of a spray, ointment and drops. The active component is interferon alpha-2b. The medication fights the acute inflammatory process, has a positive effect on the immune system, and reduces the risk of progression of complications. Actively used to prevent influenza. Side effects manifest themselves in the form of allergic reactions. Do not take in case of hypersensitivity to the active components.
- Viferon. The product is produced in the form of gel, ointment and suppositories. The active component is also interferon alpha-2b. The frequency of use and duration of drug therapy is determined only by the doctor. Do not use if you are hypersensitive to the components in the composition.
- Aflubin . If the question arises of how to treat flu during lactation, then pay due attention to Aflubin. Produced in the form of tablets and drops. This is a homeopathic remedy with a completely natural composition. Characterized by immunomodulatory properties. Thanks to its unique composition, the product lowers temperature and eliminates inflammation from the mucous membranes. The drug actively fights intoxication of the body due to illness.
These are the drugs that are allowed for breastfeeding and are as safe as possible for both mother and baby.
Antipyretics and painkillers
As soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear, women are faced with the question of what a nursing mother can do if she has the flu. Doctors recommend taking children's forms of drugs as antipyretics.
Let's look at how to treat the flu in a nursing mother:
- Nurofen for children . The drug is based on ibuprofen. Helps quickly normalize temperature, eliminates the acute inflammatory process, and is also characterized by an analgesic effect. But this medication is prohibited for use for stomach ulcers, heart, liver and kidney diseases.
- Panadol for children . The active ingredient is paracetamol. The medication fights fever and eliminates pain. Do not use in case of hypersensitivity to the components in the composition, as well as in case of pathological changes in the kidneys and liver.
- Efferalgan . It also contains paracetamol, which quickly brings down the temperature. The frequency of administration and dosage is determined by the doctor.
- Antigrippin . The drug is produced in the form of effervescent tablets and powder to obtain a solution. It is characterized by a complex effect, as it lowers temperature, relieves pain from the flu, reduces nasal congestion, and fights lacrimation. Do not take if you have a stomach ulcer.
These are the most effective and approved drugs for hepatitis B.
Medicines for nasal congestion
Women are also interested in the question of what to do if a nursing mother gets sick with the flu, how to cope with congestion. Doctors prescribe medications based on a solution of natural sea salt.
The best permitted means are:
- Aqua Maris . The product is available in the form of a spray for irrigation of the nasal passages. Sea water from the Adriatic Sea is used. The drug greatly facilitates breathing when you have a runny nose, fights swelling of the mucous membrane, and removes viruses and bacteria. Do not use for nosebleeds.
- Aqualor. Another good drug that contains sea water from the Atlantic Ocean. Available in the form of a spray for irrigation of the nasal cavity. Side effects occur extremely rarely in the form of a local allergic reaction.
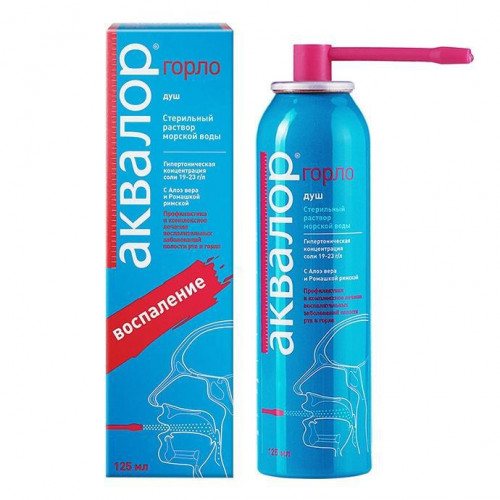

Even before using such safe products, you should consult your doctor.
Prevention
A nursing mother should avoid contact with influenza viruses, as this can lead to serious consequences. The following preventive measures will help prevent illness during the dangerous period of viral infections:
- avoid public places;
- exclude contact with a family member who has the flu;
- constantly ventilate the house and maintain an optimal level of moisture;
- strengthen the body (natural vitaminization, healthy sleep, walks in the fresh air);
- Wash your hands frequently and thoroughly with soap.