Normal yellow discharge
Healthy vaginal microflora is 90-95% represented by lactobacilli, which multiply and develop in the accumulated glycogen cells of the mucous membrane.
During the interaction of glycogen and lactobacilli, an acidic environment is formed, which prevents the development of opportunistic microorganisms:
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- candida;
- bacteroides;
- fusobacteria;
- clostridia.
In addition, in some women the presence of mycoplasma and ureoplasma in the vaginal microflora can be considered normal.
Natural vaginal discharge may be clear, white, off-white, or yellow. Vaginal secretion with a yellow tint can be caused by the reproductive system and hormonal balance in the body.
The structure of the secretion is homogeneous and does not have a sharp specific odor. Normally, it should not be abundant and intense, or cause discomfort (burning, pain and itching).
Normally, yellow, odorless discharge in women may indicate:
- the presence of blood elements in vaginal secretions, which is typical for the premenstrual period;
- the onset of ovulation;
- hormonal changes due to taking oral contraceptives;
- sexual intercourse without the use of protective measures or a change of sexual partner (reaction of vaginal microflora to the ingress of seminal fluid).
Can discharge be a symptom of thrush?
The appearance of excessive or unusual vaginal discharge, which is commonly called leucorrhoea (leukorrhea), is influenced by various factors. Thrush, or candiosis, is a disease that occurs as a result of the active development of opportunistic microorganisms in the vaginal environment, in particular Candida fungi.
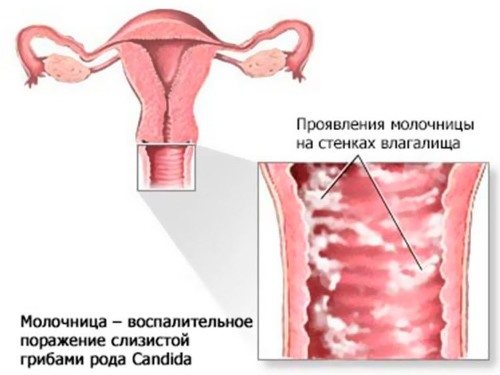
With candiosis, leucorrhoea can be of a wide variety of shades:
In most cases, thrush is characterized by the following signs of leucorrhoea:
- White color;
- lack of pronounced odor;
- curdled consistency;
- yellowish tint when dry.
A red or brown tint may occur during an ectopic pregnancy, and this may also indicate cervical erosion . The addition of a green tint may occur if a bacterial infection enters the body.
At first, thrush may not cause discomfort, but as colonies of fungal microorganisms progress and grow, it is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: itching in the genital area, burning sensation when urinating, leucorrhea with a sour odor.
In addition, sexual intercourse may be associated with painful sensations due to microtrauma of the vaginal mucosa.
Yellow discharge during pregnancy
The state of health during pregnancy can be judged by the characteristic signs of female discharge, the yellow tint of which can be either normal or a consequence of a pathological abnormality. Normally, a yellow secretion appears in the first weeks of pregnancy due to the significant amount of progesterone that the body produces. It activates the secretory function of the vagina.
As a result, part of the dead epithelium, a certain amount of healthy microflora and fragments of the developing mucus plug enter the natural secretions. The combination of these components turns vaginal discharge yellow, but does not affect the smell or consistency.
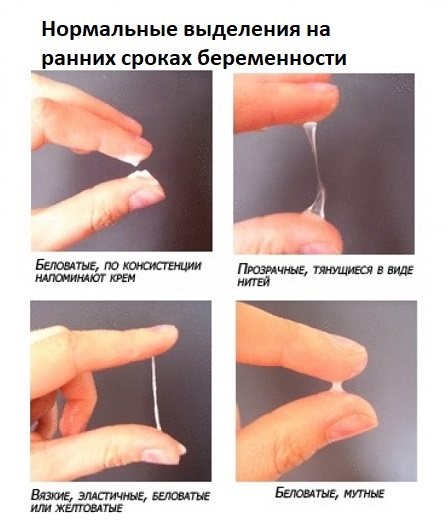
Some time before giving birth, women may also experience yellow vaginal discharge without the presence of a strong odor or severe discomfort. The cause is a detached mucus plug that created a barrier that prevented bacteria from entering the uterus throughout pregnancy.
Infection is likely to occur when the secreted secretion:
- acquired an uncharacteristic odor;
- has a thick or curdled consistency;
- associated with painful sensations;
- accompanied by itching and redness;
- has dubious inclusions.
The abundance of yellow, odorless vaginal secretion during pregnancy is physiologically justified and is the norm, since during this period the microflora of the birth canal changes, causing the production of more lubricant.
During pregnancy, yellow vaginal fluid may acquire uncharacteristic shades and a specific smell, indicating the presence of a disease:
- Yellow-white . Vaginal secretions of this kind may be normal, but sometimes indicate an allergic reaction of the body or the presence of candidiasis.
- Yellow-green . An admixture of green is not considered a natural phenomenon. In many cases, the cause of greenish mucus is bacterial infections or diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Yellow-brown . The main reason for the appearance of this shade is the appearance of blood in the vaginal secretion. It is normal to occur in the early stages of pregnancy if the blood came as a result of the attachment of the embryo to the epithelial layer of the uterus. In later stages, the phenomenon is considered normal, due to the separation of the mucous plug.
Any appearance of bloody leucorrhoea should be considered as a possible danger, since:
- in case of ectopic pregnancy, surgical intervention may be required to remove the fertilized egg;
- a frozen pregnancy will also require surgical intervention;
- secreted blood may be a symptom of spontaneous abortion;
- Placental abruption can also result in spontaneous abortion.
- cervical erosion requires constant monitoring by doctors for the successful birth of a child.
The presence of yellow vaginal secretion during pregnancy is a natural reaction of the body to the presence of an embryo in it, unless accompanied by an uncharacteristic odor and a suspicious hue.
Why might your chest hurt when breastfeeding ends?
If the breasts are a little sore, but at the same time they are soft, without compaction, then this means that there is a slight inflammation, but there is no lactostasis.
This inflammation is well treated with cold. You can add a piece of ice wrapped in a clean towel or a frozen piece of meat (packed, of course). Exposure to cold should last approximately 10-15 minutes. If there are lumps in the chest, then this is lactostasis. Minor congestion can be relieved quite easily with pumping, massage and cold compresses. In more severe cases, the entire chest becomes stiff and painful, and the temperature rises. Lactostasis can turn into mastitis. In the most severe cases, a purulent abscess forms and surgery may be necessary.
Sometimes the pain occurs due to a sudden increase in nipple sensitivity. This depends on the physiological characteristics of the woman and is not dangerous to health.
Negative breast discharge can include any liquid other than breast milk and colostrum during pregnancy, which should be discharged from one or two nipples. In other cases, this phenomenon is considered to be a deviation from the norm. Especially if the oozing consistency is greenish, brown or bloody.
If you notice discharge that does not correspond to your condition, namely if you are not pregnant, you need to go for a consultation with a mammologist. You need to visit the clinic as early as possible, because this condition can lead to more serious consequences.
It is very important to remember the fact that without pregnancy (or if there was no pregnancy before), the release of colostrum is impossible. Any fluid that is released should be examined by a doctor to rule out any possible illnesses.
Sometimes colostrum manifests itself due to the fact that a woman’s hormonal levels have changed or she has taken contraceptive medications. The doctor, in turn, will first prescribe all the necessary tests in order to determine the amount of hormones that cause colostrum.
However, before you start worrying, take care to rule out natural causes.
Namely:
- Perhaps you have recently breastfed and the colostrum is residual secretion;
- You are pregnant, but your pregnancy is too early to be determined by a test.

If all the causes have been eliminated or not detected, then we will talk about a disease that is inflammatory in nature or even a tumor (malignant or benign).
When breastfeeding
During breastfeeding, the appearance of yellow vaginal secretion indicates the manifestation of the natural process of cleansing the uterus due to changes in hormonal levels. It is during the period of breastfeeding that the secretion released from the vagina becomes especially intense and abundant.
It has a white or yellowish tint, has no odor or blood impurities, and is liquid and spreading in consistency. As a rule, secretion begins around the 10th day after birth and lasts about 20 days.
How to stop lactation correctly?
First of all, to stop breastfeeding, you need to choose the most suitable period. This should not be done when the child is ill or if sudden changes have occurred in his life (for example, the mother went to work, etc.).
Once the most favorable period for completing lactation has been selected, you need to proceed with the following actions:
- First, you should stop feeding during the day. As an alternative, you can offer your child juice, an apple or a cookie.
- Next you need to remove the morning feeding. In order to distract the baby, you can call dad or, for example, offer a new toy.
- Eliminate feeding before bedtime. This step is final. Instead of breastfeeding, you can read a fairy tale to your child or sit near his crib.
It should be noted that at the same time, a woman should take care of her breasts, making the process of completing lactation as painless as possible. To do this you need:
- Express your breasts little by little, and this should not be done until they are completely empty. Otherwise, milk production will be stimulated.
- Wear a bra that is supportive but not constrictive.
- If swelling of the mammary glands appears, compresses can be applied.
You should know that it is impossible to safely interrupt lactation in a short period of time. The amount of milk produced decreases gradually. It is best to extend this process over 2-3 months.
Before your period
Before ovulation, during the menstrual cycle, vaginal secretion can be either white or acquire a yellow tint. The main factor influencing the appearance of yellow impurities before menstruation is hormonal disorders.

Odorless yellow discharge can appear not only in adult women, but also in girls 10-12 years old. This phenomenon is also considered normal and means that the body is preparing for reproductive ability.
When to go to the doctor
If lumps have formed in the chest and they cannot be dealt with immediately, you should consult a doctor. If the breasts turn red and the woman has a fever, then a visit to the doctor must be made without delay.
After a baby stops breastfeeding, milk may continue to be produced for a long time, up to three years. But if the discharge suddenly becomes brown, mixed with blood, then you must definitely consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
A meeting with a doctor is also necessary if, after 3 years from the date of cessation of breastfeeding, milk continues to be released, and this is accompanied by menstrual irregularities, infertility, and also if the color and nature of discharge from the breast suddenly changes.
Pain is least likely after stopping breastfeeding if the process was gradual. It is even better if self-exclusion has occurred, i.e. The child just outgrew it. But even if it is necessary to abruptly stop feeding, breastfeeding can be stopped without serious consequences for health, if everything is done correctly.
In a normal situation, milk is produced and secreted in the mammary gland. Galactorrhea is a process in which colostrum is released after stopping breastfeeding after six months. This period of time is considered normal, but if there is discharge in the future, you need to go to the doctor.
Galactorrhea is considered to be the release of milk or colostrum after stopping feeding, when more than four to six months have passed. This period of time is considered normal, and if the discharge continues, you should contact a specialist. What could be the reasons for normal and pathological release of colostrum after lactation?
Read in this article
After menstruation
The odorless yellow secretion released from the vagina immediately after menstruation is also a natural process of cleansing the internal genital organs. Normally, after menstruation it is white or white-yellow, not too thick.
Yellow coloration may occur due to:
- sexual intercourse without protection;
- hormonal changes in the body due to taking contraceptives or other hormonal drugs;
- allergic response of the body to external irritants (use of synthetic underwear, components of washing powder, etc.).
During menopause
During menopause, a woman's body decreases the production of mucous contents of the cervix. Natural secretions continue to be released as during reproductive years, but the volume of secretions may decrease to such a level that vaginal dryness may develop.

The volume of fluid released during menopause is normally about 2 mm per day, and its consistency should be transparent or yellowish, reminiscent of rice water. In a healthy state, vaginal secretions should not have a pronounced odor or cause discomfort or pain.
After an abortion
After an artificial termination of pregnancy, a rather thick yellow secretion may be released for 2-3 months, occasionally acquiring a reddish tint due to damaged blood vessels.
Due to reduced immunity, the body is more susceptible to the penetration of pathogens of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system and intestines - staphylococcus and streptococcus. Since after an abortion the body’s protective functions are reduced, you should carefully monitor the consistency of the discharge, the accompanying odor and other unpleasant manifestations.
In inflammatory processes
When an inflammatory process occurs, leukorrhea is accompanied by:
- uncharacteristic odor;
- painful sensations;
- burning and itching in the genital area;
- disturbance of the urination process;
- increased body temperature;

- pain during intercourse.
To eliminate the cause of the disease, it is necessary to determine the causative agent of the pathological process, as well as to establish the patient’s predisposition to certain drugs. For treatment, medications are used, usually with a broad spectrum of action.
Normal or pathological?
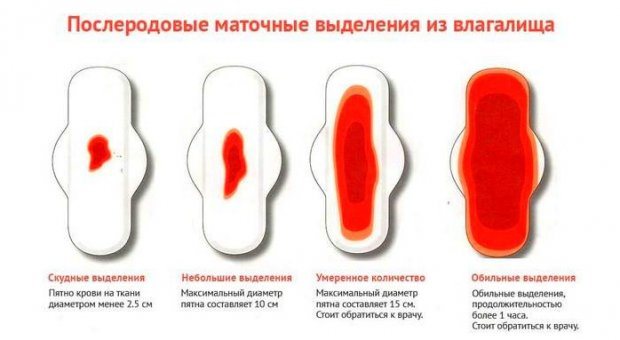
Signs of complications in the postpartum period are:
- Yellow discharge with an unpleasant odor. Evidence of suppuration and the onset of endometritis or stagnation of lochia in the uterus. Pathologies indirectly confirm pain in the lower abdomen and an increase in body temperature.
- Increased discharge, sudden uterine bleeding two months after birth. Sometimes it can be mistaken for the first menstruation. In contrast, bleeding continues for more than 10 days, accompanied by the release of blood clots.
- Curdled discharge may occur while taking antibiotics. They can provoke a deficiency of lactobacilli in the vagina, which is accompanied by thrush, an unpleasant burning sensation and itching.
Bloody discharge after 2–4 months
Bloody discharge after the end of lochia can be spotting, appear in the form of spots or be abundant. They can be provoked by a gynecological examination, sexual intercourse, increased physical activity, or heavy lifting.
Each case is individual, so you cannot do without consulting a gynecologist. It is possible that your first period has arrived since giving birth. In this case, it is also important to visit a doctor who will examine the woman and select a contraceptive method.
Brown discharge after 2–4 months
Brown discharge after childbirth is not uncommon (see also: bloody discharge after childbirth). This color indicates the presence of coagulated blood in them. The appearance of such discharge 3 months after birth is evidence of the beginning of the restoration of the cycle. They may arrive at intervals of 21–34 days. After a couple of similar periods, the discharge will turn red.
When brown discharge continues for more than a month, it does not look like menstruation. Most likely, there is a hormonal imbalance that should be corrected. For this purpose, ultrasound and tests are indicated, based on which the doctor selects treatment. Often such discharge is observed with endometritis, cervical erosion, which also requires attention and correction.
Bright red discharge after a month or later
If bright red discharge was observed a month after childbirth and disappeared within four days, we can talk about the resumption of menstruation (for more details, see the article: menstruation after childbirth and cesarean section while breastfeeding). This happens to mothers who do not breastfeed. At the same time, one should not exclude pathological processes in the pelvic organs, especially if blood flows or smears for 2 weeks or more. Such an early onset of menstruation is a reason to consult a gynecologist. After examination, he will be able to accurately name the cause of the bright red discharge.
Scarlet color may indicate the following anomalies:
- cervical wounds;
- clotting problems;
- rupture of the inner part of the uterine muscle.
Bloody discharge after 2–4 months
Bloody discharge after 2–4 months is one of the normal variants. Many women complain that such discharge either disappears or appears again. There is no pain, fever or other alarming symptoms. To reassure yourself, it is better to consult a doctor who will assess postpartum changes in the body and allow intimacy.
After childbirth
After the birth of a child, a woman begins to change in her body: prolactin and oxytocin are produced - hormones necessary for lactation. In the first hours after birth and during the first few days, the discharge is bloody, which is a consequence of the healing process of the internal reproductive organs.
For another 5-6 weeks, while the uterus acquires its usual size, the production of postpartum secretion, called lochia, continues.
At first, they are quite abundant and similar to discharge during menstruation, which indicates the natural process of cleansing the uterine cavity. White or yellow, odorless discharge in women after a natural birth lasts about two months, and after a cesarean section it lasts a little longer, since the rate of uterine recovery is slowed down.
Postpartum discharge: what should be normal?
After birth, the placenta and large blood clots should come out of the uterus. If they don't come out on their own, doctors remove them with cleaning. However, unnecessary particles still remain in the uterine cavity - these are lochia, which will leave the body of the young mother for some period of time. This is how postpartum recovery goes.
Lochia consists of fragments of mucus and blood. The first week the discharge is bright red and abundant. Then they acquire a brown color and shrink in volume. Color can vary from bright to dark and even black.
The appearance of serous and yellowish-whitish secretion is considered normal. A gradual reduction in discharge also indicates normal postpartum development. The final recovery of a woman can be judged when the lochia completely leaves the uterine cavity.
The influence of hormones: what abnormalities provoke the appearance of yellow discharge?
The appearance of yellow vaginal secretion may be due to hormonal imbalances.
The manifestation of hormonal disorders depends on age, physiological characteristics and various external factors:
- Hormonal imbalance in teenage girls is associated with the approaching onset of puberty. The discharge can be white or yellowish, sometimes transparent. In girls of older adolescence, discharge can be constant and intense, which is the norm in this age period.
- In women of reproductive age, hormonal changes can trigger the use of contraceptive medications . In addition, a regular delay in menstruation of 5 days or more also indicates hormonal disorders that provoke the appearance of a yellow tint to the vaginal secretion.
- After an abortion, a sudden hormonal imbalance causes the body to stop producing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This entails a disruption in the production of hormones and negatively affects the human endocrine system.
- After childbirth, changes in hormonal levels are associated with the need to restore the body and bring it to its prenatal state. During this period, an increase in the volume of discharge and a change in its color may be observed.
- During menopause, a radical restructuring of the female endocrine system occurs. Transparent and yellowish discharge of this period consists of mucus, plasma and lymph.
Clinical signs of pathological galactorrhea
The following clinical symptoms are characteristic of galactorrhea:
- Menstrual irregularities (delays, irregular periods);
- Neurological manifestations in the form of dizziness, headache, disruption of the sensory organs;
- Decreased libido;
- The discharge is opaque, yellowish;
- Hair growth in atypical places (chest, face, etc.).
Thus, the pathological secretion of milk or colostrum after lactation is characterized by a rather vivid clinical picture, mainly due to hormonal imbalance. It is important to understand that such a process affects several systems of the body and may not be associated with the place of external manifestation.
To make a differential diagnosis, a number of laboratory and instrumental research methods are used. The examination mainly includes: ultrasound examination of the breast and pelvic organs, mammography, blood test to determine the level of thyroid hormones and prolactin, computed tomography of the brain.
Pathological release of colostrum after cessation of feeding can have four levels of intensity. At the first level, liquid is released only when you press on the breast in the nipple area. The second level - milk or colostrum itself is released in drops. The third level - the liquid itself is released with medium intensity. And finally, at the fourth level, colostrum is released in a stream.
The intensity of discharge is also of important diagnostic value, as it allows one to determine the cause of galactorrhea in a number of doubtful cases.
However, we should not forget that normal physiological secretion of milk or colostrum after stopping breastfeeding is often mistaken for pathological galactorrhea. In some cases, taking into account the individual characteristics of a woman, discharge can be observed for up to six months. Therefore, you should consult a gynecologist only if you have at least two of the symptoms described above.
Pathological causes of yellow discharge
Yellow, odorless discharge in women may be a consequence of pathological processes:
- Adnexitis. It is characterized by itching, pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, and elevated body temperature.
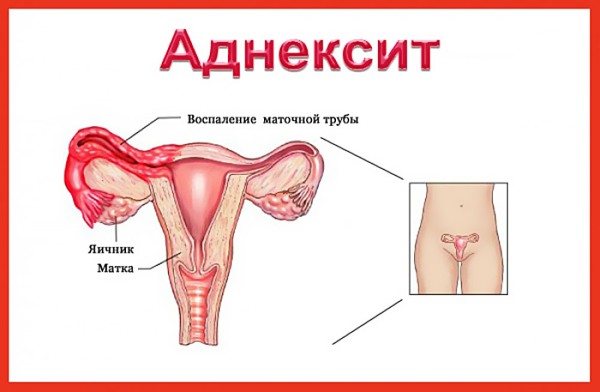
Yellow, odorless discharge in women can be a symptom of a complicated disease.
- Erosion of the cervix does not exclude the influence of natural discharge on the color change, which is explained by the presence of a small amount of blood in the physiological secretion or inflammation.
- In some cases , diseases that are sexually transmitted , causing itching and burning in the intimate area, do not have a repulsive odor, and sometimes can occur without severe symptoms: ureaplasmosis, chlamydia and mycoplasmosis.
An ailment such as colpitis, in some cases, occurs without a specific odor. However, along with other pathological conditions, it most often has a pungent odor. Expressed by hyperemia, swelling of the genitals, itching, burning when urinating.
Other causes of yellow leucorrhoea, which have symptoms similar to colpitis and a specific odor, are the following diseases:
- Vaginosis. The main symptoms are an abundance of yellow-green leukorrhea and a pronounced fishy odor.
- Sexually transmitted diseases: chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea.
- Candidiasis. Thrush is characterized by curdled white or yellow leucorrhoea with a sour odor.
- Endometriosis. Its occurrence is due to a hormonal disorder, which causes a strong proliferation of the surface of mucous tissues. The secretion secreted during this disease is dark yellow or brown, liquid and quite abundant, with a pungent unpleasant odor.
Discharges that may be a sign of pathology
If you have little discharge after childbirth or it suddenly stops, this may be a clear sign of pathology - lochiometers. The reason for the reduction or complete cessation of lochia may be a spasm of the cervix, which simply “does not release” the discharge out. This especially applies to the first days after the baby is born. This deviation from the norm is characterized by retention of lochia in the uterine cavity, due to which the organ is stretched. In this case, the woman feels heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen, the uterus increases in size, and fever begins with an increase in temperature to 38-40 degrees. If you do not consult a doctor in time, inflammation of the uterus (endometritis) may develop. For treatment, lochiometers usually prescribe antispasmodic and contractile drugs, and less commonly, antibiotics. Sometimes eliminating accumulations of lochia is possible only by emptying the uterine cavity.

Woman after childbirth
Another reason to see a doctor urgently is heavy, strong discharge after childbirth. This symptom may be a sign of disturbances in the process of uterine contraction, and also signal a blood clotting disorder. Both conditions pose a threat to a woman’s life and therefore require immediate action.
Also, sometimes in the first few hours after birth, bleeding occurs from sutures placed on tears in the birth canal. This usually happens if the requirements for ensuring maximum rest of these areas are not met - exclusion of physical activity, sexual rest, control of straining and the nature of stool, no pressure on the sutures. If this situation occurs, it is important to consult a doctor immediately.
Other signs of pathology in the nature and amount of discharge
Additional signs that should alert you in the postpartum period
In addition to a sharp change in the nature and intensity of the discharge, a woman should be alerted to other unpleasant symptoms. The first of them is pain in the lower abdomen. Of course, in the first days the uterus contracts intensely, which causes paroxysmal discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially intensifying during breastfeeding. However, increased pain and the occurrence of sharp spasms should be the reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist.

Temperature increase
Another sure sign of problems in the body is an increase in body temperature. Here it is only necessary to exclude the appearance of stagnation of milk in the breast - lactostasis, which causes a sharp and strong increase in body temperature. If there is no pain or “heaviness” in the chest, and the body temperature is above 37 degrees, then you should schedule a visit to the doctor. Perhaps this is how an infection that has entered the uterine cavity manifests itself. Additional symptoms of infectious complications include general malaise, headaches, dizziness, body and joint aches.
Video: odorless yellow discharge in women
What discharge is considered pathological, watch in the video:
Vaginal discharge, inflammatory processes:

While breastfeeding, mothers may experience unusual vaginal discharge. Although menstruation is absent for almost the entire lactation period, there is discharge during breastfeeding, which is considered normal. Which color and consistency of vaginal secretions are standard and which should cause concern. What can cause deviations, and what to do for prevention to avoid health problems in the intimate area.
What is considered normal
In the first 4-7 weeks after childbirth, all women experience so-called lochia. This is heavy bleeding.
Their appearance is associated with the departure of the placenta from the uterus and the movement of the child along the birth canal.
In this case, bleeding occurs, which ends in due time. The presence of blood clots in them is considered normal.
This is not a cause for concern, but rather evidence of correct natural processes. This means that the uterus is cleansed of the remaining parts of the placenta.
During this period, a woman may experience pain in the abdomen similar to contractions. These are spasms or contractions of the uterus.
They help speed up the cleansing process.
During traditional childbirth, already 2-3 weeks after delivery, spotting becomes less abundant and turns pale. If the mother had a caesarean section, this period may last longer.
This is explained by the fact that during the operation the uterus is severely injured - it is cut open and it takes more time to recover.
When the peak of the discharge is left behind, it turns brown.
The cessation of discharge and the appearance of a whitish or transparent secretion of mucous consistency indicates the correct passage and completion of the restoration of the uterus.
This light discharge may continue throughout the entire feeding period.
They may take on a light yellow tint. Their characteristic features are the absence of odor, pain and discomfort in the genital area.
Recovery in the postpartum period
Every woman in the postpartum period should know that breastfeeding is an excellent prevention of all kinds of complications. After all, when a baby is applied to the breast, there is an immediate release of the hormone oxytocin, which also causes contractions of the uterus. After feeding, a woman may observe a visible increase in discharge, which is associated precisely with contraction of the muscles of the uterus and should not cause concern.
To speed up uterine contractions, you should empty your bladder in a timely manner. During the postpartum period, it is advisable to do this every three hours, even if the woman does not have a pronounced feeling of bladder fullness, and to avoid constipation.
For 1-2 months after giving birth, discharge cannot be absorbed with tampons, precisely because they do not remove lochia, but simply absorb them. This can lead to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms. It is recommended to use pads or diapers instead of tampons. Choose unscented products, as you need to control not only the color and number of lochia, but also their smell.










