Women often ask doctors how to treat colds while breastfeeding. Indeed, in this case, it is necessary to exercise extreme caution when taking medications so as not to reduce the quality of milk and not cause serious harm to the child’s health. With the current level of development of medicine and pharmacology, effective and safe treatment of colds while breastfeeding is quite possible. In such cases, it is strongly recommended that you consult with a qualified professional first. The attending physician will help develop effective therapeutic tactics that are ideal for the current situation.
In addition, he will tell you what can be taken in these circumstances for prevention. A cold during breastfeeding is an everyday, generalized and fairly common name for a whole group of acute respiratory infections of viral and bacterial etiology. Each of these pathogenic agents that penetrate the female body against the background of hormonal changes and the associated slight decrease in immune status has its own incubation period, characteristics of pathological effects and localization in a certain area of the respiratory tract and pulmonary-bronchial apparatus.
Therefore, the exact answer to the question of how to treat a cold for a nursing mother depends on the composition of viral pathogens and the bacterial microflora that has joined them. A cold nose and respiratory pathology of the throat require the use of completely different therapeutic techniques. For example, rhinovirus infection is characterized by damage to the nasal mucosa and excessive secretion of mucus, and acute adenovirus syndrome contributes to the development of inflammatory processes in the nasopharyngeal region and the occurrence of pain when swallowing.
Many strains are localized in the upper respiratory tract and bronchi, which leads to coughing and fever. When such symptoms and various ailments are detected, the mother always has doubts about whether it is possible to breastfeed with a cold. About 30 years ago, in such cases, the mother simply isolated herself from the child until complete recovery. There is no need for such extremes now. Moreover, it has been irrefutably proven that if a nursing mother gets sick, lactation should under no circumstances be stopped.
Ways to protect a baby and what a woman should do when she has a cold
Proper treatment of colds while breastfeeding will not negatively affect the baby's health. Moreover, along with breast milk, a baby who has caught a cold in any organ receives specific antibodies, which are a reliable barrier to viral pathogens and bacterial agents. It is important to do everything possible to avoid infecting your baby with various infectious diseases. Unfortunately, there is no single universal recipe or right remedy. All children are purely individual in their development. Therefore, each parent must act according to the situation.
Treatment of ARVI during breastfeeding requires a responsible approach. It is highly advisable to use a special medical protective mask. Such a preventive measure may be the answer to the question of how not to infect a baby. This does not provide an absolute guarantee of the child’s safety, but it can significantly reduce the concentration of pathogenic microflora in his environment.
Since viral infections are spread by airborne droplets and direct physical contact, it is necessary to wash your hands thoroughly and often, and change the gauze bandage every 2 hours. Treating colds during lactation using these simple preventive measures will significantly reduce the risk of infection for the child. And the optimal temperature in the room will prevent your baby from catching a cold. In no case should you express or boil breast milk, since heat treatment completely deprives it of beneficial substances, antibacterial properties and antibodies, which play an important role in the immune status of the child’s body.
You can fight a mild cold with the help of gentle medications and medications based on natural ingredients. For example, treatment of a runny nose while breastfeeding involves the use of substances that reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, make breathing easier and allow you to quickly cure a runny nose while breastfeeding. Today there are many drugs of this kind that can be absolutely safely used during the lactation period. Such medications include Sanorin, Galazolin and Otrivin, which make it possible to quite comfortably and effectively treat a runny nose in a nursing mother and, most importantly, without the risk of harming the baby’s health.
Precautionary measures
Colds during breastfeeding are highly contagious, so women need to take precautions. To avoid infecting an infant, at the first symptoms of a cold, you should wear a gauze bandage.
It is recommended to change the mask every 2 hours. It is better to ask relatives to take care of the baby and do wet cleaning during the illness. Bed rest promotes rapid recovery.
If a nursing mother has a cold, she should use only her own hygiene items. For the patient, it is necessary to select separate tableware and carefully handle them. Bed and underwear should be changed every day.
Viruses can remain viable for hours in a dry and dusty room, so be sure to ventilate the room and do wet cleaning. In such conditions, viruses die quickly. Doctors recommend that parents purchase a humidifier and an ultraviolet lamp.
If the mother has a cough or runny nose, she should wash her face, hands and chest with soap before feeding. You should always sneeze and blow your nose into a tissue or disposable tissue.
During contact with the baby, you must wear a mask. You cannot kiss the baby and it is advisable to have less contact with him. To prevent infection, pediatricians recommend dripping saline solutions into the child’s nose.
Suitable medications for a nursing mother
When choosing the optimal therapeutic tactics for hepatitis B, as mentioned above, one cannot do without consulting a qualified specialist. This is a guarantee that the health of the woman and child will not be harmed. Each cold requires an individual approach. At the first symptoms, you can take completely safe medications such as Paracetamol, which is an effective antipyretic drug with good anesthetic properties. It will quickly eliminate muscle and headache pain, which often accompanies viral rhinitis and other colds.

If the nasopharyngeal region is affected by spreading respiratory bacterial infections, it is advisable to gargle with soda and iodine-saline solution, lubricate with Lugol, since treating a cold in this way is not only effective, but also completely safe. Chlorhexidine can have a good therapeutic effect in such a situation. However, before using it, you must consult your doctor. ARVI accompanied by cough in a nursing mother can be treated with expectorants based on natural herbs, for example, Doctor Mom syrup. Nazol, which is able to quickly and safely cure a runny nose in a nursing mother, demonstrates good effectiveness in the treatment of such ailments.
But treatment with drugs containing the active substance bromhexine is not recommended. Such drugs include Bromhexine Berlin-Chemie, which has a good mucolytic effect, but is harmful to the body of an infant. Local antiseptics can also solve the problem. Before taking them, it is also advisable to obtain the approval of the attending physician. If we talk about which medications can be taken without the slightest risk for sore throats, then first of all you should pay attention to Strepsils and Sebidin, Cameton spray, Chlorophyllipt, which have a good therapeutic effect and do not pass into breast milk.
Is it possible to breastfeed during a cold?
Even if a mother gets sick with a cold, she should not stop breastfeeding. Because by continuing to feed the baby with breast milk, the mother helps him.
The fact is that with mother’s milk, antibodies to the virus are transmitted to the child, against which the woman’s body is fighting at that moment. This is kind of the only unique “medicine” that he gets through breast milk.
However, during feeding, the mother must wear a disposable mask. This way it will reduce the risk of mucus and sputum with viruses getting into the environment.
An increase in temperature during a cold is a natural reaction of the body. Nursing mothers, like everyone else, should lower their temperature only when the temperature is above 38.5 °C or when there is severe discomfort and headache.
If a woman is breastfeeding her baby, and she has ARVI, and the temperature rises above 38.5 °C, then ibuprofen or paracetamol can be used. These medications will not harm the baby.
If the mother has a stuffy nose, it is advisable to use a hypertonic saline solution for rinsing. It will help relieve swelling and cleanse the nasal mucosa.
But vasoconstrictor drops can cause unwanted side effects in a baby, so this group of drugs is prescribed only if absolutely necessary.

Cough is also a defense mechanism of the body during colds. It removes mucus and foreign bodies from the airways to make them easier to pass.
What will help a nursing mother with a cough:
- If a nursing mother's cough is caused by mucus flowing down the back wall of the nasopharynx during a runny nose (this most often occurs during acute viral infections), then the main treatment method will be to drink plenty of fluids, use a saline solution as a nasal spray, and gargle.
- If the cough is accompanied by hoarseness and shortness of breath, you should consult a doctor to prescribe treatment.
Mothers often ask whether it is possible to breastfeed if you have a cold. Many people wean their baby from the breast, but pediatricians do not recommend this.
Once viruses enter the body, they do not manifest themselves immediately. And after three days, protective proteins (immunoglobulins) begin to be produced, which counteract the proliferation of pathogens. These substances pass into breast milk.
Even when the mother does not know that she has a cold, the baby receives antibodies along with the milk. It is for this reason that the baby remains healthy. When a woman stops feeding, she deprives him of protection and provokes stress from weaning. The child spends a lot of energy digesting artificial formulas.
Antiviral drugs during lactation
Currently, there are a huge number of drugs on sale that are positioned as effective antiviral agents. The vast majority of the items on this extensive list have a purely psychological effect, known as the placebo effect. Others are generally prohibited during lactation. These include Arbidol, Remantadine and others. The approved and recommended drug is Aflubin, but its effectiveness has not been clinically proven.

The advisability of using antiviral drugs during lactation is still in question. But it is known for sure that homeopathic medicines will not harm the child’s health. Such medications, under certain circumstances, can serve as the correct answer to the question of how to treat a runny nose during lactation. Only drugs based on recombinant human alpha interferons have high and clinically proven effectiveness in treating acute respiratory viral infections.
However, even they should be taken correctly and only as prescribed by the attending physician, and in precisely calculated doses. To effectively treat colds during lactation, medications in this category such as Grippferon and Viveron are suitable. For a mild cold while breastfeeding, it makes sense to take Paracetamol, which quickly brings down the temperature. An effective and completely safe remedy for a runny nose is aloe juice mixed with honey. But this is from the category of traditional medicine. If the mother has a cold, this option should also be considered as an auxiliary, preventive or even alternative.
Prevention of influenza and ARVI in a nursing mother
During the cold season, a nursing mother needs to be especially attentive to her health so as not to catch a cold herself and not infect her child with ARVI.
- The most important thing to prevent colds is to ventilate the room. The fact is that in dusty, dry and still air, virus particles can persist for a long time. This means that the baby and other family members are at risk of contracting ARVI.
- In addition, it is necessary to maintain an optimal temperature in the room within 19–21 °C and air humidity (40–60%).
- Also try to walk in the fresh air as often as possible, but avoid crowded places during the epidemic period.
- Always wash your hands thoroughly.
Now you know how to treat a cold while breastfeeding your mother, and also what you need to do to avoid infecting your breastfeeding baby.
READ ALSO: Letter to the husband of a nursing mother: “Do you know what your wife does all day?”
READ ALSO: Treating colds with home remedies: advice from a pediatrician
READ ALSO: How to treat a sore throat: 10 tips for adults
It must be remembered that preventing acute respiratory diseases is easier than treating them. To prevent a cold, a woman should avoid walking with her child in crowded places during an outbreak of influenza and ARVI.
When visiting hospitals or clinics, you must use a mask. To prevent colds, you must follow a number of rules:
- Wash your hands often with soap.
- Use ointment with oxoline before going outside during epidemics.
- Dress for the weather.
- Include foods rich in vitamin C in your diet.
- Humidify the air in the room.
Following these simple guidelines will prevent viral infections. However, if you still have a cold, you need to feed your baby milk.
Not only the health of the baby, but also the health of the mother depends on this.
Antipyretics
An effective antipyretic and recommended for colds while breastfeeding is Ibuprofen, a non-steroidal drug that has a good anti-inflammatory effect. However, before taking it, you should consult a specialist. You should avoid medications whose effect on the child’s body has not been thoroughly studied. These include TeraFlu and Pharmacitron. Many women are interested in the answer to the question of what to do if I am feeding a child and have a chest cold. Such situations are quite common and are always accompanied by an increase in body temperature and the development of mastitis.
In this case, it is recommended to take antipyretic drugs on a natural basis. Before feeding your baby, you need to warm up the cold and inflamed area of the chest by applying a heating pad to it. Also pressing for women is the question of whether such a disease can negatively affect the quality of breast milk. In case of colds affecting the mammary glands, it does not lose its natural properties. However, if the breast has a cold or is affected by an infectious disease, this makes it somewhat difficult for the baby to suck milk.
It is important to remember that you can only take safe antipyretics that are fully compatible with the lactation period.
A diseased organ that provokes an increase in temperature can be treated without the use of drugs: with good old remedies, which include compresses, cups, mustard plasters and rubbing. They are certainly not capable of harming a child. Modern answers to the question of how to effectively treat colds while breastfeeding include ultrasonic inhalers, called nebulizers, which have an excellent therapeutic effect on the respiratory tract and pulmonary-bronchial system. If a mother has a cold, she should under no circumstances deprive her baby of breast milk.
Treatment of colds while breastfeeding
Before treating a cold while breastfeeding, consult a doctor. Many pharmacological drugs cannot be taken during lactation.
Methods and means of treating viral pathologies are chosen by the doctor. A nursing mother will be helped against a cold by a set of measures that includes:
- Bed rest.
- Prevention of dehydration.
- Balanced diet.
- Taking medications.
- The use of safe traditional methods of treatment.
If you have a runny nose, you can moisturize your nasal mucosa with saline solutions. If the baby is prone to allergies, the woman is recommended to take antihistamines.
You should treat a cold by following all the doctor's recommendations. Proper treatment will prevent secondary infections.
General recommendations
Doctors recommend that women be treated only with proven means. Taking antibiotics is possible only after consulting a doctor, who will advise what you can take for a cold.
Some antimicrobial drugs are prohibited when feeding a baby. In addition, antibacterial drugs do not act on viruses. They are prescribed only in cases where there is a bacterial infection.
In case of complications (pneumonia, sinusitis), treatment of colds during breastfeeding is carried out with non-toxic antibiotics, which are prescribed even to newborns.
When such a drug cannot be found, breastfeeding is interrupted. In this case, the ideal option would be to feed milk that has been frozen in reserve.
Antibiotics destroy not only pathogenic microorganisms, but also beneficial microflora. To avoid dysbiosis, it is recommended to include probiotics and lactulose-based products in complex treatment. Fermented milk products should be present in the diet. You should drink plenty of fluids (at least 1.5 liters). This will allow you to quickly get rid of intoxication and lower the temperature of a nursing mother with a cold.
Drinking plenty of fluids also prevents dry mucous membranes and facilitates the passage of sputum during coughing. Instead of water, the following are allowed:
- dried fruit compotes;
- green tea with lemon;
- decoction of chamomile, rose hips or calendula;
- mineral water "Borjomi".
For fever up to 38.5 0C, it is not recommended to take antipyretic drugs. It is believed that at this temperature the body most effectively fights infection and produces antibodies.
However, it is necessary to reduce the high temperature. The safest drugs for children, pregnant and lactating women are paracetamol-based products.
What not to do during lactation:
- Boil breast milk. When heated, biologically active substances and immunoglobulins necessary for the baby are destroyed.
- Take medications containing alcohol.
- Starve.
- Any drug in overdose can negatively affect the condition of the baby. It is advisable not to put the baby to the breast during the period of maximum concentration of the drug in the blood.
Treatment of acute respiratory infections during breastfeeding often cannot be done without prescribing cold medications. Since malaise is associated with the penetration of viruses into the body, it is recommended to take antiviral drugs at the onset of the disease.
Safe medications for the child and mother are immunomodulators containing interferons. They are easily tolerated and have no contraindications. Homeopathic drops or tablets will not cause harm. Other drugs can cause allergic reactions and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract in an infant.
For a runny nose and nasal congestion, oil drops based on herbal raw materials with anti-inflammatory and decongestant effects are a good medicine for nursing mothers. If treatment does not work, as a last resort, vasoconstrictor medications with the active ingredients naphazoline, xylometazoline, and oxymetazoline are prescribed.
A prerequisite for treating a runny nose is irrigating the nasal cavity with saline solutions. You can buy seawater sprays at the pharmacy.
If your throat hurts, anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed that do not pass into milk during breastfeeding. If there is no allergy, use iodine-based gargles or chlorhexidine. Plant-based sprays that contain eucalyptus extract help a lot. An alternative to rinsing is lozenges with antiseptics.
In case of cough, syrups with licorice root, thyme, anise or thyme are recommended. Mucolytic cough tablets based on thermopsis are contraindicated during lactation.
Instead of pharmaceutical drugs for bronchitis, it is better to take inhalations. For procedures it is better to use a nebulizer. Solutions of alkaline non-carbonated mineral waters dilute sputum well and alleviate the condition. You can use a drug containing the active substance ambroxol diluted with saline.
Drugs containing decamethoxin and chlorhexidine do not enter the systemic circulation during sanitation of the tracheobronchial tree. For the procedure, they are diluted with a 0.9% NaCl solution in a 1:1 ratio. Depending on the stage of the disease, the procedure is carried out 1 or 2 times a day.
What not to drink
The following medications should not be used:
- With the active ingredient bromhexine.
- Multicomponent herbal medicines that can cause unwanted reactions in a child.
- New, insufficiently studied drugs.
- Barbiturates.
- Codeine cough suppressants.
- Toxic agents (tetracyclines, sulfonamides).
Prescribed with caution for hepatitis B: pyrazolone derivatives, macrolides, combined cold medications, acetylsalicylic acid. Such medications often cause allergies and have a negative effect on the baby’s nervous system and intestines.
Folk remedies
Sometimes they turn to traditional medicine, since it is impossible to treat a cold in a nursing mother with pharmacological drugs. There are many non-traditional methods used for respiratory viral diseases during lactation. Effective inhalation products:
- The most affordable way to relieve a cough and sore throat is boiled potatoes in their skins. Drain the water from freshly boiled potatoes and breathe over the pan, covered with a towel, for 10–20 minutes.
- Decoctions of chamomile, birch leaves, and linden have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
- To make breathing easier, it is recommended to breathe in vapors of eucalyptus essential oil. Add 5-10 drops of oil into the kettle, make a funnel out of thick paper, insert it into the spout of the kettle and inhale the steam for 15 minutes.
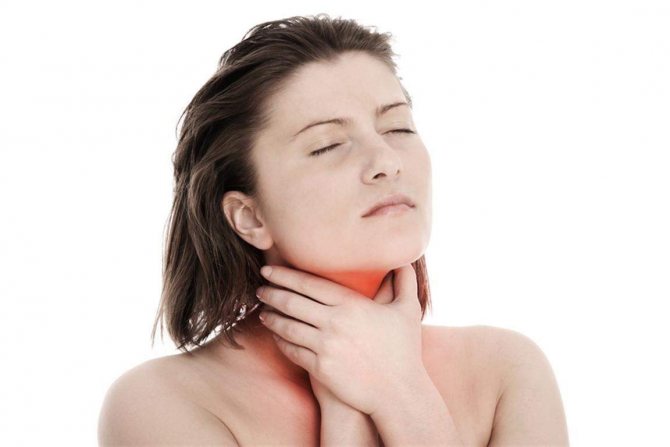
For rhinitis, the following methods are used:
- Lubricating the active points near the nasal passages with essential oils of mint, pine, spruce, eucalyptus or tea tree helps relieve a runny nose during a cold.
- Nasal drops made from aloe juice and honey with the addition of 1 mummy tablet.
- Diluted Kalanchoe juice helps clear mucus from the nasal passages. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and eliminates swelling of the mucous membranes.
- A mixture of olive oil and aloe juice is instilled into the nose. To prepare the emulsion you will need 4 drops of juice and 2 drops of oil.
When breastfeeding, if your throat hurts, herbal cold remedies help. Rinse:
- Thyme, sage, chamomile, and calendula have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- It is recommended to gargle with a saline solution with the addition of soda and iodine. To 200 ml of water add half a tablespoon of salt, half a teaspoon of soda and 4 drops of iodine. The solution should not be swallowed during the procedure.
- Apple cider vinegar solution relieves swelling and inflammation of the throat. Add a teaspoon of vinegar to a glass of warm boiled water. Rinse several times a day.
For coughs, traditional medicine offers the following remedies:
- Black radish juice helps with dry cough and difficult coughing. The top of the vegetable is cut off, the pulp is removed, leaving 2–3 cm from the peel. The inner edges of the radish are cut with a knife for better outflow of juice and smeared with honey. After a few hours, juice will appear in the cavity, which you can drink. Only fresh root vegetables are used.
- Milk with honey and butter relieves a woman’s condition, helps her cough, and softens her throat. You need to heat half a liter of milk, add a teaspoon of honey and 10 g of butter. It is better to take in the evening, before bedtime. This drink also calms and improves sleep.
It is recommended to drink vitamin herbal teas with raspberries, chamomile, linden, viburnum, calendula, and black currant. Honey and lemon are added to tea. It is useful to include garlic and onions in your diet, which contain natural antimicrobial substances.
A general tonic that helps you endure the symptoms of a cold more easily and get rid of it faster is a mixture of garlic and honey in a 1:1 ratio. A teaspoon of the mixture is taken once a day and washed down with plain water.
For nasal congestion and low fever, hot foot baths with mustard are recommended. You can also pour mustard powder into cotton socks at night. Relieve the condition of high body temperature by wiping with warm water with the addition of vinegar.










