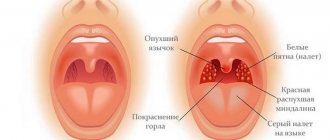
A satisfied mother means a happy baby! Painkillers for toothache while breastfeeding
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are not only a joyful and happy event, but also a great burden on a woman’s body.
Therefore, toothache can often bother a woman during such unforgettable moments in life.
This problem occurs due to a lack of calcium in the body there are not enough vitamins and minerals to maintain healthy bones and teeth .
Also, with the birth of a child, there is a catastrophic lack of time to visit dentists and take proper care of teeth.
ontakte
Odnoklassniki
Anesthetic medications may be needed to relieve severe pain before or after a dental appointment.
Important! You should not self-medicate , because an infection in the oral cavity can spread to other organs.
Breastfeeding is not a reason to forget about dental treatment , especially since there are no serious contraindications to this. But it is imperative to inform the doctor that the woman is breastfeeding so that he can select medications based on these circumstances.
Photo 1. Two painkillers in the form of a suspension (Nurofen and Ibufen), which are allowed to be taken by children starting from 3 months.
For toothache while breastfeeding, you can safely take Paracetamol and Ibuprofen .
Important! The course of taking medications is a maximum of 3 days . To minimize the risk for the child, it is recommended to take the tablets before bedtime , since during the interval between feedings most of the medicine will be eliminated from the body.
When choosing a remedy for toothache, you need to follow simple rules .
- Any medications must be agreed with your doctor .
- Carefully study the instructions before using the medicine and take only when it says what is allowed during lactation.
- Medicines allowed for a child can also be taken by a young mother in the form of tablets and injections.
Modern medicine does not stand still; medications have appeared that are available in the form of tablets, but do not harm the baby’s health.
also take special pain-relieving ointments .
How to relieve pain? Anesthetic medications for toothache during breastfeeding
There are universal “lifesavers” for a nursing mother with such an illness. The list of approved medications includes :
- Ketanov tablets , which effectively relieve acute pain, but do not fight its cause.
- Lidocaine or its analog Ultracaine is an injection for sanitation and treatment by a dentist.
- Kalgel is an ointment based on lidocaine.
- Traumeel ointment is a homeopathic remedy.
- Kamistad Baby gel with chamomile extract.
- Dentol Baby not only relieves pain, but also inflammation, and also cools.
Tablets to relieve discomfort: Paracetamol and its derivatives Panadol and Efferalgan
Despite the fact that there are a large number of drugs that help in the same way as Paracetamol, but are less dangerous , for some reason many are accustomed to taking this particular medicine.
After taking the medicine, the pain disappears within five minutes .
WHO recommends taking this particular remedy to pregnant and nursing mothers, because it considers it the safest and most effective .
It has been scientifically proven that Paracetamol is safe not only for a young mother, but also for a child .
The taken drug still enters the baby’s body during breastfeeding. Experts say that 8–24% of the maternal dose of the drug can enter the child’s body with milk.
It is better to use the medicine after feeding , because the maximum concentration of Paracetamol in the blood occurs one and a half to two hours after administration.
Rules of application:
- A safe dose for a nursing mother is 325–650 mg , taken at intervals of 4–6 hours.
- Stop taking it immediately when the pain subsides.
- Do not use with coffee or strong tea, so as not to increase the concentration of the drug in the blood.
- Avoid taking the medicine if you are allergic to its components.
- If there is any deviation in the child’s behavior, immediately stop taking Paracetamol.
An alternative to Paracetamol is the soluble analogues Panadol and Efferalgan .
What to do when a tooth hurts while breastfeeding
When choosing medications for toothache, you need to follow simple rules:
- Any medications must be approved by a doctor.
- When deciding to take a particular medicine, a young mother should carefully study the instructions for it and take it only when it says that the drug is approved for breastfeeding.
- Medicines in the form of tablets and injections, which are allowed for a small child, can also be taken by a young mother.
Modern medicine does not stand still. There are certain medications in tablet form that do not harm the child's health. You can also take for toothache .
Painkillers and dental drops
Dental treatment during lactation is usually carried out with the use of painkillers such as Ultracaine or Lidocaine, which are safe during breastfeeding.
Lidocaine is also found in a pain reliever called Kalgel, which is prescribed to children during the teething period.
Therefore, you can be confident in the safety of taking such a drug for toothache. In addition, for severe toothache, you can use dental drops that effectively relieve toothache if you have:
- caries;
- periodontitis;
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis.
Dental drops are absolutely safe during breastfeeding, because their composition is dominated by herbal components : camphor, peppermint and valerian.
Toothache during breastfeeding: how to relieve pain, how to treat?
Few young mothers can boast that their teeth remained healthy after childbirth. Oral diseases begin to bother you from the first months of pregnancy. The main reason is a lack of calcium, which is almost completely removed from the woman’s body for the development of the fetus and strengthening the child’s skeletal system. Toothache is unbearable - it is also dangerous for the little one.
When carrying a baby and feeding, some medications are used to help reduce discomfort. Teeth during pregnancy and after childbirth can and should be treated - it is absolutely safe.
Causes of toothache
During gestation and after childbirth, tooth sensitivity increases. This is due to hormonal changes and the severe stress that a woman receives when a baby is born.
The gums of a nursing mother become irritated and sore, and the body’s recovery occurs only during the two months following childbirth.
It lacks minerals and vitamins, which is why almost all pregnant women and new mothers develop dental problems.
READ ALSO: Do pregnant women have their teeth pulled out using anesthesia?
Pain when chewing, sensitivity to cold and hot food occurs if a tooth is cracked (due to injury). Young women may experience the eruption of wisdom teeth. In any situation, treatment cannot be delayed - the condition of the expectant or established mother is reflected in the child. The infection can be transmitted through breastfeeding, licking a pacifier, and kissing.
READ ALSO: what to do if a tooth cracks vertically?
During pregnancy
Tooth decay or inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is common. Most oral diseases appear in the first trimester and continue to develop after childbirth.
The way the body works completely changes; processes occur in it to which it gradually adapts. At the same time, most vitamins and minerals are delivered to the unborn child, and their absorption by the mother’s organs is reduced.
The main causes of discomfort in the mouth are:
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve,
- failure of the woman’s immune system due to intrauterine growth of the fetus,
- lack of calcium in the blood (it is used to strengthen the baby’s bones at 20-30 weeks),
- severe toxicosis, which promotes the removal of beneficial microelements from the body,
- worsening of untimely cured caries,
- gingivitis and inflammation in the oral cavity.
When breastfeeding
Toothache during breastfeeding can occur for various reasons, including the fact that the mother was afraid to resort to treatment during pregnancy, and the disease of the teeth or gums has reached an advanced stage. The situation is aggravated by the systematic loss of nutrients that are concentrated in milk for feeding the baby. The causes of toothache can be:
- constant stress state,
- thinning of enamel,
- loss of antiseptic properties of saliva that protects teeth,
- inflammation of periodontal tissues,
- incorrect installation of the seal,
- minor gum damage that is susceptible to infection.
How to relieve pain?
A woman is primarily concerned about the baby’s health, but there is no point in enduring unpleasant sensations.
During pregnancy and after childbirth during lactation, some medications are allowed that will help temporarily relieve pain (on weekends, on holidays) if it bothers the mother.
Women often use Analgin, but it is contraindicated during breastfeeding and pregnancy. As soon as possible, you should contact your dentist for treatment. What painkillers can you take?
READ ALSO: Is it possible to treat or remove teeth while breastfeeding?
Drug treatment
Any painkiller during pregnancy can be used after consultation with a specialist. For the expectant mother, Analgin is replaced by a safer drug - Paracetamol, since it does not have a negative effect on the fetus. You can drink No-shpa, Riabal, Papaverine, Ibuprofen.
A nursing mother can use some medications. Panadol and Nurofen are intended for babies, which means they can be taken by women during lactation. They also resort to the use of analogues: Ibuprofen, Ivalgin, Ibuprex. The drugs are available in the form of tablets, ointments, suppositories, and injections.
Is it possible to drink Ketanov while breastfeeding? Painkillers are allowed, but should not be abused. To relieve pain, use local remedies: Lidocaine and Ultracaine. If the gums hurt, mothers can use children's anesthetics: (we recommend reading: what to do at home if your tooth hurts badly?)
- drug Dentol Baby,
- Kamistat Baby gel,
- Kalgel product,
- Chlorhexedine and Furacilin solution are suitable for rinsing.
Ketanov is a strong drug that allows you to quickly relieve tooth pain (we recommend reading: how to use Ketanov for toothache?). It should not be taken more than 2 times a day and it is advisable not to use it for more than three days, like any other means.
Folk remedies
Natural substances are the safest, especially if treatment with traditional methods involves only rinsing the mouth (without ingestion). During and after pregnancy, teeth are treated with decoctions:
READ ALSO: Can teeth be treated using anesthesia during pregnancy?
- 1 tbsp. pour a cup of boiling water over oak bark, boil for 15 minutes, rinse 2 times a day,
- Mix 0.5 cups of water with the juice of half a lemon, irrigate the oral cavity several times a day,
- 1 tsp dissolve soda in 200 ml of water, apply 6 times a day,
- apply a piece of lard (without salt), beets or onions to the tooth,
- use a weak solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) to rinse twice a day.
Painkillers prohibited during pregnancy and lactation
Most medications should not be taken during the first trimester. Painkillers are contraindicated if a woman has chronic diseases. Medicines affect the baby’s endocrine, nervous and cardiovascular systems. The list of prohibited drugs for toothache during breastfeeding and pregnancy includes:
READ ALSO: What painkillers can you take for toothache during pregnancy?
- tablets and injections of Aspirin, Ketorol, Ketorolac (we recommend reading: how to take Aspirin for toothache?),
- Citramon, Analgin and their analogues pills,
- drugs Nimesil, Nimid,
- Phenobarbital and the like.
READ IN DETAIL: cheap tablets for toothache
Dental treatment for pregnant and lactating women
The dentist must be warned about pregnancy, indicating the due date, or notified about breastfeeding. It is advisable to express milk for the baby before performing manipulations in the oral cavity.
For pain relief, the doctor selects drugs that do not penetrate into milk or are released in small doses that cannot have an effect on the child.
You should not be afraid of treatment - this is important both for the mother and for the peace and health of the baby.
Anesthesia
Most of the drugs used by specialists are eliminated from the body 2-3 hours after the injection.
Frequently used medications are Lidocaine and Ultracaine in small doses (up to 2 ml) - they do not penetrate the placental barrier.
The use of drugs with adrenaline is prohibited; implants are not installed during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Anesthesia is given only after 14-16 weeks of pregnancy. Modern local anesthetics are well tolerated.
Features of tooth extraction
Tooth extraction at a special time for a woman is carried out only if conservative methods have not yielded results, and the diseased unit is injured, inflamed and is a source of infection (we recommend reading: how to quickly relieve pain after tooth extraction?).
It is advisable to postpone surgical intervention to the postpartum period, when the operation can be performed under anesthesia and antibiotics can be taken (Amozzicillin, Erythromycin, Cefazolin, etc.).
In this case, means are used that allow the mother not to take a break from breastfeeding.
X-ray
A pregnant woman need not worry if she has been prescribed a dental x-ray. Fetal development defect is possible in 4-5% of cases with 1 rad irradiation. To receive this dose you need to go through the procedure multiple times.
However, doctors will insist on taking an image only if the patient’s condition is extremely serious. Today it is possible to use an electronic radiovisiograph, in which the radiation exposure is many times lower than in a classical device and is close to the background radiation.
The impact lasts several seconds, and the beam passes exclusively through the tooth, without spreading to other tissues.
Doctors often hear from mothers before an x-ray: “I’m breastfeeding and I’m afraid that the milk will disappear or I’ll pass on radiation to the baby.” During lactation, this procedure is completely harmless. Many women note a decrease in milk production after it, but this is a short-term phenomenon.
Preventive actions
It is better to solve all health problems before conception. At this time, fissure sealing, fluoridation and oral care can be performed. Due to the likelihood of dental diseases, it is worth carrying out prevention:
- visit the dentist at 6-7, 16-18, 26-28 and 36-38 weeks to monitor the condition of the enamel and gums,
- use a paste to strengthen the gums and a product with minerals,
- adhere to a nutritious diet with a minimum of sweets, do not eat hot or cold food,
- brush your teeth 2 times a day, rinse your mouth with water after each meal,
- add foods containing large amounts of calcium to your diet.
Loading…
Source: https://spacream.ru/stomatologiya/kakie-obezbolivayushhie-mozhno-prinyat-ot-zubnoj-boli-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii
Treatment procedures
The cause of toothache in a nursing mother can be a chronic lack of calcium in the body. And the associated premature destruction of dental tissue. According to Yakov Yakovlev, a member of the AKEV medical council, the situation is typical for young mothers who did not pay enough attention to a proper diet during pregnancy.
“If calcium deficiency has formed in the body during pregnancy, it will only progress during lactation,” comments Yakov Yakovlev. — A woman should definitely take medications containing calcium and vitamin D3. Dietary supplements will not help, since they contain the minimum recommended dose to eliminate the risk of deficiency of essential substances.”
However, toothache during lactation can occur in the absence of calcium deficiency. If the mother watches her diet, eats enough dairy products and fresh vegetables, the cause of the disease is probably different.
The following factors can provoke a painful symptom:
- damage to hard or periodontal tissues, which stimulates the inflammatory process in the jaw and surrounding soft tissues;
- reflex effect on the jaw in case of abnormal pathological bite;
- caries with destruction of tooth tissue and the formation of an inflammatory cavity;
- a complication of caries with inflammation of the deep layers of the tooth (pulpitis) or the tissues surrounding the root (periodontitis).
In each case, toothache during breastfeeding is pathological in nature, that is, it will not go away without treatment. Any measures taken, even if they bring relief, are only temporary. Therefore, an urgent visit to the dentist if pain in the oral cavity occurs is mandatory for a nursing mother.
The risk of delaying treatment is the possibility of inflammation spreading to the tissues of the jaw, skull, and brain area. Self-medication and waiting for an “opportunity” are unacceptable if the painful condition is accompanied by an increase in temperature, the spread of pain, or a deterioration in the general condition. In the latter case, the woman may be indicated for inpatient treatment.
First aid
It is important to know and use the rules of first aid if your tooth hurts or aches during breastfeeding in the evening, at night, and there are still several hours before visiting the dentist. In this situation, you can use rinses and painkillers that will alleviate the condition.
Pills
They are not used for dental treatment during lactation, but for temporary relief of pain. Standard painkillers that have minimal effect on the child’s body are recommended.
Tablets with proven safety - paracetamol and ibuprofen, approved for use in infants.
They enter the baby's body through breast milk in a minimal amount that cannot cause negative reactions. Paracetamol is effective for up to six hours.
Ibuprofen has an anti-inflammatory effect and works for up to eight hours. The drugs should be taken in standard dosage for adults.
Rinse
It is allowed to use local agents that have an antiseptic and analgesic effect. Rinsing will help reduce the fullness of the carious cavity, if it is open, or clean the gums from accumulated food debris and pus.
Rinsing teeth is allowed in dentistry during breastfeeding, since the drugs are not swallowed, but spat out. The doctor may recommend them as an addition to the main treatment to speed up recovery.
As first aid, you can use ready-made solutions or make them at home.
- "Furacilin" ("Nitrofural"). Broad-spectrum antiseptic, inhibits the growth of microbes, used to cleanse wounds. Dissolve four tablets in a glass of warm water, rinse your mouth regularly, every one and a half to two hours. Rinsing with Furacilin is especially effective for inflammatory gum diseases.
- Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). Prepare a weak solution of two manganese crystals in a glass of warm water. Treat the affected area regularly.
- Hydrogen peroxide. Serves as a complete alternative to potassium permanganate. Use a three percent solution for periodic rinsing. Do not rinse your mouth with peroxide often, as it worsens the condition of tooth enamel.
- Chlorhexidine bigluconate. A modern, safe antiseptic in the form of a ready-made solution. Does not have a negative effect on tooth enamel, reduces the intensity of the development of microbes and bacteria.
Even if rinsing brings relief within one evening, do not delay visiting your doctor. The toothache only dulled when feeding the baby, and without eliminating the problem it will return in a few days.

During breastfeeding, a full list of dental procedures is allowed. They are local in nature, so they do not have a pronounced effect on either the mother’s body or the child’s body. It is only important to warn your doctor that you are currently breastfeeding. And the specialist will select drugs that are compatible with lactation.
Anesthesia
The use of local anesthetic drugs is a generally accepted requirement of modern dentistry. They reduce the psychological stress of the patient, who does not develop a “fear of dentists” complex, and eliminate physical discomfort.
A young mother should not refuse the anesthesia recommended by the doctor when deciding how to treat toothache while breastfeeding. Medical manipulations “live”, according to experts, cause much more harm to the baby than the residual amount of the drug in the milk.
The fact is that during tooth treatment without anesthesia, the hormone adrenaline is produced in a woman’s body. It causes vasospasm, which disrupts the natural level of lactation. Adrenaline remains in the blood and milk for a long time, causing emotional stress and nervousness in the child.
Safe painkillers during lactation for toothache and for medical procedures are the drugs “Lidocaine”, “Ultracaine”.
- "Lidocaine." Fully compatible with breastfeeding, according to the international drug directory E-LACTANCIA. A small amount is excreted into breast milk. Within two hours, 98.5% of the initially administered volume of the substance will remain in the mother’s body. As a local anesthetic it has minimal absorption. Therefore, it is allowed to be used as an anesthetic in the composition of children's gels recommended for painful teething. Compatibility with lactation has been confirmed by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
- "Ultracaine" ("Articaine"). A drug similar in chemical structure to Lidocaine. Is compatible with breastfeeding in dental practice. It is characterized by almost zero absorption in the body and a short half-life.
The drugs “Lidocaine” and “Ultracaine” allow us to solve the problem of how to anesthetize medical procedures without risk to the baby. Provided there is no individual intolerance, dental treatment during breastfeeding becomes painless and completely safe.
If necessary, the doctor may recommend additional diagnostic and treatment tactics. The following are recognized as fully compatible with the lactation period:
- X-ray of a tooth during breastfeeding - does not affect the quality and production of milk;
- arsenic, antiseptic pastes - have a local effect and do not enter the systemic bloodstream.
If you follow the doctor's recommendations for additional treatment and the frequency of visits, therapy brings rapid relief and complete recovery. In some situations, when the inflammatory process cannot be eliminated with local remedies, the doctor recommends taking antibiotics.
When treating a number of penicillins (natural and synthetic) with antibiotics, there is no need to interrupt breastfeeding. Such drugs include Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav and others.
Antibiotics from the cephalosporin group (Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin, Cefepime) and macrolides (Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin) are considered relatively safe.
Their use is permissible during breastfeeding.
Dental treatment while feeding a child requires an individual approach from a doctor. But the availability of a large number of modern drugs for anesthesia and antibiotic therapy eliminates the danger for the baby and makes the treatment comfortable and painless for the mother. The sooner it is started, the less risk of complications there is, and the sooner recovery will occur.
Dental disease during lactation is caused by the following problems in the oral cavity:
- caries, periodontitis, gumboil;
- incorrectly installed seal;
- the integrity of the enamel is damaged;
- the root part of the tooth is exposed.
All these diseases require timely treatment, because if there is caries, the mother can transmit the infection to the child through a simple kiss. The problem of advanced caries will not go away on its own; it must be treated. You shouldn’t let dental diseases reach an advanced stage.
If a toothache occurs suddenly, you need to decide what can be used and in what way.
Proven folk remedies:
- Brush your teeth, rinse with a solution of soda. You can use a saline solution. For 200 mg of water, a teaspoon of salt or soda.
- A decoction of medicinal herbs will help relieve pain: chamomile, calendula.
- For inflammation of the gums, furatsilin solution helps well. Mix 4 furatsilin tablets in a glass of water and rinse every 2 hours.
To prevent caries, it is necessary to replenish the amount of calcium in the mother’s body. In addition to vitamins, during the lactation period a woman should eat more dairy products: kefir, milk, cottage cheese. You must first check your child for allergies to dairy products.
Toothache in a nursing mother: treatment cannot be tolerated
Dental treatment while breastfeeding is not only allowed, it is necessary. Cavities grow larger over time and become a source of infection.
Teeth tend to decay during lactation, and dental pathologies progress rapidly. The earlier it is treated, the lower the risk of complications.
If you put off going to the dentist for fear of harming your child, you may eventually lose a tooth.
How to relieve pain before visiting a doctor
Toothache during breastfeeding often becomes the reason for a visit to the dentist. Many women put off going, even if they know about tooth decay.
Having waited until pain occurs, mothers grab medications. In this case, the usual Analgin and Citramon will not work. These tablets are contraindicated as they can harm the baby.
The list of prohibited medications includes Aspirin, Nimesulide, Ketorol and others.
The best pain reliever for toothache is treatment. If your tooth hurts on weekends or holidays, you can take approved medications. They will eliminate unpleasant symptoms, but will not solve the problem. Therefore, one way or another, when a tooth hurts while breastfeeding, you will have to consult a dentist.
You may take safe medications prior to your consultation. For hepatitis B, this is Paracetamol or Ibuprofen, as well as their structural analogues. A nursing mother can take any medicine that is allowed for children: Nurofen, Panadol.
In this case, the age dosage should be observed. Sometimes women take approved medications in pediatric doses, but do not get results.
If you need to relieve pain once, it is better to use an adult portion of the medicine - Ibuprofen 200-400 mg or Paracetamol 500 mg.
Frequent rinsing with Furacilin solution helps get rid of pain. You can use warm water with the addition of soda and salt. During rinsing, food debris is washed out of the cavity. After eliminating the irritant, the pain subsides.
Traditional medicine suggests using chamomile decoction or saline solution with the addition of a few drops of iodine. It is better to discuss this treatment regimen with your dentist first, since chamomile and iodine can cause allergies.
To numb the tooth and hold out until a visit to the doctor, you can use children's gum gel , for example, Kamistad. In case of acute pain, it is permissible to treat the cavity once with a solution of Ultracaine or Lidocaine.
Dental treatment for nursing mothers
Obviously, breastfeeding can treat your teeth. It’s worse when a woman puts off going to the doctor, even if she knows about caries. During breastfeeding, mothers experience enamel destruction.
Even a small hole can lead to the formation of a large cavity. A preventative examination should be carried out at least once every six months in order to find out about the problem in a timely manner.
In the initial stages, caries treatment is painless and does not require the use of medications.
If a tooth begins to hurt during lactation, then its damage is deep. Pain is associated with nerve inflammation or damage to the hilar (periapical) tissues. This condition cannot be ignored. Over time, the pathology will progress and lead to tooth loss. Moreover, the pain is difficult to bear. Torment causes stress in a nursing woman, which can lead to decreased milk production.
Toothache during breastfeeding: how to relieve pain so as not to harm the baby?
Due to hormonal disruptions and serious physiological stress during pregnancy, a woman’s teeth after childbirth are weakened. The body is exhausted and unable to resist harmful microorganisms. As a result, teeth are susceptible to caries much more often after childbirth than before.
Ordinary people have the opportunity to relieve pain and general condition with various medications, but most analgesics are contraindicated for young mothers during breastfeeding.
What to do if you have a toothache while breastfeeding? What painkillers can I take? We will now consider the answers to these questions.
Features of taking painkillers while breastfeeding
For a woman nursing a baby, it is undesirable to use medications, including analgesics. Sometimes situations arise when the painful sensations are so strong that it is impossible to endure. In particular, toothache. The best way to get rid of it is to visit a dentist, but it is not always possible to quickly get to a clinic.
In such cases, it is allowed to use analgesics, following the recommendations for taking medications:
- when choosing a pain reliever, consultation with a doctor is required;
- it is necessary to carefully study the instructions for the drug, pay special attention to the paragraph on use during pregnancy and lactation;
- do not exceed the dosage specified in the instructions for the medicine;
- remember that even approved drugs, one way or another, have a negative effect on the child, so they must be used carefully;
- When using an analgesic, monitor the baby's reaction.
There may be cases when taking the drug is necessary, but it is undesirable due to its passage into milk.
In such situations, after using the medicine, pumping is carried out, taking into account the time the active substances enter the blood (from the instructions).
If after giving birth your mother has inflammation of the gums, a tooth is cracked and hurts, or there is bad breath, you should not delay visiting the doctor and treat any problems that have arisen without delay.
Approved drugs
There are no painkillers that are completely safe to take during lactation. You can relieve pain with conditionally approved analgesics, with the use of which the expected benefit for the mother is high, and the potential risk for the child is minimal. Such means include:
- Paracetamol and its analogues (Efferalgan, Rapidol, Milistan, Panadol, Paralen, Apap light). The drug is most often prescribed to mothers, since the risk is relatively minimal. There is a certain rule for taking it during breastfeeding - during or immediately after feeding. The maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is reached 30 minutes after administration, the active substances are completely eliminated from the body within 4 hours. By the time of the next feeding, a small amount of active substances (about 0.5%) will remain in the blood, which will not be dangerous for the baby. Just in case, you can express a little milk before using the medicine so that you can feed the baby until the drug is completely removed from the body. When taking paracetamol, you need to take into account that this drug contains additional substances that may be contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation. For example, Paracetamol from certain pharmaceutical companies contains Povidol, which is prohibited for a nursing mother.
- Ibuprofen (Nurofen, Ibuprom) is prescribed during breastfeeding as an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic agent. It is allowed because it passes into milk in small quantities without causing any particular harm to the baby. The drug is taken immediately after eating and feeding the baby. It is advisable to express milk for the next feeding, since the highest concentration of active substances in the blood is achieved 1.5-2 hours after taking the drug.
For example, Nurofen-Plus is the same as Ibuprofen, but each tablet contains 8 mg of codeine, which is strictly prohibited during lactation.
Many people recommend Ketorolac, Ketorol, Ketanov and Naproxen.
However, the instructions for these drugs indicate that they are contraindicated during lactation and their use is possible only when prescribed by a doctor, when the benefit to the mother outweighs the negative effect on the child. But not every mother will agree to improve her well-being at the expense of the baby’s health. It is better to drink not Ketanov, but Ibuprofen or Paracetamol.
When treating teeth, it is allowed to use painkillers - Lidocaine and Ultracaine (more details in the article: how is dental treatment performed while breastfeeding?). When using other anesthetics, it is advisable to express milk.
What painkillers should not be taken during lactation?
Most analgesics are contraindicated during breastfeeding, as their use can cause irreparable harm to the baby's health. Let's look at strictly prohibited painkillers during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Acetylsalicylic acid. All medications that contain it (Aspirin, Citramon, Citropak, Askofen, etc.) are prohibited for use during lactation. When used by the mother, the child may develop the following diseases:
- bronchospasms;
- asthma attacks (with a tendency to allergies);
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- liver dysfunction and acute liver failure;
- the risk of Reye's syndrome, in which the child experiences cerebral edema.
Analgin. Drugs based on metamizole sodium (Analgin, Baralgin, Andipal, Pentalgin, etc.), prohibited in a number of countries around the world, when used during lactation, can become a source of the following negative consequences:
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines;
- dysfunction of the bone marrow;
- disruption of the kidneys and liver (most often occurs in infants who have taken Analgin with milk);
- allergic reaction - from skin manifestations (hives, red spots, peeling) to anaphylactic shock;
- spasms of the respiratory system;
- blood diseases (for example, Analgin causes agranulocytosis, which is characterized by a high percentage of deaths or serious complications).
Codeine. By itself, it is not used as an anesthetic for toothache, but is contained in many drugs (Solpadein, Nurofen Plus, Pentalgin-N, Sedal-M, Caffetin).
Under the influence of enzymes, codeine is converted into morphine and enters the mother's blood and milk. The effect of the substance is quite toxic.
Morphine can cause increased drowsiness, arterial hypotension, severe difficulty breathing, indigestion in a child, and in clinical cases, acute respiratory failure with a fatal outcome develops.
Prevention of toothache in nursing mothers
After pregnancy and childbirth, it is necessary to restore hormonal balance and not lose teeth. Prevention rules include:
- brushing your teeth - at least twice a day, for 3 or more minutes without violating the technique of the process;
- the toothbrush should be of medium hardness and changed every 2-3 months;
- To remove food debris between the teeth, dental floss and a special mouthwash are used;
- Do not use toothpicks after meals;
- professional teeth cleaning with tartar removal and remineralization, if the enamel is weakened, is carried out 2 times a year;
- preventive examinations at the dentist at least once every 3 months;
- The daily diet of a nursing mother should include foods enriched with calcium and the required amount of microelements and nutrients.
Source: https://AzbukaZubov.com/stomatolog/bol/zubnaya-bol-pri-grudnom-vskarmlivanii.html
How to choose painkillers for nursing mothers?
Toothache during breastfeeding most often occurs due to the fact that the expectant mother did not cure all dental problems before pregnancy. But you are not here to find out what needed to be done, but to find out what painkillers the mother can take to numb problem teeth.
Yes, the surest way is to take painkillers. Almost all of them are able to relieve pain during lactation, however, not all are safe. Now let’s figure out what pills you can take to soothe a toothache and not harm your baby, and what alternative exists in folk medicine.
What to do if it is not possible to urgently visit a doctor? A toothache can strike at the most inopportune moment: at night or when it is not possible to leave the child and go to the doctor. In this case, you can take a painkiller tablet approved for young mothers. The main thing is to follow several important rules.
A nursing mother should take medications for toothache correctly and only after consulting a doctor. Some women try to relieve unpleasant pain with the first medicine they find in the medicine cabinet, although not all pills are compatible with breastfeeding and can harm the baby through milk. Before use, be sure to read the instructions.
Do not exceed the dosage. The painkiller is taken once, in rare cases several times a day, but with a mandatory interval of 4–5 hours.
When breastfeeding, the following groups of medications are clearly permitted.
Paracetamol and its derivatives with other commercial names - Panadol, Efferalgan, Acetaminophen.
Paracetamol Panadol Efferalgan Acetaminophen
Ibuprofen (MIG 400, Nurofen), as an antipyretic and analgesic. For constant and severe pain, they can be taken 4 times a day or every 3 hours.
Ibuprofen MIG400 Nurofen
Lidocaine and Ultracaine are local anesthetics that are used as injections only. They can be placed 2-3 hours before breastfeeding or immediately after. In some situations, the drug can cause allergies and increased nervousness in the child due to the penetration of active substances into milk.
Lidocaine Ultracaine
Diclofenac, Ortofen, Voltaren, as drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the concentration of which after getting into milk for 1-2 hours is minimal.

Diclofenac Ortofen Voltaren
Despite the low concentration of the active substance already 1 hour after administration, during lactation it is strictly forbidden to use painkillers based on metamizole - Analgin, Baralgin, Spazmalgon.
Analgin Baralgin Spazmalgon
Some other drugs are also prohibited:
- Tempalgin;
- Nimesulide;
- Nise;
- Nimesil.
Tempalgin Nimesulide Nise Nimesil
Before taking any medication, it is best to consult your doctor. Since it is not always possible for a young mother to see a doctor promptly, it is worth discussing the list of acceptable medications in advance with a specialist upon discharge from the maternity hospital or with the pediatrician supervising the baby.
Folk remedies are very popular among nursing mothers. To soothe a sore tooth, you can try one of the following recipes:
- mix salt with soda (1 tsp per 1 glass of warm water) and rinse your mouth up to 6 times a day;
- pour oak bark with water (in the proportion of 1 tablespoon of product per 1 glass of boiling water), heat in a water bath for 15 minutes and rinse your mouth after each meal;
- for inflammation, you can treat your mouth with Chlorhexidine or Bigluconate;
- rinse with a weak solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide;
- dilute Furacilin for rinsing (3 tablets per glass of water).
Oak bark in a water bath
If an attack of pain occurs at night, it is better to immediately rinse your mouth with plain water or infusion of chamomile or oak bark. This will stop the inflammatory process and minimize toothache.
The use of folk remedies also requires prior consultation with a specialist.
Of course, the best measure for toothache while breastfeeding is to take preventive measures. To do this, experts recommend adhering to the following rules:
- use high-quality toothpaste;
- rinse your mouth with warm water after every meal;
- do not abuse sweets (especially candies, caramel, etc.);
- Avoid eating too hot, cold or spicy foods;
- adjust your diet, add more foods containing calcium;
- undergo preventive examinations with a dentist at least twice a year;
- Be careful with painkillers.
When breastfeeding, some women experience increased swelling of the mucous tissues and bleeding of the teeth. This is due to changes in hormonal levels, lack of vitamins, calcium and microelements. With proper support from the body, negative manifestations can be stopped at the initial stage.
Toothache in a nursing mother is not a reason for self-medication! Unknown painkillers for toothache while breastfeeding can harm the baby and lead to poisoning of the fragile body.
Modern methods of pain relief can be used for breastfeeding, so there is no need to delay treatment or even tooth extraction until feeding is completed. Most importantly, do not forget to inform your doctor about your situation in advance.
Toothache during breastfeeding: causes, ways to relieve pain
If it is necessary to get rid of a toothache, it is customary to use painkillers, since toothache cannot be tolerated.
But what if acute toothache occurs during breastfeeding? What will help relieve pain in a tooth or gum and how safe is it for the baby’s health? Almost every nursing mother turns to dentists with these questions, because not everyone had the opportunity to have their teeth treated during pregnancy, and the causes of pain can be different. Even a mother who carefully monitors her health is not immune from the loss of an unsuccessfully installed filling or thinning of the enamel, since her body is under a lot of stress.
The causes of toothache are always varied, and no one, even the most careful nursing mother, is immune from them.
Why does toothache occur during toothache?
When a toothache occurs during breastfeeding, the first question that arises is: why does the tooth hurt? The answer is obvious - after childbirth, the female body does not recover immediately, hormones return to normal, the nursing mother experiences stress, and in parallel with the lack of useful microelements in the mother’s body, the sensitivity of the teeth increases. This is why during lactation women often turn to dentistry, especially in the first couple of months. And the causes of toothache are always varied:
- advanced caries, which a pregnant woman for some reason did not cure;
- A nursing mother can inherit oral diseases from her baby, for example, stomatitis, which often occurs in infants;
- minor scratches or damage with a weakened immune system can lead to gum inflammation, causing a lot of inconvenience;
- outdated or incorrectly placed seal;
- thin tooth enamel, as well as inflammation of the tissue directly at the roots of the tooth.
What will help relieve pain at home?
Absolutely every person uses painkillers for toothache, the only thing is that when breastfeeding, the list of such drugs is much smaller. No one dares to say that a nursing woman must endure debilitating toothache; usually there is no question of whether to take medicine or not. The question arises - what are the best painkillers to take?
Painkillers prohibited during hepatitis B
No matter how leaps and bounds modern medicine moves forward, most painkillers are still prohibited for use in cases of guards. First of all, these are products containing:
- Acetylsalicylic acid, which is strictly prohibited during breastfeeding, can even lead to problems in the development of the infant or provoke acute liver failure;
- Analgin - is part of such drugs as Baralgin, Pentalgin, has an extremely negative effect on internal organs, especially the kidneys and liver, and also causes inflammation of the stomach;
- Codeine, in its pure form, is rarely used for dental pain relief, but is contained in Nurofen Plus, Sedal-M. During the digestion process, it turns into morphine and negatively affects the health of the mother and baby - from increased drowsiness to difficulty breathing.