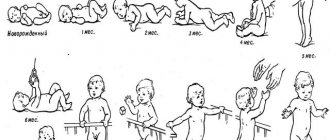
Baby development at 4 months
A four-month-old child continues to actively learn about his own body and improve his skills in mastering it.
Motor skills
- At this age, the first physiological curve of the spine should already be formed - cervical lordosis. Outwardly, this is manifested by confidently holding the head.
- As the second curve develops, the baby becomes more mobile, lifts his head from a position lying on his back and stomach, and can lean on his forearms.
- Most children have already mastered all the options for turning the body: on the back, on the tummy, on the side and in the horizontal plane.
- Some particularly nimble children use new skills to move in a chosen direction or even attempt to crawl.
- It is possible that a small person may try to sit or even stand up by grabbing and pulling himself up on the bars of the crib, but at such a tender age these skills are optional and quite rare.
Important! You cannot sit your baby down until he starts trying to do it himself. There is also no need to fix the sitting position: the ability to sit down and the ability to hold the body in this position are different things, the baby himself changes the position, focusing on his own sensations.
Attitudes towards the new capabilities of one’s own body are also very different. The child can begin to use them at every suitable occasion and violently protests against attempts to restrain his activity, but it also happens the other way around. Having made sure that everything is working out for him, the little thinker will plunge into long thoughts about whether it is worth doing “this nonsense.” Several weeks or even months may pass between the actual mastery of a skill and its active practical application.
The pace of a child’s physical development is very individual: some develop as if consulting a pediatric textbook, others move according to their own, sometimes very non-standard, schedule. It may be that the baby is already making attempts to sit and crawl, but does not know how to roll over and learns this much later than average. If the baby is completely healthy, there is no need to worry. Also, you should not compare the child’s skills with the skills of any other peer, including siblings and brothers, and, moreover, you should not try to force events at all costs.
Important! There are still no fundamental differences in the development of girls and boys in this period. The pace of development of the baby largely depends on the state of health, heredity and mother’s attention.
Cognition of the surrounding world (perception)
- The baby's vision gradually becomes sharper, and the world around him becomes wider. The child is already able to clearly distinguish objects located at a distance of more than a meter and focus his gaze on particularly interesting details. At this age, children begin to distinguish different shades of familiar colors and consciously examine the details of the situation. A change of scenery and the appearance of new objects in the nursery evoke strong emotions. At this age, the baby can already begin to show books with large, bright drawings.
- The grasping reflex is replaced by a conscious choice, capture and still awkward manipulations with the object of interest. The baby takes the toy, “tests it”, shakes it, examines it. A very correct decision is to offer the baby rubber squeaky toys.
- Babies already grasp the simplest cause-and-effect relationships and remember the sequence of actions. For example, when changing clothes, a child can “hand” a clean diaper or some clothes to the mother. Such actions can and should be encouraged, turn to the child with a request, and praise him if he manages to “fulfill” it. The presence of feedback stimulates the physical, mental and intellectual development of the baby, enriches his passive vocabulary.

Speech development
- A four-month-old baby distinguishes familiar sounds well, actively reacts to them, melodiously “sings along,” chanting individual syllables.
- At this age, the first attempts to imitate the facial expressions and intonations of adults appear. Children experiment with intonation and timbre of their voice, repeating the same syllables for a long time.
- Babies can already engage in dialogue and make different sounds in response to what their mother says. The more the mother talks to the child, the more actively the development of speech occurs.
Emotional development
- At four months, a little person discovers new ways of communication, and the range of emotions expands sharply. Children express their attitude to what is happening by changing their intonation or some specific sound, smiling, or active movements. Laughter is not a necessary reaction for this age, and if the baby already knows how to laugh, this is considered an advance in development.
- One of the signs of normal development of a small person is an emotional motor reaction to music. Hearing his favorite melody, the baby waves his arms and legs, laughs or makes other sounds. The same reaction is caused by the voice of mom or dad.
- People whom the child rarely sees are perceived by him as strangers, even if it is his dear and loving grandmother. Children react to guests in different ways: some willingly go to the arms of almost any person (in the presence of their mother, of course), some are selective, some perceive any manifestations of attention from third parties with hostility. Strange as it may seem at first glance, the little person’s opinion must be respected and given time to get used to the stranger.
- The baby is already reacting to the reflection in the mirror and can make faces at his own reflection. He shows the first signs of a sense of humor - the child can already be made to laugh.
Surprisingly, at such a young age a person is already able to remember particularly vivid or repeated events. There are cases when, at the age of two or three years, children described in some detail individual episodes of their infant childhood.
In the first years of life, physical and mental development may occur unevenly: breakthroughs in one area sometimes slow down the development of another. This can be noticeable from the age of three months, but over time the emerging gaps level out.
Video recommendations on the development of a 3-6 month old child from neurologist M. A. Krasnova.
Video calendar of child development from 4 to 5 months
Child's health
Fourth month: visit to the local pediatrician
As always, the doctor checks the physiological state of the child: his general mental and physical condition, his development and new skills (described above), the state of his immune system, his size: the average height of a baby at four months is 62 cm, weight is about 6 kg , and the skull circumference reaches approximately 41cm.
The doctor again evaluates the functioning of all major organs and systems (cardiac, respiratory, vascular systems), checks for anomalies that may indicate any pathology.
Then, as always, the doctor asks the mother (and father, if present) about their relationship with the child. This is done in order to assess how parents are coping with their task, as well as to advise them and answer their questions.
Vaccinations
If you follow the national immunization schedule, your baby should receive a second vaccination against diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus and polio at four and a half months. If you want to reduce the impact of the vaccine on your child's body, try to follow the schedule.
Monitor closely for adverse reactions
Be careful: if after the first vaccinations your baby develops eczema, ENT complications, digestive difficulties, sleep problems, etc., or if he suffers from even a minimal infection at the time when the vaccination is due, postpone it. Consult your local pediatrician or homeopath and wait until the child’s body returns to normal; Give your baby the vitamins that suit him. Then, when the problem is resolved, continue with the vaccination, but proceed very carefully and do not forget to use homeopathic remedies.
How to work with a child
The process of child development is ongoing, from birth, so it is important to devote time to a variety of activities and games with the baby, including them in everyday communication.
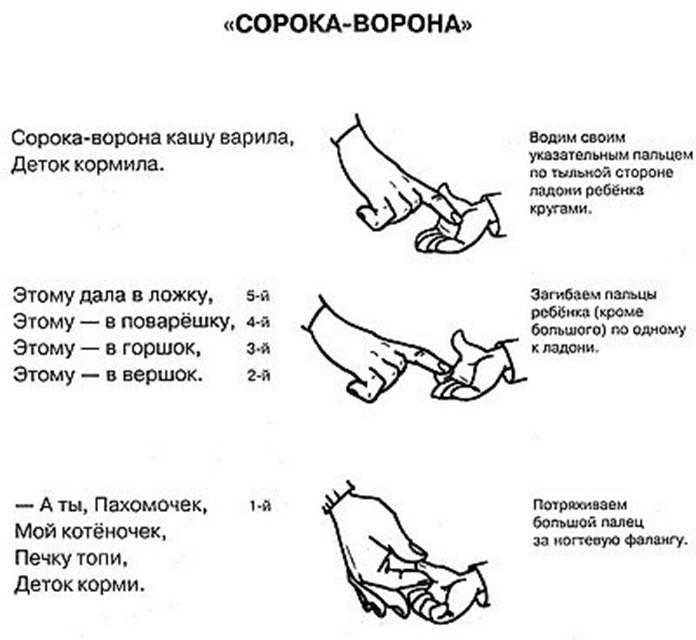
Finger games
In addition to the simplest hide and seek behind a diaper, leisure time can be diversified with finger games.
Toys
To develop the volitional sphere and coordination of movements, a little person can be offered to take two different toys at once. You can show your child how a toy on wheels rolls down an inclined plane. Such games stimulate the development of logical thinking. At this age, you can already try using educational mats for your child’s development.
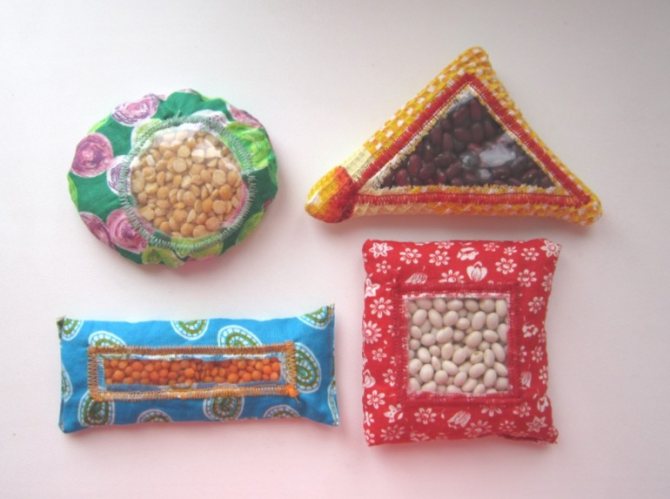
Magic bags
Tactile sensations are very important. For your baby, you can sew small bags from different materials and fill them with different types of cereals. Exploring materials of different textures develops fine motor skills, which will further accelerate the development of speech.

Enriching vocabulary through communication
The child’s passive vocabulary is constantly expanding and the more you talk to him, the faster the baby will begin to understand his mother. When changing clothes, bathing, feeding, you can and should comment on your actions, name the objects or parts of the body involved. When addressing a child, slightly exaggerated intonations and emotions are desirable, as well as clearly defined pauses between phrases. At four months, a little person is already able to “carry on a conversation” by making certain sounds and combinations of sounds. You can ask your child to show him where his favorite toys are, certain parts of the body, well-known objects, and be sure to praise him when he manages to respond correctly to a question.
Listening to music
Listening to children's songs and classical music, playing games with imitation of different sounds is very useful. If the child makes any sounds, the mother can repeat them, building a dialogue with the baby.
Video recommendations on educational toys for children 3-6 months old by neurologist M. A. Krasnova.
When baby is awake
As soon as a child has an object in his hands, he looks at it for a short time, and then always tries to put it in his mouth. In addition, the baby may begin to salivate profusely. The first tooth usually appears only at five to six months, but some children begin to feel the teeth pressing on the gums from the inside as early as four months.
The baby discovers his own hands and feet, which are objects of tireless admiration for him; Now he can play on his own. He begins to make articulate sounds: “ma-ma” or “pa-pa” (however, he does not yet associate these sounds with his parents); he can already imitate the sounds that others make. The child begins to understand cause-and-effect relationships - for example, the connection between pressing a button and the fact that after that the light comes on or the music plays. Among other things, at this time he may begin to react a little more “unsociable” to strangers.
If something went wrong
Young mothers are recommended to keep diary entries and record the baby’s achievements. Firstly, using the records it is easier to determine how age-appropriate the baby’s development is and, if necessary, remember important details. It should be noted that pediatricians really do not like non-standard options for developing certain skills in children, and official entries in the cards do not always correspond to the actual state of things. Secondly, these recordings will give a lot of sweet memories years and decades later.
If the baby does not have any pathologies, but he still does not know how to do something, this is not yet a reason to panic. Sometimes in such cases it is enough to give the child a little more attention.
The following developmental deviations should be considered a cause for concern:
- lack of interest in toys;
- lack of reaction to sounds and the approach of parents;
- lack of pronounced emotions;
- wandering gaze and uncoordinated eye movements;
- a smile unrelated to what is happening;
- decreased physical activity;
- inability to hold the head;
- no buzzing.
If your baby notices at least one symptom from the list, you need to consult a pediatrician. It is better to make sure that the problem is relatively easy to correct and eliminate it in time than to miss the early signs of serious pathologies.
What should a premature baby be able to do?
Babies born prematurely at 4 months are still noticeably behind the average level of development of their peers. The delay depends on the degree of prematurity. Among pediatric neurologists, it is common practice to take as a starting point not the actual date of birth, but the day when he was supposed to be born. That is, the adjustment to the actual age can be quite large, but there are simply no general norms for the rate of development.
If the child was born about a month prematurely, you need to focus on the level of development of three-month full-term children. The development of babies born two months earlier is compared with the skills of two-month-old babies, and so on.
Table of weight and height gains in premature babies
| Degree of prematurity | |||||||
| IV (800-1000 g) | III (1001-1500 g) | II (1501-2000) | I (2001-2500) | ||||
| Weight, g | Length, cm | Weight, g | Length, cm | Weight, g | Length, cm | Weight, g | Length, cm |
| + 600 | + 3,5 | + 600-700 | + 3,7 | + 600-900 | + 3,8 | + 700-900 | + 3,3 |
Some of the most common skills for premature babies include:
- ability to voluntarily fix gaze;
- hold and lift the head;
- the children start to play;
- Many people are able to react to their mother’s approach with a meaningful smile.
What should a baby be able to do at the beginning of the 4th month?
A four-month-old baby, almost all the time when he is not sleeping or eating, tries to communicate with others, babbling individual sounds and syllables. Among all the sounds pronounced by the baby, adults with emotion highlight such syllables as: “ma”, “pa”, “ba” and “da”. However, you should not place high hopes on them: the first meaningful word will come later.
- By the way, it was noticed that until the 4th month, the sounds that babies make all over the world are approximately the same. But starting from the 4th month, babies begin to imitate exactly the language spoken by the people around them. Therefore, talk to your baby as much as possible - this will be very useful for developing his speech skills.
At this age, the child can distinguish familiar sounds from unfamiliar ones, including voices. Hearing an unfamiliar voice, the child becomes wary and may even cry. He is already responding to his name. He does not express any special emotions, but usually turns his head towards the one who calls him by name.
At this age, the child already develops his first preferences: he has favorite and unloved toys. The baby will quickly explain to you what's the point of crying indignantly if you don't give him the toy he likes or take it away.
The digestive system has already developed well enough that the baby is much less bothered by colic. After 4 months, he has already become so comfortable that when feeding he can play with his mother’s breast and press on it if the milk flows slowly.