A sharp decrease in a woman’s immunity after childbirth makes her body vulnerable to various pathologies. Pathogenic microflora receives all the conditions for active reproduction. Therefore, postpartum infections are widespread. One of them is thrush. The disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida. In addition to its vaginal form, women quite often encounter breast thrush during breastfeeding. The causes and treatment of this pathology will be discussed in today's article.
Medical certificate
Thrush or candidiasis is a disease caused by the activity of fungi of the genus Candidae. They are present in the body of absolutely healthy people. However, under the influence of certain factors, they begin to multiply at an accelerated pace, causing symptoms of thrush. The disease can affect both a woman, a man, or even a child. The favorite location of the fungus is warm and moist places, such as the mouth or vagina.
During lactation, it primarily affects the mammary glands. In this case, unpleasant sensations arise in the nipples and milk ducts. If left untreated, the disease can harm both the woman and the newborn baby.
Features of diagnosing thrush
The diagnosis is clarified by visual examination of the mammary gland and collecting a pathological history. The presence of the disease is confirmed by laboratory tests necessary to correctly identify the type of pathogenic organism. Laboratory diagnostics involves taking:
- Nipple swab.
- Clinical blood test.
- Glucose test.
In addition, an immunogram may be required. You should definitely discuss with your gynecologist the possibility of not interrupting breastfeeding.
Main reasons
The causes of mammary thrush during breastfeeding are varied. Most often, the disease develops against the background of decreased immunity and disruption of the microflora in the affected area. Such disorders usually occur due to hormonal imbalance. It, in turn, is a consequence of the processes of bearing a child and giving birth.
There are other reasons that cause pathology:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- treatment with glucocorticoids;
- progression of chronic diseases;
- increased skin moisture.
Breast thrush during breastfeeding often develops in women suffering from metabolic disorders in the body due to diabetes, obesity or anorexia. Among the additional factors provoking the disease are the following:
- damage to the nipples during feeding;
- improper diet with a predominance of yeast products and confectionery products;
- progression of vulvovaginal candidiasis;
- persistent anemia.
Lack of quality sleep in combination with chronic fatigue creates additional conditions for the functioning of fungal flora.

Causes of the disease
Opportunistic microorganisms and fungi live on human skin, which under normal conditions do not cause harm. However, when unfavorable factors appear, such as changes in the physicochemical properties of the skin, skin secretions, sweat, these fungi become pathogenic and lead to diseases.
The most important place in the development of thrush belongs to the background state of the body. The following points are important:
- tumors and pre-tumor diseases;
- primary, secondary immunodeficiency;
- autoimmune problems in the body, for example, damage to the thyroid gland;
- the use of medications that cause immune suppression, for example, hormonal ointments;
- during sexual contact with an infected man. In this case, the woman’s previous infection, which led to a decrease in local immunity of the external genitalia and urethra, is important;
- unreasonably frequent use of broad-spectrum antibacterial therapy in pursuit of the desire to kill all microflora in the body and improve health;
- violation of cellular immunity;
- diabetes;
- age over 35 years;
- stress and fatigue;
- maintaining a job outside the home despite the birth of a child;
- pathology associated with environmental disturbances.
Breast thrush during breastfeeding can be caused by 10 types of fungal infections. The skin becomes susceptible to them against the background of reduced immunity, and candidiasis develops. The fungus can also enter cracks in the mammary gland and nipple from the mouth of an infected child.
First symptoms
Many inexperienced mothers who have not previously had to deal with the process of lactation may not be aware of the symptoms of mammary thrush during breastfeeding. However, the lack of timely treatment is dangerous both for the woman herself and for her child. To prevent the spread of infection, you should carefully listen to your own feelings.
The main symptoms of mammary thrush during breastfeeding are:
- itching and burning in the chest area;
- nipples acquire a bright pink color and a shiny surface;
- areolas may peel;
- wearing tight-fitting underwear is accompanied by pain;
- Bubbles and a cheesy coating appear on the nipples.
During lactation, burning pain may occur, which only intensifies towards the end of feeding. Discomfort is usually felt not only in the nipples, but also in the depths of the mammary glands. However, such pain can also occur due to improper attachment of the baby. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a doctor.

Clinical picture of the disease
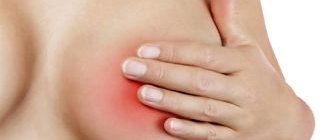
Superficial candidiasis of the skin in nursing mothers manifests itself in small, millet-like nodules. These formations are filled with clear liquid. After opening, a surface with erosion is exposed. Areas of damaged, destroyed skin tend to merge and increase in size. The damaged skin structure looks like a burgundy glossy surface, around which there is flaky epithelium. These are characteristic skin symptoms of mammary thrush. Periodically, peeling is present in the center, and small bubbles on the periphery, which indicates screening and a tendency to spread the infection.
Thrush on the mammary glands becomes wet and itchy when breastfeeding. If there are cracked nipples, women report symptoms of pain in the affected area. The trouble with the disease is that it has a wavy, relapsing course and is quite difficult to get rid of.
The appearance of the above unpleasant sensations in the mammary gland forces a woman to spare the affected breast during feeding. Poor milk flow from the breast leads to symptoms of lactostasis, which is a favorable factor for the development of postpartum mastitis.
Thrush damages the skin of the nipples and creates favorable conditions for a secondary bacterial infection to occur. Severe purulent mastitis develops.
Manifestations of the disease in a newborn
Thrush can be passed from mother to baby during breastfeeding. In newborns, the disease always manifests itself with a pronounced clinical picture:
- the appearance of white plaque in the oral cavity;
- the baby becomes whiny, irritable, and may refuse food;
- red ulcers form in the groin area;
- increase in body temperature.
Also, thrush in infants manifests itself in the form of progressive irritation on the surface of the buttocks. Small blistering diaper rash usually does not go away for a long time, even with the use of various diaper rash remedies.
Treatment of thrush during breastfeeding
The scope for therapeutic solutions during breastfeeding (breastfeeding) is narrowed due to the threat of the “ingredients” of the drug getting into the biolactate when taken orally or the child licking them directly from the surface during local treatment. The other side of the risk is infection with pseudomycelium and spores of the baby with the subsequent development of oral candidiasis if the activity of the pathogen cannot be extinguished in time.
This will inevitably happen anyway - the causative agent of thrush is transmitted from surrounding adults to children even before the transition to adolescence. But for painless entry into the microflora, its appearance as late as possible is desirable.
Effective drugs
The optimal solution for not interrupting lactation (just wash both nipples before the next feeding if the fungus has “settled” on them) for candidiasis is local remedies - ointment, gel, cream, aqueous solution of base powder:
- with nystatin - an inexpensive (up to 80 rubles per tube of ointment of the same name) and effective, although old by medical standards, antibiotic;
- with ketoconazole, an imidazole derivative that is unsafe for the liver, like all substances in this series. The cream with it is called Nizoral (like shampoo). If it is consumed internally, the baby will definitely have to be weaned from the breast. Locally, it is safe, if you do not forget to remove its remains, it will cost around 500 rubles;
- with natamycin - another antibiotic for 300-375 rubles.
If you need a general dose, it is better to stick with Fluconazole (up to 65 rubles), Mikosist (630 rubles at most) or Diflucan (980 rubles for the same volume as the previous ones). They all have the same active ingredient – fluconazole, which is still considered the safest for humans while maintaining toxicity to fungi. The famous Ukrainian pediatrician Dr. E. Komarovsky also recommends lubricating the itching areas with miramistin, a surface antiseptic.
ethnoscience
When thrush occurs in a nursing mother, treatment is allowed not only with medications. A significant portion of people believe that folk remedies are safer in terms of side effects. In general, this is, of course, incorrect, but among those that are definitely not harmful to the child, you can focus on douching and wiping:
- homemade kefir, whey. This option is prohibited if there are deep sutures in the vagina;
- 1 tbsp. l. a mixture of 50:50 sage leaves and raspberries, brewed with a glass of boiling water for an hour in a thermos;
- a tablespoon of calendula flowers, boiled in 250 ml of boiling water, 20 minutes, over low heat.
One of the traditional remedies for persistent candidiasis is 3 tsp. St. John's wort herbs, brewed with 0.7 liters of boiling water plus fresh grated onion. It helps, but is not suitable for wiping nipples or for injuries of any scale at the application sites (it will burn, but is otherwise harmless). Its other drawback is that over time, breast milk also develops an onion taste, and the baby may refuse it.
Diagnostic methods
When the first signs of breast thrush appear during breastfeeding, you should consult a gynecologist. Diagnosis of the disease begins with studying the patient's medical history and physical examination. Laboratory research methods are required. A scraping from the affected nipple and a sample of breast milk are taken from the woman. The biomaterials are then subjected to microscopic examination, based on the results of which the causative agent of the developing infection can be determined. After a comprehensive examination, the doctor selects therapy.
Sometimes a general blood test, glucose test and immunogram may be additionally required. To exclude mastitis, an ultrasound examination is suggested.

Diagnostics
To diagnose Candidiasis, the doctor simply needs to examine the nursing mother and listen to her complaints. But in order to prescribe the correct treatment, you need to do tests. A fingerprint smear will help identify the strain of Candida fungus, and a general blood test and glucose test will help identify the cause of the disease. Without this, it is impossible to provide high-quality treatment in full.
Drug therapy
Treatment of mammary thrush during breastfeeding is a long and labor-intensive process. Drug therapy is prescribed only in extreme cases, when the pain becomes literally unbearable. The doctor selects treatment for both mother and child. Therefore, you should additionally consult your pediatrician. Otherwise, the likelihood of relapse of the disease increases.
For local therapy, various creams and ointments are used:
- "Ketoconazole". This antifungal drug helps to quickly eliminate itching and redness in the chest area. It is recommended to apply a thin layer twice a day. The duration of therapy is 14 days.
- "Nystatin" This ointment is a classic treatment option for breast thrush during breastfeeding. It can also be used for therapeutic purposes in children, but only after consultation with a pediatrician.
- "Candide". The cream is characterized by a wide spectrum of antifungal effects.
- "Pimafucin". The drug is used for local therapy and has virtually no side effects. Its active substances destroy fungal colonies well and do not pass into breast milk.
It is best to carry out treatment after feeding the child to prevent drugs from entering the oral cavity. In between, you can additionally treat your nipples with Purelan ointment. It allows you to speed up the healing process of cracks.
Systemic antifungal drugs are practically not used for the treatment of mammary thrush during breastfeeding. Most of them are prohibited due to the high risk of penetration of active substances from the woman’s blood to the child during lactation. The exception is fluconazole-based medications, for example, Diflucan. However, during therapy, lactation should be stopped. Breast milk may be temporarily frozen or artificially mixed. The break is quite short. Typically, such treatment takes no more than 3 days.
Help from traditional medicine
When initial signs and symptoms appear, breast thrush during breastfeeding can be cured using traditional medicine recipes. In combination with drug therapy, they can speed up the healing process and quickly relieve discomfort.
The most effective method is treating the affected areas with a soda solution. To prepare it, a teaspoon of the product must be dissolved in a glass of warm water. Then you can begin treatment. It is recommended to treat the breast immediately after feeding. After the procedure, you should not dry yourself with a towel. It is better to let the breasts dry naturally, and then lubricate them with moisturizer.
This remedy is also suitable for the treatment of thrush in infants. A cotton swab soaked in the solution should be used to carefully clean the baby’s oral cavity.
Another traditional anti-inflammatory remedy is chamomile decoction. It relieves itching well. To prepare it, you will need to fill 2 filter bags of raw materials with 0.5 liters of water and leave for about half an hour. It is recommended to wipe the affected area with the solution every time after feeding.
Tea tree oil has regenerating and antimicrobial properties, but can cause allergies. Before using it to treat breast thrush while breastfeeding, a simple test must be performed. A few drops of the product should be applied to the inside of the wrist and rubbed. If there is no itching or redness of the skin in the area within two hours, it can be used. To prepare the medicine, you will need to mix 5 ml of any herbal and 2-3 drops of tea tree oil. Then the affected nipple should be lubricated with the resulting mixture no more than three times a day.

Doctor treating
If any symptoms of thrush appear on the breast, a woman should consult a gynecologist. He must order all the necessary studies to exclude the development of psoriasis, mastitis, herpes and other breast diseases that have similar symptoms.
To exclude mastitis, an ultrasound of the mammary glands is performed. When breastfeeding, clots or stagnation of milk can often form. If there are bubbles on the nipple, a scraping is taken from them to conduct a microscopic examination of the contents.
Possible complications
If treatment of the disease is neglected, breast thrush during breastfeeding can cause complications. First of all, it causes a decrease in the nutritional value of milk and its quantity, which occurs against the background of a feeling of pain during lactation. If the disease is passed on to the baby, he may be reluctant to breastfeed or lose his appetite altogether.
Another common complication of thrush during lactation is mastitis, blockage of the milk ducts, and lactostasis. In a newborn, the disease can lead to dysbiosis and progression of tonsillitis. Therefore, it is so important not to neglect its first manifestations and immediately seek medical help.
How to recognize nipple thrush
Thrush of the mammary glands during breastfeeding can be masked so that it is sometimes difficult to establish the correct diagnosis. Still, there are some symptoms characteristic of this disease:
- When a fungal infection of the breast occurs, areas of hyperemia appear, mainly affecting the nipples and areola. Reddened skin may peel or become wet; small blisters with whitish, cloudy contents are characteristic. The nipple may increase in size, whitish spots resembling cream may appear;
- there is severe itching of the skin and the mammary gland as a whole, sometimes without changes in the skin;
- pain covers the entire gland, radiating to the back or arm;
- The pain syndrome is especially pronounced between feedings, and when the baby sucks the breast, the pain decreases.
If candidiasis is transmitted to a newborn, hyperemic areas with a white coating appear on the inner surface of the baby’s cheeks, tongue, and gums. The baby becomes restless and does not want to breastfeed. In addition to the oral cavity, candidiasis can appear in the inguinal folds, presenting as pinpoint red or bright pink rashes.

Prevention methods
In the photo, breast thrush during breastfeeding looks quite unpleasant. Therefore, many women have a question about how to prevent its occurrence. It is not possible to completely exclude the causes of the disease. However, it is easy to reduce the likelihood of relapse by following simple rules:
- After feeding the baby, gently blot the breast and leave it open for a while. The disease develops better in a warm and humid environment.
- When using special bra pads, it is better to choose thin and “breathable” options and change them as often as possible.
- The appearance of cracked nipples requires immediate treatment. For this purpose, you can use creams “Purelan” and “Medela”.
- If a woman has previously been diagnosed with vaginal thrush once, her symptoms should not be ignored or treatment refused. It is better to additionally consult with a gynecologist about measures to prevent relapses.
- One of the main causes of thrush is decreased immunity due to chronic fatigue. Therefore, a woman should pay attention to her daily diet and lifestyle: give her body more rest, eat a balanced diet, and walk in the fresh air more often.
- It is recommended to choose underwear from natural materials.

Breast thrush is a fairly common occurrence. Various factors can lead to its appearance, ranging from reduced immunity to untreated vaginal candidiasis. The disease manifests itself aggressively, accompanied by unpleasant symptoms such as itching and pain. All this can negatively affect the well-being of the woman and child and the lactation process. Therefore, the disease cannot be started. If initial symptoms occur, you should immediately contact a gynecologist or pediatrician. The doctor will be able to select the most effective means to eliminate thrush without harming the baby’s health.
Causes of mammary candidiasis during lactation
To determine how to treat such a pathological process as thrush on the mammary glands during breastfeeding (breastfeeding), it is necessary to identify the cause of its development, among which are:
- Disturbed intestinal microflora. This can be explained by the fact that for a woman during the feeding period there are some restrictions on the products consumed. The new mother tries to compensate for the vitamin deficiency with sweet or flour products, which have a beneficial effect on the proliferation of candida fungus.
- Reduced immune defense of the female body during the postpartum period.
- Changes in hormonal balance.
- Mechanical trauma to the nipple can trigger the development of candidiasis. This is facilitated by uncomfortable underwear made of synthetic fabrics, dry nipple skin, or the use of inappropriate hygiene products.
- Damage to the nipple caused by incorrect positioning of the baby during breastfeeding. It should be remembered that when feeding, the baby should capture the entire nipple with its lips along with its areola.
- Taking antibiotics.
- Transmission of a fungal infection from a sexual partner or an infant suffering from candidal stomatitis.
- Failure to maintain hygiene of the mammary glands, the area of the body under the breasts, and hands.