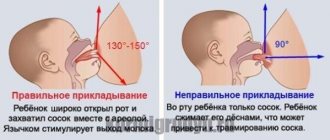
Thrush in nursing mothers is considered the most common infectious process. The mucous membrane of the external genitalia is most often affected.
Thrush is caused by yeasts of the genus Candida. These microorganisms are found in almost every healthy person. They first come into contact with the baby's skin and mucous membranes during birth. Passing through the birth canal, the baby becomes infected with the mother's microflora, including Candida fungi. Then the person lives quietly with such flora, without any signs of disease. Fungi can be detected in the mouth, intestines, skin and external genitalia.
Under certain conditions, the number of microorganisms increases sharply. Then the disease thrush (candidiasis) develops. Thrush in nursing mothers is associated with a decrease in immunity, hormonal imbalance, and dysbiosis of the vagina and intestines.
Thrush during breastfeeding is partly a consequence of increased prolactin and the absence of ovulatory menstrual cycles. Although this condition is, of course, absolutely physiological for the female body, it nevertheless contributes to the development of candidiasis. A decrease in the functional activity of the immune system is associated with previous pregnancy and childbirth. The female body needs vitamins, microelements and simply time to recover. Due to the depletion of protective forces, thrush occurs in every third woman during breastfeeding.
Is it necessary to treat thrush in nursing mothers?
Sometimes women do not have enough time for themselves during the postpartum period and throughout lactation. However, you should not neglect the treatment of thrush in nursing mothers. Discomfort when urinating, pain, and burning reduce a woman’s emotional background, contribute to the refusal of sexual relations, and the development of depression.
The consequences of thrush during breastfeeding lie not only in the field of psychology and family relationships. Inflamed mucous membranes become especially vulnerable to other infections. Sometimes nonspecific inflammation of the external genitalia and urinary tract develops. Infections of the bladder and kidneys are especially dangerous.
Thrush when breastfeeding is potentially dangerous for the baby. Dysbacteriosis in the mother contributes to the development of a similar pathology in the baby. Candidiasis in newborns and children of the first year of life is associated with thrush in nursing mothers. Oral candidiasis in a child can lead to refusal to eat. In severe cases, thrush in children is treated in a hospital setting. Self-medication in women with thrush during feeding is extremely dangerous for the baby. Many medications can harm a baby's health through breast milk.
Drug therapy
Treatment of thrush during breastfeeding is carried out at home. It is aimed at eliminating itching and burning while maintaining breastfeeding. Remedies for thrush during breastfeeding are prescribed only by a doctor. It is generally accepted that breastfeeding women are not prescribed antifungal drugs in capsules and tablets. This is due to the fact that such drugs have a high degree of toxicity.
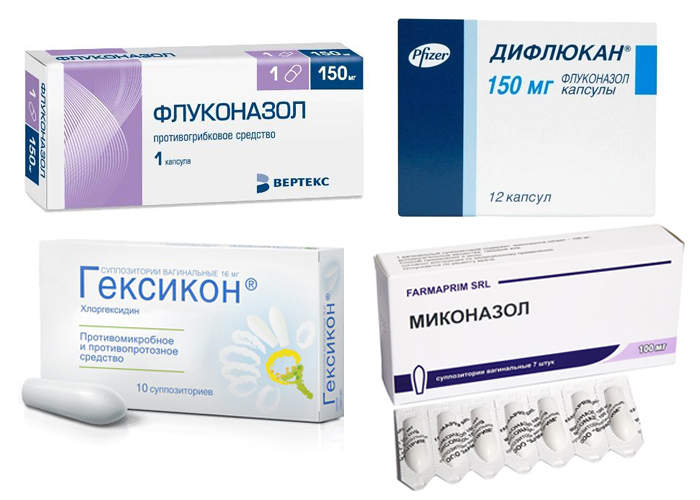
There are several drugs that can be used during lactation. What can you do for thrush while breastfeeding? Fluconazole, Diflucan and Miconazole are compatible with breastfeeding.
are also prescribed for thrush during breastfeeding - the most effective remedy that causes the least harm to the baby. Hexicon, Terzhinan, Pimafucin are used for treatment.
Local antifungal drugs are prescribed to breastfeeding women without restrictions. This is due to the fact that the amount of active substances that penetrate the blood is very small. Is it possible to take No-shpu during breastfeeding - described in a separate article.
It is important to follow your doctor's recommendations when applying local treatment. Often women stop treatment when the first symptoms subside. This causes thrush to reoccur. The minimum course of treatment for the disease should be 7 days. If necessary and as prescribed by a doctor, the course is repeated.
Treatment of thrush on the nipples
Thrush on the mammary glands during breastfeeding requires the use of additional measures. To get rid of pathology you need to:
- Change disposable breast pads before each feeding.
- If your nipples are sore, cool them before attaching the baby.
- After each feeding, do air baths for the breasts for 15 minutes.
- Rinse nipples with soda solution. It can be prepared by dissolving a teaspoon of baking soda in one glass of boiled water.
- If the nipples are severely inflamed, you can apply the antifungal cream Nizoral twice a day, but it must be washed off thoroughly before each feeding.
If the mother has cracked nipples, it is recommended to use Bepanten or its analogues for rapid healing.
If the pain is so severe that a woman is unable to feed her baby, doctors recommend not giving up breastfeeding, but expressing milk into a bottle until the pain subsides a little.
How to reduce lactation is the topic of this article. If it needs to be stopped, follow the recommendations in this publication.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods are popular for treating thrush during breastfeeding. They are considered the safest for both the nursing mother and the newborn.

Chamomile relieves inflammation well, and most importantly quickly, it is great for the douching procedure
Traditional methods do not give such a quick effect as medications , but they have a gentle effect on the body. However, the woman does not need to stop breastfeeding.
The most common traditional medicine recipes against thrush are:
- Chamomile decoction can be used as a hygiene product for both the genitals and breasts. It will not only relieve itching and reduce inflammation.
- Douching with herbal infusions helps get rid of the disease well. To prepare the product, you can take oak bark, chamomile and calendula in equal proportions. The volume of herbs should be two tablespoons. They are poured with one liter of boiling water and infused. The resulting solution is used for douching.
- Wash your genitals and breasts with a solution of water several times a day. To prepare it, a teaspoon of soda is dissolved in one liter of warm water.
Green tea has a beneficial effect on getting rid of fungi. Regular consumption of green tea by the mother helps remove excess yeast from the body.
Lifestyle
Thrush is the body’s response to a decrease in immunity levels . For treatment to be effective, an integrated approach to solving the problem is needed. Without lifestyle adjustments, you will not be able to achieve results quickly. The most important thing for a young mother is good nutrition. Not all foods can be eaten and drunk during this period. For example, coffee, alcohol during breastfeeding.
This also includes healthy sleep and adherence to a daily routine. Walk with your baby at any time of the year, but the first walks with a newborn in winter require some organization. These rules are described here.
It is important that if thrush is detected, both partners should undergo treatment . Despite the man's lack of signs of thrush, he is also a carrier of fungi.
Complaints of women with thrush during breastfeeding
Most often, thrush during breastfeeding occurs in those who have previously encountered a similar problem. The manifestations of thrush in nursing mothers are the same as in other women. Inflammation occurs on the mucous membrane of the external genitalia. Many people are bothered by severe constant itching and burning. Discomfort increases when urinating and during sexual intercourse. A very characteristic manifestation of candidiasis is copious vaginal discharge in the form of white cheesy flakes.
All these complaints should be a reason to seek medical help. Sometimes manifestations of thrush in breastfeeding women are almost invisible. In this case, it is especially important to be examined by a doctor at the slightest discomfort. When visiting a gynecologist as planned, report all your complaints.
Symptoms
Thrush in a nursing mother is a common disease, which is primarily manifested by vaginal discharge that is white in color and has a cheesy appearance. In addition, the disease can affect the bust area. Breast thrush during breastfeeding can affect the mother's nipples. A woman may notice small cracks forming on them, and a white coating can be seen inside. Also, thrush during breastfeeding has the following symptoms:
- Itching and burning sensation in the area of the genitourinary system and nipples.
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
- General weakness, sudden loss of strength.
- In advanced forms of the disease, body temperature may rise.

This problem cannot be left to chance, because treatment of thrush during breastfeeding must occur in a timely manner. Otherwise, the child may become infected with this disease. But curing a baby is much more difficult. No mother would like to expose her tiny body to drugs once again.
Confirmation of the diagnosis of thrush during feeding
A gynecologist at a antenatal clinic or any other medical center will most likely prescribe an additional examination if thrush is suspected in nursing mothers.
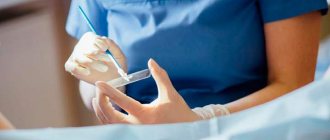
Taking a smear from the vaginal mucosa for analysis is considered sufficient. The resulting material contains various microorganisms. They are placed on special laboratory dishes with a nutrient medium. Next, the microorganisms are grown in favorable conditions for 24 hours. After this, the laboratory assistant evaluates the resulting colonies of bacteria and fungi. Among them there may be colonies of the fungus Candida. If there are many such colonies, and the normal flora of the vagina is practically absent, then a diagnosis of thrush in a nursing woman is made. Next, the sensitivity of microorganisms to various antifungal drugs is determined. Knowing the medications that are effective in this case, the gynecologist will be able to choose the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy can develop for various reasons. Below are the causes of ectopic pregnancy according to the specific type of ectopic pregnancy.
Causes of tubal pregnancy
This usually occurs due to a violation of the peristalsis of the fallopian tube, that is, due to a violation of its ability to contract, or due to other processes that impede the patency of the fallopian tubes (with adhesions, tumors, disruption of the structure of the fimbriae, bending of the tube, underdevelopment of the tubes (genital infantilism ) etc.)
Thus, untimely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the tubes (salpingitis, hydrosalpinx, for example) or previous operations on the fallopian tubes are usually the reasons for the development of tubal pregnancy.
Causes of ovarian pregnancy
After the dominant follicle ruptures, the egg meets the sperm while still in the ovary. Further, the fertilized egg, for one reason or another, does not continue its movement to the uterine cavity, but is attached to the ovary.
The cause of such a failure during pregnancy may be a previous infectious disease of the uterine appendages or inflammation of the endometrium, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, endocrine and genetic disorders, etc.
Causes of cervical pregnancy
Cervical pregnancy occurs due to the fact that the fertilized egg cannot attach to the wall of the uterus. Implantation of the fertilized egg to the wall of the cervical canal occurs due to a previous mechanical abortion or cesarean section, the formation of adhesions in the uterine cavity, fibroids, and due to various anomalies in the development of the uterus.
Causes of abdominal pregnancy
Abdominal pregnancy develops with obstruction of the fallopian tubes and other acquired or congenital pathologies.
Typically, abdominal pregnancy is a consequence of the release of a fertilized egg into the abdominal cavity after a rupture of the fallopian tube (after a tubal abortion).
There are several reasons why the egg cannot reach the uterus:
- Disturbances in the condition of the walls and functioning of the fallopian tubes (when they contract poorly and are not able to move the egg further). This often happens due to previous diseases of the pelvic organs, as well as chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, in particular STDs.
- Anatomical features of the fallopian tube (for example, infantilism): a tube that is too narrow, tortuous, scarred or scarred makes it difficult and slows down the passage of the egg.
- Previously undergone tubal surgery.
- Previous abortions, especially if the woman’s first pregnancy was artificially terminated.
- Slowness of sperm: the egg is “waiting” for fertilization, which is why it does not have time to get to the right place in time, that is, to the uterus - hunger forces it to settle earlier.
- Hormonal disorders in the body of a pregnant woman.
- Tumors on the uterus and appendages.
- Changes in the properties of the fertilized egg.
- A woman wearing a contraceptive intrauterine device.
- Some artificial insemination technologies.
- A woman’s constant nervous overstimulation, in particular, the fear of getting pregnant and unreliable methods of contraception, do not allow her to relax, which is why the fallopian tubes spasm.
READ MORE: Chamomile decoction for thrush reviews
Of course, ideally it is necessary to try to exclude all possible causes of the development of an ectopic pregnancy at the planning stage.
How to treat thrush while breastfeeding?
The arsenal of antifungal drugs is wide, but not all of them can be used by a nursing mother. Some medications can harm the baby. Capsules and tablets for oral administration have a particularly strong effect. Their active ingredients first enter the mother's blood and then into breast milk. By feeding on this milk, the child also receives a certain dose of the drug.
Creams, suppositories, and douching act mainly only locally. They almost do not penetrate into the blood and breast milk. But you should also be careful with local remedies when treating thrush in nursing mothers.
You can independently undergo treatment with an infusion of medicinal herbs in the form of douching twice a day. The most effective remedies for thrush during breastfeeding are chamomile, calendula, and oak bark. A solution of soda (1 spoon per liter of water) will help relieve itching and burning. If all this turns out to be ineffective, be sure to consult a doctor.

The most popular remedies for thrush are prohibited during lactation. Flucostat, Diflucan, Mikosist, Clotrimazole will have to be excluded from the treatment regimen. In tablet form, only the modern antifungal drug Pimafucin is considered safe. Most often, gynecologists recommend local treatment with suppositories and vaginal tablets. To treat thrush in nursing women, Pimafucin, Livarol, Terzhinan, Hexicon, Iodoxide and Betadine are used. These medications are effective and safe during breastfeeding.
Alternative medicine will come to the rescue for thrush during breastfeeding
Thrush during breastfeeding can recede in a fairly short time if traditional medicine is used. But in most cases, they only remove symptoms without affecting the causes. That is why folk recipes should be used in combination with medications. In addition, all actions of a nursing mother in this direction must be coordinated with the attending physician. It is not uncommon for a mother or child to develop individual intolerance to one or another decoction. In turn, this is quite dangerous for their health.
The most popular folk remedies are:
- soda solution. To prepare it, take half a liter of boiled water and add a couple of tablespoons of soda. Mix everything thoroughly. Using a gauze swab, wipe the affected areas. They also treat the mammary glands and nipples themselves. After this procedure and the breasts are completely dry, you should lubricate them with a nourishing cream;
- green tea. Its use can remove yeast from the mother’s body and enhance lactation. In addition, it can slightly reduce pain;
- tea tree. Taking a bath with the oil of this plant can eliminate the symptoms and pain of candidiasis. If a rash appears, stop using the product. This is how an allergic reaction to a plant manifests itself;
- chamomile. Its famous anti-inflammatory effect can relieve itching and burning, and its antibacterial effect can stop the proliferation of candida. To prepare the decoction, take a few spoons of flowers and pour a glass of warm water. After the liquid has infused, it needs to be filtered. Douching with infusion is carried out twice a day.

Important! Thrush started during breastfeeding tends to develop into mastitis. This is a very dangerous disease for the female mammary glands. Her timely treatment is urgently needed.
How to prevent thrush in nursing mothers
Ideally, prevention of thrush in nursing mothers begins before conception. The woman should be examined by a gynecologist. If hidden thrush or vaginal dysbiosis is detected, women planning pregnancy are prescribed a course of antifungal drugs. In this group of patients, both immunomodulators and preparations of normal bacterial flora can be used.
Proper nutrition also helps prevent thrush during breastfeeding. It is necessary to avoid overeating and excess consumption of carbohydrates, especially sugar. Eat more vegetables, especially those rich in fiber and microelements. Lingonberry leaves and berries, garlic, and red pepper may be useful. To normalize the microflora of the intestines and vagina, eat fermented milk products daily.
Properly selected complex preparations of vitamins and microelements can be useful for the treatment and prevention of thrush in nursing mothers.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
How to treat thrush while breastfeeding: list of drugs
Treating thrush while breastfeeding requires a slightly different approach. The wrong medicine can negatively affect the composition and quantity of breast milk. This, in turn, can affect the baby's development.
Only the attending physician can prescribe medications for the treatment of thrush. This is especially true for nursing mothers.
When breastfeeding, doctors recommend using ointments and suppositories. You will have to give up the pills. Cream and ointment are recommended to be used when the disease is still in its infancy, at its initial stage. Ointments are great for treating nipples.
Approved medications for breastfeeding
Pimafucin ®
One of the most popular drugs prescribed for thrush. Antifungal antibiotic. This is one of those remedies that is allowed during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The main active ingredient is natamycin [1].
Available in the form of cream, suppositories (candles) and tablets. The cream is sold in plastic or aluminum tubes of 30 g. Candles are packaged in boxes of 3 or 6 pieces. The cream is applied to damaged skin one to four times a day, depending on the severity of the disease. Suppositories are used intravaginally every day before bedtime. The course of treatment lasts from 3 to 9 days, usually 6 days are enough. As a rule, suppositories are used for treatment.
Primafungin
Analogue of Pimafucin. Antifungal antibiotic. The active ingredient is natamycin [1]. Available in the form of suppositories (candles) of 3 pcs. Suppositories are used intravaginally every day before bedtime. The course of treatment lasts 6 days.
Ecofucin
Analogue of Pimafucin and Primafungin. The active ingredient is natamycin [1]. Available in the form of suppositories (candles) of 3 or 6 pcs. The method of application is similar to the indicated drugs.
Hexicon
Is an antiseptic. The active ingredient is chlorhexidine [2]. Available in the form of vaginal tablets or suppositories (suppositories). Candles are sold in 1 or 10 pieces. Vaginal tablets – 5 or 10 pcs. It should be noted that Candida fungi are insensitive to chlorhexidine. That is, Hexicon cannot be prescribed as monotherapy against thrush.
Suppositories are used 1-2 times a day for 7-10 days. The tablets are used intravaginally, pre-moistened with water, 1-2 times a day for 7-10 days. Absolutely harmless during breastfeeding.
Conditionally approved drugs
Zalain ®
Antifungal drug. The active ingredient is sertaconazole [3]. Available in the form of cream or suppositories (candles). Candles are sold 1 pc. Cream - in tubes of 20 g.