Over the past hundred years, the natural and natural process of breastfeeding has become overgrown with myths and has come a long way from the irreplaceable and only way of feeding newborns and children in the first years of life to replacing breast milk with artificial formula.
Of course, there are situations in which a child requires additional feeding with an adapted milk formula or completely artificial feeding. But we will not consider these cases now and talk about the benefits of breastfeeding for mother and baby.
The benefits of breast milk for a baby
To date, it has been proven that breast milk is the only completely suitable food for a newborn. Until now, no laboratory in the world has been able to recreate its unique composition and analogue of equivalent benefits.
Human milk contains growth factors, anti-infective and anti-inflammatory components, hormones, many enzymes, etc. And since it contains sufficient amounts of clean water, not susceptible to any bacteria or infections, the child does not need to supplement with water before introducing complementary foods.
Based on the results of numerous studies, it has been proven that breastfeeding has a beneficial effect on the development of all body systems:
- Immune;
- Digestive;
- Cardiovascular;
- Endocrine;
- Respiratory;
- Central nervous system;
- Visual apparatus;
- Brain, etc.
Breastfeeding strengthens the immune system
From the beginning of pregnancy, breast fatty tissue is gradually replaced by glandular tissue.
From the middle of pregnancy, the mammary gland begins to produce colostrum - immature thick milk, which the baby will feed from birth until the arrival of mature milk on the second to seventh day.
It is very important that the mother can put the baby to the breast in the first minutes after birth. Already with this first attachment, he receives from his mother immune complexes and antibodies that protect his body. In addition to nutrition, breastfeeding is a unique and not fully understood mechanism for immunizing a child.
Breast milk as prevention and treatment of diseases
Since mother and baby are constantly in close contact, through the baby’s saliva and skin, the mother’s body receives information from the child’s body about the baby’s health status.
For example, even if the mother is healthy, but the child has ARVI, the mother’s body produces antibodies and passes them on to the child through breast milk. Once in the blood, they help the child’s body quickly overcome the source of the disease and develop immunity to it.
If a nursing mother has been exposed to a viral disease, then by feeding the child, she also transfers antibodies to him and the risk of infecting the baby from her is very low.
Breastfed children get sick less often, recover faster and have fewer complications and consequences after illnesses.
Breast milk is the ideal food for a newborn
The immature digestive system of a newborn is easily susceptible to intestinal infections. The risk of intestinal diseases with proper organization of breastfeeding is significantly lower than in bottle-fed children.
The fatty acids contained in breast milk are easily absorbed by the immature digestive system of the newborn. Milk contains lipase and other enzymes that help the baby’s body digest mother’s milk.
Colostrum, which is produced in the first 2-7 days after birth and before the arrival of mature milk, contains, in addition to a large number of nutritional and protective components, laxative components. They help the body eliminate meconium - thick original feces, which is more difficult for a bottle-fed baby to get rid of on its own.
Children fed breast milk are less likely to suffer from constipation.
It has also been proven that people who received breast milk for at least the first six months of life are less susceptible to food allergies, gastrointestinal diseases, obesity and diabetes.
Breast sucking helps the proper development of the nervous system
Breast sucking itself promotes the formation of a correct bite, the development of the articular apparatus, and also has a beneficial effect on the development of the baby’s nervous system.
The first days after childbirth, the Montgomery gland, located on the areola of the nipple, secretes a secretion similar in composition to amniotic fluid. Inhaling this secretion, the newborn plunges into the intrauterine state, easily calms down and falls asleep. This helps him cope more easily with adaptation to a new world for him.
Satisfaction of the sucking reflex is very important for the development of the central nervous system. Therefore, in the first months of a baby’s life, it is recommended not to limit the amount and duration of the baby’s sucking on the mother’s breast.
Breastfed children are less likely to have bad habits such as finger sucking, biting nails, pens, pencils, etc.
Breastfeeding strengthens the mother-baby bond
A very important aspect of breastfeeding is its ability to quickly and gently establish, establish and maintain a bond between mother and baby. Especially if there was a difficult pregnancy, difficult or premature birth, or cesarean section.
The baby's sucking of the breast and constant close skin-to-skin contact help the woman's body begin to produce the necessary hormones that prevent or help cope with postpartum depression, and fully feel the mother-baby bond, love and tenderness.
Since night feedings are an important point in the proper organization of breastfeeding, a nursing mother and her baby often practice co-sleeping. This allows the mother to constantly monitor the child’s condition, feel and hear him even through sleep, providing the baby with a sense of security, warmth, love and care.
It has been proven that breastfed children are much less likely to suffer from sudden infant death syndrome.
Does the content change after a year of feeding?
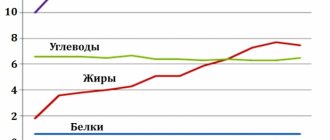
The composition of mother's milk changes throughout the breastfeeding period. After a year, it increases its energy value, increases the content of vitamins and antibodies, because the child’s body has become larger, which means that its needs have increased. Total, on average, mother's milk after a year provides the child with useful substances in the following proportion: nutrients by 35%, vitamin C by 60%, vitamin A by 75%, vitamin B12 by 94%, calcium by 36%, folic acid derivatives - by 76% based on the daily requirement.
Lactation is the key to women's health
The hormone oxytocin, produced when the baby is applied to the breast, causes the uterus to contract, which helps it return to its original size much faster and prevents bleeding. A woman who breastfeeds recovers faster physically and psychologically after childbirth.
During lactation, it is possible to cure breast pathologies such as mastopathy.
According to research, breastfeeding is recommended for women with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer. Since women who breastfed are 50% less likely to get breast cancer and 30% less likely to get ovarian cancer.
Breastfeeding allows mother and baby to live an active life
Another undeniable advantage of breastfeeding is its cost-effectiveness (completely free), environmental friendliness and accessibility. With the right clothes, a young mother can feed, breastfeed, and lull her baby to sleep almost anywhere.
Breastfeeding a baby often does not require any additional equipment or actions. Milk at the right temperature is always at hand, in unlimited quantities.
At night, with proper and safe organization of joint sleep, the mother can get enough sleep, while continuing to feed the baby, maintaining lactation and strengthening the child’s nervous system.
Optimal age for completion of lactation
Breastfeeding specialists and pediatricians often argue about at what age it is best to stop breastfeeding. They agree on one thing - weaning should be carried out at a time when it will not harm the physical and psycho-emotional state of the mother and child. Russian mothers usually stop feeding during one of these periods:
- Reaching 6 months of age. Experts are unanimous: you should feed for at least six months. The exception is diseases for which the mother is prescribed antibiotics.
- One year old. Many experts try to convince mothers that a grown baby no longer needs breast milk, as he receives a variety of complementary foods.
- Two years. At this time, the mother is forced to interrupt lactation, because the baby goes to the garden, and she has to work.
A two-year-old child who begins to attend kindergarten should gradually wean off the breast
There is no upper age limit for stopping breastfeeding. Weaning before one year and in a stressful situation, according to psychologists, leads to problems during puberty. At 2.5-4 years, the sucking reflex fades, which allows breastfeeding to be completed naturally.
The decision when to wean the baby from the breast is made by the nursing mother independently, based on personal conditions or under the influence of the opinions of people important to her. When lactation has been maintained for up to a year, you should not interrupt it intentionally. There are many reasons in favor of long-term feeding, the main one of which is the benefit for the child.
The value of mother's milk. What are the benefits of breastfeeding?
Despite the widest range of existing milk formulas for artificial feeding, none of them can replace breast milk. Mother's milk has a completely unique composition, which includes more than 100 components: proteins, fats, carbohydrates, water, various micro- and macroelements, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, hormones, growth factors, immunologically active substances and other nutritional components.
All this is in optimal quantities and proportions for the baby, perfectly balanced. For comparison: the best mixtures of components contain no more than 40. Mother’s milk will provide the child at the first stage of his life with everything necessary for normal growth and normal development, and will increase the child’s body’s resistance to any infections.
The benefits of mother's milk
Breast milk is perfectly absorbed and easily digested by the baby’s body, does not cause allergies in the baby, is sterile - does not contain any bacteria, and is always at the right temperature.
In addition, the quantity, composition and properties of mother's milk are not constant, they change depending on the state of health and nutrition of the mother, and most importantly, on the physiological needs of the baby at each stage of its development. In an amazing way, mother's milk adapts to the changing needs of the child's body.
Breastfeeding has another important aspect - psychological. It promotes proper emotional development of the baby and brings him closer to his mother. It has a positive effect on the development of the child’s central nervous system and his psyche.
Breastfeeding is also important for the mother herself: it promotes rapid postpartum recovery and generally has a beneficial effect on the body of a nursing woman. It is believed that there is a direct relationship between breastfeeding and the development of breast cancer; it is much less common in women who breastfeed.
- Article on the topic - Pregnancy and childbirth - caring for a child in the first month
To make milk completely safe and healthy, a nursing woman’s diet must be extremely balanced, rich in all necessary vitamins and microelements. During breastfeeding, mothers need to limit themselves to certain foods. One that can cause an unpleasant reaction in a child’s body - garlic, onions, chocolate, coffee, citrus fruits. Not only limit, but also completely give up alcohol and cigarettes. Take any medications only on the recommendation of a doctor.