03/01/2018 Category: Nutrition for a nursing mother Author: Lyudmila Morozova
Shrimp are popular among gourmets all over the world due to their excellent taste, low calorie content and rich vitamin and mineral composition. This type of seafood is consumed both as an independent dish and as a component for salads, appetizers, and soups. However, the product rightly raises concerns among nursing mothers, because doctors do not give a clear answer to the question of whether shrimp can be consumed while breastfeeding. Despite its high nutritional value, this product can cause allergies, but the reaction is individual for each baby.
- Composition and calorie content of the product
Table: chemical composition and calorie content
- How to choose and cook
What types of shrimp are there?
Shrimp can differ in length, color, and place of catching.
Shrimp are a subspecies of crustaceans from the order Decapods. The size of these creatures, depending on the species, varies from a few centimeters to 30. The most common crustaceans on sale in our country are 10–12 cm in size. Initially, shrimp lived only in the seas and oceans, but today they are also grown on special farms in freshwater waters Such crustaceans differ not only in their “place of residence,” but also in their nutritional properties, and for the worse. Real shrimp differ in several ways:
- warm-water or cold-water;
- deep-sea and coastal.
Warm-water crustaceans include crustaceans brought from Asia and Latin America. Cold-water ones come from Norway, Denmark, Canada, Greenland and other countries. According to the method of extraction, they are divided into deep-sea - those living in the depths of the seas, and coastal - those caught near the shore.
The most beneficial for nursing mothers are deep-sea sea shrimp - they contain valuable nutrients in higher concentrations than freshwater or coastal ones.
You can find dozens of varieties of shrimp on the shelves, but the most popular are:
- Royal. They are distinguished by their “royal” size - the length of an individual can reach 25 cm. The color of such shrimps in their raw form can be greenish-blue. They are caught in the seas and raised on farms.
- Tigers. They have gigantic sizes (up to 40 cm) and characteristic stripes on the shell. Tiger prawns contain a lot of meat and can be farmed or caught from the sea.
- Northern (Chilims). The smallest representatives of shrimp on the domestic market. They are grown and caught mainly in the Atlantic, and the size does not exceed 11 cm.
Crustaceans go on sale in chilled, frozen, boiled-frozen, canned form.
Can a nursing mother eat shrimp?
Can a nursing mother eat shrimp?
Seafood is gaining more and more popularity every year. They are loved not only for their amazing taste, but also because they contain few calories.
They contain a lot of useful microelements. Many people no longer consider seafood such as shrimp to be a delicacy and eat quite a lot of it. But the question arises: can a nursing mother eat shrimp?
How are shrimp caught?
Shrimp are either marine or freshwater.
The latter are grown by people on special farms and their nutritional properties are worse than those of sea fish, although they are larger in size.
Shrimp are either cold-water or warm-water:
- King and tiger prawns are warm-water. They are mined by countries in Asia and Latin America.
- Cold-water shrimp are caught off the coast of Denmark, Greenland, Canada, and Norway. Some Baltic countries also fish cold-water shrimp.
There are two ways to catch shrimp: deep sea and coastal. In the latter case, the shrimp are of poorer quality and, therefore, cheaper.
What are the benefits of shrimp for a nursing mother?
The small crustacean shrimp is unique in its content of useful substances:
- They contain many rare amino acids.
- Shrimp is rich in protein, which helps maintain youthful skin as it forms collagen fibers.
- Shrimp iodine and calcium increase immunity and help the thyroid gland.
- Zinc helps strengthen hair and nails, and sulfur helps joints and blood vessels. This microelement also helps regulate the functioning of the sweat glands, as well as the sebaceous glands.
- Shrimp contain more iodine and copper than other seafood.
- The potassium they contain is important for the human cardiovascular system. This system is also strengthened by the substance astaxanthin, thanks to which shrimp have their color.
- In addition, shrimp contain iron, phosphorus, fluorine, sodium, magnesium, selenium, and chromium.
- By consuming shrimp, a person helps his kidneys, hematopoiesis, the formation of muscle and bone tissue, and the synthesis of hormones (zinc is responsible for this).
- In addition to microelements, shrimp contain many vitamins that have a beneficial effect on many body functions. For example, vitamin A helps the skin to be young, provitamin A is responsible for good vision, vitamins E and D protect the circulatory system, vitamin C guarantees good immunity. In addition, the small crustacean contains vitamins H, PP, B12 and almost all other vitamins from group B.
- Shrimp also contain Omega-3, which is a polyunsaturated acid. This acid is needed so that the body can develop well. In addition, it has a positive effect on hair, nails and skin.
Shrimp crustaceans contain little fat and are low in calories, which is a very important property when feeding a nursing mother.
The cholesterol contained here is harmless to the body, since it penetrates into the blood only with fats.
Many researchers claim that people who eat shrimp are less susceptible to cancer and also suffer less from various types of allergies.
This happens because shrimp contain powerful antioxidants.
You might think that such a wonderful composition of shrimp should convince the mother of a breastfed child to eat a lot of this product. However, is it possible for a nursing mother to have shrimp?
Harm from shrimp while breastfeeding
Before the baby turns one month old, the mother should not eat shrimp, because they are strong allergens.
In addition, we must remember that shrimp crustaceans accumulate harmful substances, such as heavy metals and radioactive compounds, and the ecological condition of our water areas is poor.
Shrimp raised by humans contains many antibiotics and hormones that are used to enhance growth.
It often happens that shrimp are stored incorrectly and are subjected to repeated freezing. In this case, their beneficial properties are significantly reduced. It is best to eat freshly caught shrimp. However, at the same time, you need to make sure that the seller is reliable.
In any case, you should use this product with caution, because you can harm not only yourself, but also your baby.
Eat 2-3 shrimp, and for the first time it will be enough, wait 3 days and analyze the child’s behavior, the cleanliness of his skin - are you still clean? No redness? This is already a good sign!
You can try shrimp in larger quantities in a week!
Please tell us in the comments what your experience is - did you eat shrimp while breastfeeding or did you try to avoid it? How did the child react?
Composition and calorie content of the product

Exquisite taste, varied chemical composition and low calorie content make shrimp a valuable delicacy in the diet of a nursing woman. The meat of these crustaceans contains substances necessary for the full development of the baby and the speedy recovery of the mother after childbirth. Low energy value allows you to include shrimp in the menu without fear of gaining excess weight. The following components stand out most in the product:
- Vitamins A and E ensure beautiful skin and hair.
- Vitamins of group B and PP are necessary for proper metabolism and maintenance of the nervous system.
- The potassium contained in shrimp helps the heart function.
- Iron ensures the necessary level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Like most seafood, shrimp are high in iodine, which is necessary for the full functioning of the endocrine system.
- Cobalt is involved in the synthesis of amino acids and is necessary for the formation of red blood cells.
- Copper is required for high-quality absorption of iron and is involved in the formation of collagen and elastin in the skin.
- Zinc ensures the formation of bone tissue, stimulates memory and attention, and brain activity.
- Selenium has a positive effect on the condition of the heart, reproductive system, skin, hair and removes mercury from the body.
- Shrimp contain high concentrations of chromium, a trace element involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, which prevents the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- Calcium and phosphorus are responsible for strengthening bones and tooth enamel.
- Fatty acids are necessary to maintain women's health, regulate hormonal levels, improve brain activity, beautiful hair and skin elasticity.
But the benefits of shrimp are ambiguous when it comes to feeding a nursing mother, because it is a product with a high allergenic status. Shrimp allergy occurs even in adults. Aggressive components can enter the baby’s body along with breast milk, causing allergic reactions or digestive disorders. This property of shrimp is partly explained by the fact that their meat accumulates heavy metals and other chemicals that are present in seawater. If the crustaceans were grown in an artificial freshwater environment, antibiotics and growth hormones used by unscrupulous producers pose a danger.
Table: chemical composition and calorie content
| Nutrient | Quantity | % of the norm in 100 g* |
| Calorie content | 87 kcal | 5.2% |
| Squirrels | 18.3 g | 24.1% |
| Fats | 1.2 g | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 0.8 g | 0.4% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin A, RE | 16 mcg | 1.8% |
| beta carotene | 0.01 mg | 0.2% |
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.06 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.07 mg | 3.9% |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.26 mg | 5.2% |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.11 mg | 5.5% |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 13 mcg | 3.3% |
| Vitamin B12, cobalamin | 0.8 mcg | 26.7% |
| Vitamin C, ascorbic acid | 1.4 mg | 1.6% |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 2.3 mg | 15.3% |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 1 mcg | 2% |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 5 mg | 25% |
| Macronutrients | ||
| Potassium, K | 260 mg | 10.4% |
| Calcium, Ca | 100 mg | 10% |
| Magnesium, Mg | 60 mg | 15% |
| Sodium, Na | 150 mg | 11.5% |
| Sera, S | 210 mg | 21% |
| Phosphorus, Ph | 220 mg | 27.5% |
| Microelements | ||
| Iron, Fe | 2.2 mg | 12.2% |
| Yod, I | 110 mcg | 73.3% |
| Cobalt, Co | 12 mcg | 120% |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.11 mg | 5.5% |
| Copper, Cu | 850 mcg | 85% |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 10 mcg | 14.3% |
| Nickel, Ni | 11 mcg | |
| Fluorine, F | 100 mcg | 2.5% |
| Chromium, Cr | 55 mcg | 110% |
| Zinc, Zn | 2.1 mg | 17.5% |
| Selenium, Se | 41.7 | 76% |
| Fatty acid | ||
| Omega-3 fatty acids | 0.45 g | 50% |
| Omega-6 fatty acids | 0.02 g | 0.4% |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 1.06 g | 5.6% |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.47 g | 4.2% |
% of the norm in 100 g* - approximate values for a middle-aged nursing woman.
Can it be used during breastfeeding?
The use of this product has its own timing, since seafood is considered allergic.
Despite the benefits of shrimp, pediatricians do not recommend including them in the diet for breastfeeding. Some people talk about introducing it no earlier than three months after the birth of the baby, since seafood is fraught with invisible dangers, which will be discussed below.
It is best to eat shrimp boiled. In large stores they are sold frozen, sometimes semi-boiled. In any case, cooking is always necessary. As for canned shrimp, they need to be treated with caution, as some manufacturers may use additives that will not bring any benefit to either mother or baby.
Shrimp are a storehouse of protein, which is easily absorbed by the body. In addition, seafood contains large amounts of:
- rare amino acids that have a positive effect on the body;
- iodine and calcium, which are needed for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland;
- zinc, which is responsible for the proper production of hormones;
- a wide range of vitamins;
- a set of amino acids that are valuable for the nervous system;
- potassium, which strengthens the cardiovascular system;
- rare elements that participate in metabolism, optimize and increase it;
- magnesium and sodium, which affect the normal functioning of body systems.
100 g of shrimp contain the daily requirement of iodine.
Beneficial features

Mother and baby can experience all the benefits of shrimp only if the product does not cause allergies or individual intolerance, and its quality is beyond doubt. In this case, reasonable consumption of shrimp will enrich the composition of breast milk and obtain valuable nutrients. We list the main beneficial properties of shrimp:
- Contains rare amino acids and easily digestible protein.
- Iodine and calcium help the thyroid gland. Shrimp contain these components in concentrations exceeding many other seafood.
- The rich vitamin and mineral composition ensures the coordinated functioning of all organs and systems, improves hematopoiesis, promotes the formation of bone and muscle tissue, the synthesis of hormones, and strengthens the immune system.
- Contains Omega-3 fatty acids, which are especially valuable for the intellectual development of infants.
- They are a powerful antioxidant and prevent the development of cancer cells.
- Provide skin elasticity and preserve youth.
Is it possible while breastfeeding

Shrimp are not included in the list of foods prohibited during breastfeeding: they can be consumed in the absence of allergies and individual intolerances.
Nutritionists note the likelihood of harm to shrimp due to the ability to absorb radioactive substances from sea waters. The fact has not been proven by science, but indicates the need for the right choice of product, especially during breastfeeding.
As for the FDA's recommendation, the agency does not see a need to ban the consumption of shrimp while breastfeeding. Moreover, according to the FDA, women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consume 220 to 340 grams of a variety of seafood per week from lower-mercury options [3].
How to include in the diet during breastfeeding
Due to the risk of allergies in infants, the product is introduced into the diet very carefully. The first test is done before 12 noon, the baby’s reaction is monitored for 48 hours. Signs of allergies - rash, bowel movements, bloating, colic.
Rules:
- The permissible norm for 7 days is 220-340 grams.
- The reaction to the test is monitored for at least two days (preferably 3 days).
- If signs of allergy appear, the introduction of the product is postponed for a month.
Even if the baby reacted calmly to seafood, it is unacceptable to overuse shrimp.
Not uninteresting pediatrician E. O. Komarovsky does not recommend shrimp during breastfeeding due to the risks of containing heavy metals. The doctor notes that the product’s ability to absorb toxins threatens the baby’s fragile body with severe poisoning. But if the child is not prone to allergies, and the nursing mother is confident in the safety of seafood, shrimp can be included in the diet.
Is it possible to eat shrimp while breastfeeding?

Unfortunately, the potential danger of shrimp for a nursing mother and child is high. This product is a strong allergen. We must not forget about the ability to accumulate harmful substances from the water in which shrimp lived. The meat may contain radioactive compounds and heavy metals if the crustacean was caught in its natural environment. Individuals raised on special farms are often fed chemicals that ensure rapid growth and antibiotics. Harmful components are not destroyed during heat treatment or freezing. Even if the shrimp is initially “clean”, there is a risk that the product has spoiled due to improper storage or long-term transportation.
The least dangerous are freshly caught shrimp caught in ecologically clean marine areas, the origin of which is beyond doubt. However, obtaining such a product is problematic.
In general, seafood is an allergen, but exactly how your baby will react can only be known through experience. Try a few things first, rather than a whole plate, so that if anything happens, the consequences are minimal.
*koza*
https://www.u-mama.ru/forum/kids/0–1/193566/index.html
This is a very strong allergen. I wouldn't eat.
Katy
https://www.baby.ru/blogs/post/46573782–33597392/
Seafood is one of the most powerful allergens! My child was so sprinkled with caviar that he was then treated for almost a month :(( but my friend’s child does not have any reaction to seafood. Try a little, look at the reaction, just don’t overdo it, the allergy can have a cumulative effect, it may not work for 3 pieces nothing, but if you eat a lot or often, you may shy away.
Olga
https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/breastfeed/1110329
Why are shrimp dangerous during lactation?
It is important for a nursing mother to eat right. It should be remembered that shrimp are strong allergens and should not be eaten in the first 3-4 months after birth. A child may have an allergy to seafood, which is expressed in the appearance of red spots, itching, swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat and nose.

The shrimp sold in the store are not grown in natural conditions. They often contain antibiotics and a variety of growth hormones. All these substances also pose a danger to a fragile child’s body.
Mom also needs to remember that seafood, especially shrimp, also contains radioactive compounds, heavy metal salts and other harmful substances. Throughout their lives they accumulate them in their bodies. As a result, such a product is dangerous not only for the mother, but also for the baby, since all these substances penetrate into breast milk.
Prawns that have been re-frozen or stored incorrectly will also not be beneficial. It is best for a nursing mother to eat freshly caught ones. But such an opportunity is not always available. Therefore, it is important to select and store the product correctly.
Directions for use for nursing mothers
If, after weighing the pros and cons, you decide to include shrimp in your diet during lactation, try to follow the following recommendations:
- Include in the menu no earlier than the child turns 3 months old.
- Use only boiled. Fried, smoked, raw, salted, spicy shrimp can cause digestive problems for mother and baby and negatively affect the taste of breast milk.
- You can try a small piece of shrimp for the first time. Observe your child's reaction for two days. If a rash, redness of the skin or digestive disorders appears, the product must be excluded from the diet. If there is no negative reaction, increase the amount of product gradually - include it in the diet once a week.
- It is allowed to consume more than 100 g of boiled shrimp per day no more than once a week.
- If the shrimp are bright pink, they have been previously boiled. Freshly frozen crustaceans have a translucent hue.
- Include in your diet only high-quality shrimp, the freshness of which is beyond doubt.
How to choose and cook
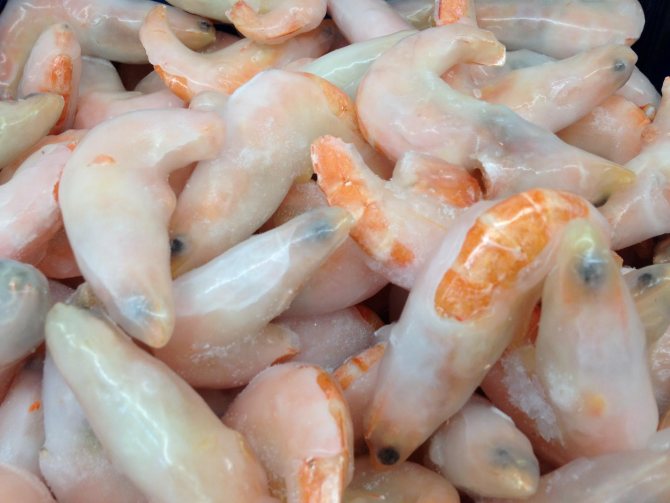

When choosing shrimp in a store or market, be guided by the following principles:
- Preference should be given to freshly frozen shrimp in the shell, which have not been previously cooked. Heat treatment and re-freezing have an extremely negative impact on the nutritional value of seafood.
- The safest shrimp are cold-water shrimp grown in Canada, Norway, Lithuania, and the Atlantic. Look on the packaging for information about where it was caught.
- Consider the shrimp themselves. Black heads are a sign of improper storage or re-freezing of crustaceans. Green heads are a normal variant, which means the shrimp fed on plankton in the sea.
- There should not be a thick layer of ice on the shrimp. Ideally, the surface is smooth, with a thin glaze of transparent ice.
Before boiling, the shrimp are thawed at room temperature. Cook crustaceans in boiling water with a little salt for 3–5 minutes. Immediately before consumption, shrimp are peeled and only the meat is eaten.
How to properly introduce shrimp into the diet of a nursing mother
The introduction of a new product into the diet is always carried out according to the same scheme. You should try shrimp for the first time when your baby is at least three months old. It is best to start trying crustaceans six months after giving birth. You need to monitor the child’s reaction for three days: if signs such as redness of the skin or mucous membranes, rash or itching appear, you need to stop eating shrimp for another 2-3 months. But in the absence of unpleasant symptoms, you can safely eat the product. The following rules should also be taken into account:
- For the first time, it is enough to try only one medium shrimp. Such a portion will not harm the child even if an allergic reaction occurs.
- Closely monitor the baby's reaction to the introduction of a new product into the diet of a nursing mother.
- Experts recommend that if an allergy occurs, you should postpone the introduction of shrimp until the end of lactation. Only after this can the mother eat the product without fear of harming the child.
- The norm of shrimp for a woman who is breastfeeding is only 3 medium-sized pieces. You can eat up to 10 shrimp per week.
- The product is tried for the first time in the morning. This makes it possible to monitor the child throughout the day and, if necessary, take measures so that the baby is not bothered by colic and other unpleasant symptoms at night.
Compliance with simple rules contributes to the normal course of the period of introducing shrimp into the diet of a nursing mother and reduces the risk of unpleasant consequences.
Benefits of shrimp
Like many seafood, shrimp is a valuable protein. We need it to build muscles, form collagen fibers, and maintain youthful skin. In addition, the product contains vitamins A, B, D, E, C, Omega 3 acids, trace elements Ca, K, Fe, P, F, Cu, Zn, Se and, of course, I, such an important element for the proper functioning of the thyroid glands. The content of I in shrimp is very high. For understanding, 100 g of product contains its daily requirement.
Another big plus is the low calorie content of the product. 100 g contains only 90 kcal. Therefore, they are indispensable in dietary and healthy nutrition.
Regular consumption of shrimp reduces the likelihood of tumors, has a positive effect on the human circulatory system, normalizes metabolism, and improves the condition of hair and skin.