Why does anemia occur?
Prerequisites for the development of anemia during breastfeeding arise in the third trimester of pregnancy and during childbirth.
The volume of blood in the vascular bed increases, since most of it is constantly in the placenta, oxygenating both the mother and the fetus, but the red blood cells remain insignificantly, which leads to a “dilution” of hemoglobin. In a woman after 30 weeks, a relative decrease in hemoglobin is physiological - this means that there is more plasma than formed elements. This is a mechanism of adaptation to the upcoming birth, so that this amount of fluid does not in any way affect the general condition of the woman, when a woman can simultaneously release up to 500 ml of blood.
What is hemoglobin and how important is it after childbirth?
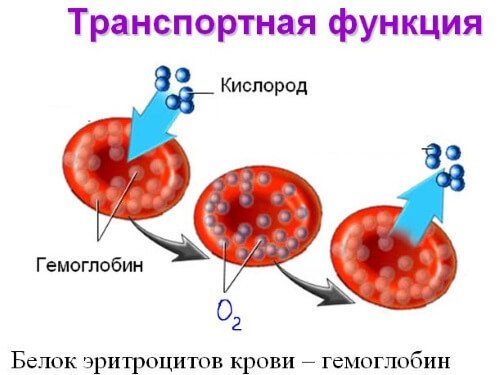
Hemoglobin is a protein compound with an iron molecule that is important for the proper functioning of the body. Hemoglobin, thanks to iron, has a red color and gives the same color to the red blood cells that it contains. Erythrocytes are also called red blood cells. The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen molecules throughout the body, which provides each cell with “breathing”.
Firstly, low hemoglobin has bad consequences for the woman herself, and even more so for the fetus and after childbirth there should not be low hemoglobin. When hypoxia occurs in the later stages of development, the child’s brain is the first to suffer, and growth and development slows down. If the problem is not resolved before delivery, the birth may be premature. This includes early breaking of water and increased blood loss during childbirth. In the worst cases, the baby may die in the first day of life.
After childbirth, low hemoglobin can occur for several reasons. If you did not pay enough attention to the hemoglobin level during pregnancy. If a lot of blood was lost during childbirth. If there are diseases of the circulatory system, heart failure, some infectious diseases. If the above symptoms appear, then you must definitely reconsider your diet, add meat, fatty sea fish, beef tongue, egg yolk, green apples, walnuts, and dried fruits to your diet.
You shouldn’t put off taking care of your health until later, because you simply won’t have the strength to care for your baby, and fainting and headaches may become more frequent. If nutrition no longer helps, then you should definitely consult a doctor to prescribe special iron-containing medications that are approved for breastfeeding.
Anemia in a nursing mother develops as a consequence of a deficiency of a chemical element such as iron. It is necessary not only in the process of hematopoiesis, but also to maintain other vital functions of the body. Iron is an important component of the complex protein hemoglobin, which helps transport oxygen molecules throughout the body.
Anemia after childbirth
Anemia cannot be diagnosed based on clinical presentation or laboratory tests alone. This diagnosis is made based on a set of signs of iron deficiency. So, low hemoglobin after childbirth has the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- dyspnea;
- weakening of muscles;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- “mesh” or veil before the eyes;
- headache;
- decreased physical and mental activity.
Such a state of health in itself, without a blood test, does not indicate anemia, but it should be a reason to determine the level of hemoglobin. To diagnose anemia after childbirth, you will need not only a general blood test, which will show the level of hemoglobin in the blood, but also a biochemical analysis. After two weeks of treatment, the tests will have to be repeated in order to determine the effectiveness of the chosen way to overcome iron deficiency.
Hemoglobin is normal in women after childbirth. How to quickly raise?
A woman's body requires more iron-containing protein than a man due to monthly blood loss. But the hemoglobin rate increases even more with the onset of pregnancy. This need is explained very simply - the mother’s body must supply all the necessary substances, including iron, to the fetus growing in the womb.
Doctors recommend that pregnant women increase their hemoglobin levels as the fetus grows. Because not only a lack of iron has a detrimental effect on both the organism growing in the womb, but also on the maternal one. Excess hemoglobin also entails adverse consequences. Therefore, there are iron standards for a pregnant woman depending on the trimester:
- I trimester - from 114 to 134 g/l.
- II trimester - from 112 to 128 g/l.
- III trimester - from 111 to 129 g/l.
Hemoglobin levels are determined in the laboratory. To carry out a blood test for hemoglobin, it is enough to donate capillary blood from a finger. And to determine the indicators of glycosylated hemoglobin, blood substance is taken from a vein.
A woman's body requires more iron-containing protein than a man due to monthly blood loss. But the hemoglobin rate increases even more with the onset of pregnancy. This need is explained very simply - the mother’s body must supply all the necessary substances, including iron, to the fetus growing in the womb.
- I trimester - from 114 to 134 g/l.
- II trimester - from 112 to 128 g/l.
- III trimester - from 111 to 129 g/l.
Hemoglobin is a type of protein, thanks to which oxygen is freely transmitted in the body and fully absorbed by it.
A reduced level of hemoglobin thus prevents the organs from receiving oxygen in the required quantity, and this can cause the development of various problems both in the pregnant woman herself and in the fetus:
- Problems with the development of the child's brain.
- Problems with the development of internal organs and the circulatory system.
- Weakness of a pregnant woman, nausea and lethargy, a sharp deterioration in health.
- Problems with the child’s absorption of other beneficial substances and microelements.
- The likelihood of premature birth.
- Increased bleeding during childbirth.
- Water breaking too early.
A drop in hemoglobin before childbirth can even cause the death of the child - therefore this indicator must be treated very carefully.
Immediately after birth, hemoglobin may drop, but after a month or so it should return to normal levels of around 120 g/l. If this does not happen, then you need to consult a doctor.
Many girls in the first months of pregnancy do not suspect that the cause of their illness is iron deficiency anemia. Its symptoms are weakness, pale skin, fatigue. They arise due to the fact that during this period the mother’s body also provides blood to the fetus.
Low levels of iron protein indicate anemia. Its minimum value of 110 g/l is the starting point during pregnancy and during the first months after the birth of the baby. After some time it stabilizes. The norm for women after childbirth is 120 g/l.
What is anemia?
The main culprit of the disease is a blood protein combined with iron. It takes part in gas exchange, since these molecules exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen and distribute it to all tissues. A decrease in the level of this microelement is called anemia. It is also popularly called anemia.
During anemia, hypoxia occurs, that is, oxygen starvation. This provokes a disruption of all body activities.
The acute form most often occurs during or after the birth process. The woman in labor has a hard time bearing it because the body does not have time to adapt.
The chronic form of this pathology occurs due to a gradual decrease in the number of red blood cells.
Their body gets used to being constantly in a state of oxygen starvation and therefore tolerates everything much easier. We will discuss further how to increase hemoglobin after giving birth to a nursing mother.
Representatives of the fairer sex require more iron than men. This is due to monthly bleeding. With the onset of pregnancy, the hemoglobin norm in women increases, because during this period the body must provide nutritional components to the developing fetus.
Read also Treatment of anal fissure after childbirth
After the birth of a child, the need for an iron-containing element does not decrease, since the lactation period begins. And only when the baby begins to eat on his own, the mother’s responsibility to provide the child with useful substances is removed.
Pregnant women should increase its level as the baby develops in utero. Low levels have a bad effect on fetal growth. But a high level of this protein can cause complications. Thus, its level should normally correspond to the trimester:
- In the first trimester from 114 to 134 g/l.
- In the second trimester from 112 to 128 g/l.
- In the third - from 111 to 129 g/l.
A pregnant woman's iron level is determined from blood tests.
Reasons for the decline
Before treating anemia, the cause of its occurrence must be found. By eliminating factors that negatively affect the body, you can find out how to quickly increase hemoglobin after childbirth. Without finding out why hemoglobin is low, no medications will help.
In pregnant women, as well as in postpartum women, the causes of this disease may be the following:
- If there are several fetuses in the womb.
- Filling the needs of the placenta and umbilical cord.
- Excessive bleeding during the birth process.
- An increase in blood plasma, resulting in a decrease in the number of circulating red blood cells.
- Haemorrhoids.
- A lot of calcium, which prevents iron from being absorbed.
- Complications of chronic pathologies.
Since any open bleeding can result in low hemoglobin in mothers after childbirth, there can be many causes. It is possible to find out the specific source of the disease only after a complete examination.
Deficiency Symptoms
After labor, iron deficiency is very acute. Symptoms of low levels of this trace element are as follows:
- headaches and dizziness;
- hard to concentrate on one subject;
- weakness and apathy;
- drowsiness;
- decreased performance.
An urgent visit to the doctor is necessary for a nursing mother if she experiences vomiting, nausea and fainting. This should not be attributed to overwork or anemia; pathologies with identical symptoms may have worsened.
How can a nursing mother increase hemoglobin after childbirth, since she cannot take medications and needs to adhere to a diet during lactation? There is no need to panic, as deficiency can be eliminated with proper dietary adjustments.
Treatment for breastfeeding includes the use of the following products:
- buckwheat and wheat groats;
- dried mushrooms;
- eggs;
- apples preferably homemade;
- beet;
- asparagus;
- currant;
- oatmeal porridge;
- sauerkraut.
This list can be continued for a long time, but in other products the amount of iron is slightly less. A new product is introduced into the diet gradually. It is imperative to observe the reaction of the child’s body (with breastfeeding) to the innovation. If a child has an allergy or intestinal problems, the product is removed from the diet.
Nowadays, many children suffer from food allergies. And it happens that it is difficult to raise low hemoglobin with food after childbirth.
In this case, the doctor can tell you how to increase hemoglobin after childbirth by prescribing a general blood test. The doctor will prescribe iron supplements in the correct dosage so as not to harm either the mother or the baby.
A woman will need to adhere to the correctly calculated norm of this microelement.
Medicines containing iron:
- Ferrum Lek.
- Actifferin.
- Sorbifer Durules.
- Fenyuls and so on.
Taking these medications helps to effectively increase iron levels in women during the postpartum period. The drugs are mainly prescribed for moderate (70-90 mg/l) and severe (69 ml/g and below) forms of anemia.
Conclusion
Let us repeat what to do after childbirth if the mother is diagnosed with anemia. If you feel unwell after the birth of your baby, contact your doctor. Anemia is a serious pathology that causes complications in the cardiovascular system, blood pressure problems and other diseases that do not improve the life of the mother and child.
Methods for increasing hemoglobin after childbirth in a nursing mother
Low hemoglobin after childbirth in a nursing mother is increased using different methods. A number of foods are great for raising iron levels. But in especially severe or advanced cases of hemoglobin deficiency in a woman in labor, one cannot do without pharmacological preparations containing iron and ascorbic acid for its rapid and high-quality absorption.
How to increase hemoglobin after childbirth in a breastfeeding mother using products (iron content is indicated in micrograms):
- Asparagus (9000 mcg).
- Buckwheat (6650 mcg).
- Oat milk or Hercules cereal (3630 mcg).
- Doctor's bread (2800 mcg).
- Wheat cereal (2700 mcg).
- Dried mushrooms (2600 mcg).
- Chicken eggs (2500 mcg).
- Fresh domestic apples (2200 mcg).
- Wine beet (1400 mcg).
- Black currant (1300 mcg).
- Sauerkraut (1300 mcg).
There are actually many more foods rich in iron. True, the iron content in them may be less significant. It is necessary to select a diet during breastfeeding, taking into account the fact that some products and ingredients in food can cause an undesirable skin reaction in the baby or in the digestive system.
Lactation directly depends on the diet of the nursing mother.
How to increase hemoglobin after childbirth in a nursing mother through medications should be consulted with a doctor. Because each iron-containing drug has a different dosage. And in order to avoid overdose of the mother and newborn, you need to strictly adhere to the prescribed daily iron intake.
- Sorbifer Durules.
- Fenyuls.
- Actifferin.
- Ferrum Lek.
- Maltofer and others.
The advantage of pharmaceutical drugs is their quick effect. And the advantage of food is complete safety and no risk of overdose. The choice of method to replenish hemoglobin after childbirth in a nursing mother depends on the stage of anemia. With mild (90–110 mg/l) iron deficiency anemia, you can get by with foods rich in iron. But even with moderate (70–90 mg/l) and especially severe (69 mg/l and below) it is better to resort to professional means to restore hemoglobin levels.
In nursing mothers, the causes of iron deficiency anemia are varied:
- large loss of blood during childbirth,
- decreased blood levels due to postpartum discharge, which can last up to 10 days,
- blood loss associated with the restoration of menstruation,
- frequent infectious and viral diseases,
- liver diseases,
- chemical air pollution and excessive mineralization of drinking water, which leads to poor absorption of the mineral,
- lack of ascorbic acid and other vitamins also cause iron deficiency,
- reduction in the amount of iron received from ready-made meals due to dietary intake (limitation in fresh cow's milk, raw fruits),
- high iron consumption associated with breastfeeding,
- another pregnancy that coincides with continued natural feeding,
- early conception, which occurred shortly after childbirth.
Diet and nutrition
Reviewing the diet is an important condition for the successful treatment of iron deficiency anemia. Natural sources of iron are certain foods, which should be consumed daily.
High concentrations of iron are found in the following foods:
- carrots, radishes, turnips;
- garlic, celery, onion, horseradish;
- pumpkin, beets;
- blueberries, blackberries;
- lettuce, sorrel, nettle;
- potatoes, cucumbers, tomatoes;
- strawberries, strawberries;
- all types of cabbage;
- peaches, apples, pear, quince;
- lentils, peas, beans.

However, the main sources of natural iron are all types of red meat, liver, white meat fish, chicken yolk, cocoa, nuts, seafood and cereals.
The daily requirement of a nursing woman is 18-20 mg of iron. An overdose of iron occurs when 200 mg of the substance enters the body per day.
How to increase hemoglobin in a baby who has already been introduced to complementary foods
Every effort must be made to establish breastfeeding, and for the first months (or even years) of the baby’s life, breastfeed. This will be the best prevention of anemia in a child. Immediately after birth, you need to put the baby to the breast, then colostrum, once in the baby’s intestines, will start the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, the intestinal cells will learn to absorb all the necessary substances from food, including iron.
Nevertheless, the mother needs to monitor her diet, at least in order to replenish the supply of substances necessary for her health. To maintain normal hemoglobin levels, it is necessary to consume foods containing iron in sufficient quantities. And it is not at all necessary that these are products of animal origin.
Here are the top foods that are leaders in iron content:
- Turmeric, spirulina.
- Green sprouted buckwheat.
- Pomegranate and beets.
- Green apples.
- Sea kale.
- Pumpkin seeds, flax.
- Dried apricots.
- Spinach.
- Walnuts.
- Rose hip.
- Lentils and beans
— vitamin C helps its absorption (you can, for example, cook lentils with broccoli or add lemon);
- calcium complicates the absorption of iron, as it slows down its absorption;
- Tea and coffee are also not advisable if you want to maintain healthy hemoglobin levels, as they flush iron from the body.
If the child has already been introduced to complete complementary feeding (preferably no earlier than six months), then hemoglobin can be increased by adding the iron-containing products listed above to his diet. If your baby is introduced to complementary foods before six months, the absorption of iron from breast milk will become worse. It has also been noted that anemia is common in children who are fed cow's and goat's milk.
Be sure to include berries in your child’s diet (even frozen or dried, if it’s winter): blueberries, strawberries, black currants, cranberries.
With the beginning of life, all the baby’s organs are actively forming and growing. Hemoglobin ensures the movement of oxygen throughout the cells of the body.
Lack of oxygen - hypoxia - slows down the development of the baby. Of course, at first it is difficult to notice, since the baby is very small. But soon it is possible to detect inhibition in development in comparison with healthy peers.
How can you increase hemoglobin?
The first question that should be answered when making a diagnosis is how to increase hemoglobin in a nursing mother after childbirth? There are several ways to solve this issue, namely:
1. Drug therapy aimed at replenishing daily iron deficiency. 2. Prescribing a diet rich in foods high in iron. 3. Traditional methods.
Taking medications for anemia is the main measure to eliminate it. You cannot self-medicate or prescribe medications on your own. Only a doctor can choose the right medicine and the required dosage. At the moment, several iron-containing drugs can be distinguished:
Maltofer; Totema; Ferrum Lek; Sorbifer Durules.
Drug therapy can last from 2 months to six months, depending on the well-being of the nursing mother. At the same time, some people mistakenly believe that such treatment has a bad effect on the child’s health, but this is not the case. Iron is not concentrated in breast milk and does not cause side effects. When taking the medicine, it is best to drink it with juices rich in vitamin C. This will allow iron to be better absorbed in the body.
Diet and healthy foods
A proper diet is the key to successful recovery and the return of laboratory parameters to normal. The diet for anemia should be varied and necessarily balanced. A nutritionist can help in this matter and can easily create an optimal nutrition plan that is beneficial for both the mother and the infant. First of all, you need to decide on a list of foods rich in iron. In this case, this list is very extensive, but when talking about the lactation period, it is significantly reduced. After all, any new product consumed by a nursing mother can negatively affect the child in the form of allergic reactions or intestinal colic.
Products with high iron content
There are several foods that are rich in iron:
Spinach; egg yolk (recommended 1 piece per day, quail ones are especially useful); walnuts (up to 150 gr.); seaweed; dairy products; rosehip decoction; fresh pomegranate juice diluted with water 50/50; green pea; fish; apricots; black currant; meat (veal, rabbit, beef, chicken); raisins, dried apricots and prunes; buckwheat; apples; honey; radishes and turnips; potato; White cabbage; strawberries or wild strawberries (eat with caution, allergic rashes are possible in the baby); pear; wheat bran, etc.
It is best to cook food by steaming or in the oven, avoiding heat treatment with vegetable oil. With each new product introduced into the diet during the lactation period, be sure to monitor the child’s reaction.
There are also a few other key points worth paying attention to:
1. Iron is better absorbed in the body if taken with foods enriched with vitamin C (vegetables and citrus fruits).
2. Be sure to monitor the amount of iron entering the body. The norm is 20 mg, of which about 2.5 comes with food, and the rest due to the action of medications. 200 mg per day will be an overdose, so you should be careful.
3. Black tea, coffee and fermented milk products contribute to poorer absorption of iron. Replace it with green or avoid consuming it during meals.
4. Pomegranate juice is very beneficial for the body, but it can cause constipation.
5. When replenishing iron deficiency, you need to pay more attention to animal products. Plant proteins are only 5% useful in this regard. But at the same time, vegetables and fruits contain a lot of valuable vitamins that help in the absorption of iron. Harmony can only be achieved with the correct diet. Attention: It is best to consult a doctor and agree on the possibility of consuming recommended products. This will help avoid complications in the child.
Treatment
A young mother should not attribute the appearance of the first signs to general fatigue after pregnancy and childbirth. Of course, caring for a baby takes a lot of energy, but with good health, the mother’s condition will be good. If symptoms of anemia appear, it is very important to consult a physician and get a blood test.
To restore iron levels, it is important to strictly follow all medical instructions.
To increase the amount of iron, you should include iron-containing foods in your diet. Special preparations and vitamin-mineral complexes also play a major role in treatment. The type of medications, their dosage and course duration can only be prescribed by a therapist. The condition can improve significantly quickly. However, for complete recovery it is important to complete the therapeutic course, otherwise a relapse of the pathology with a more vivid clinical picture is possible.
What does a doctor do
Based on the results of a clinical blood test, studying the patient’s medical history and appearance, the doctor develops a treatment regimen. Treatment mainly consists of several principles:
- taking medications - the duration of the course and dosage of medications is determined individually,
- following a special diet - increasing the diet of foods high in iron and limiting foods with calcium and phosphorus,
- lifestyle change,
- protection from risk factors.
Do not underestimate the seriousness of anemia, which can cause oxygen starvation of the body, suppression of the nervous system, preconditions for developmental delays and deterioration of the child’s condition. You can prevent the occurrence of this phenomenon by creating a competent menu for your baby.
During breastfeeding, the baby will be able to receive the necessary iron until six months of age, since milk contains much more nutrients than other foods. By the first year of life, the child’s menu expands, and therefore it is necessary to introduce buckwheat, apples, beets, meat, liver, apple juice to replenish the iron deficiency in the body.
In order to increase the level of red blood cells in the blood, the diet of an infant should include:
- Fruits: blueberries, pomegranate, strawberries, apples, dried apricots;
- Meat: beef, turkey, liver, veal;
- Wheat flour products.
If drug therapy is required, it is best to consult a pediatrician who can recommend the necessary medications. Parents themselves can purchase special products containing iron. They are released in drops. The treatment will not take much time, but will be effective and with long-term results.
Treatment is based on the cause that caused it, as well as the degree of neglect. Thus, signs of mild anemia after childbirth go away with a diet enriched with iron. But moderate and severe cases must be subjected to drug therapy. A hemoglobin level below 70 g/l and the presence of other symptoms (pallor, tachycardia and others) are an indication for transfusion of blood components.
Treatment of anemia is a long process, at least a month. Even with normal test results, you still need to take the pills for some time to replenish your iron reserves.
Drugs
There is a wide variety of drugs to increase the level of iron in the blood, which will also increase the formation of hemoglobin. Almost all of them are allowed both during pregnancy and during breastfeeding. The most popular and effective are totema, maltofer, ferronal, dzheferol and the like.
Many of them, in addition to iron, contain additional microelements that contribute to better absorption of iron. Most often these are vitamin C and B12, manganese, copper, folic acid. Also, when choosing a drug, you should take into account which iron - divalent or trivalent - is included in the drug. This affects the degree of absorption of decao. In the gastrointestinal tract, trivalent is absorbed, and for two, an oxidizing agent is required, often vitamin C plays this role.
In most cases, tablet forms are used, but intramuscular injections are also possible. They are most often prescribed to treat moderate to severe anemia.
It happens that iron supplements cause stool disturbances such as constipation, as well as a change in its color to a darker one. If necessary, you need to take, for example, lactulose and others.
The dosage regimen can only be prescribed by a doctor, based on the severity of symptoms and test results.
The use of dietary supplements and homeopathic remedies is possible, but they are more suitable for preventing relapse or in combination with iron-containing drugs.
Lifestyle
Plays an important role in maintaining normal blood counts. If you have anemia, you should include as many red foods and its shades as possible in your diet. This is meat (beef, pork to a lesser extent), (beef in this case is better than chicken), buckwheat, legumes, apples, pomegranates and others. Of course, breastfeeding women should use them with caution, as they can cause allergic reactions in the baby, problems with gas formation, etc.
Fresh air is also important for girls with anemia. Regular walks will help to quickly reduce symptoms, as more oxygen is consumed in such conditions.
Traditional methods
If a woman is diagnosed with anemia after childbirth, treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor. And only in addition to it can you use various traditional medicine recipes.
Recipe 1. To do this, you need to take nettle leaves, yarrow flowers and dandelion root in equal parts. Then you should brew the resulting mixture in water and let it brew for several hours. Everything is done at the rate of 1 - 2 tbsp per 300-400 ml of water. The resulting infusion should be taken half a glass 3-4 times a day for several weeks.
Recipe 2. You need to grate fresh carrots on a fine grater. Radish and beets should be chopped in the same quantity. Then squeeze the juice out of these vegetables. The resulting solution should be stored in a cool, dark place. Drink 1 tbsp. l. 2 - 3 times a day for several weeks.
Recipe 3. You need to take 50 - 70 g of hawthorn berries and 200 - 250 ml of dry red wine. Mix the ingredients and let it brew for 2 - 3 weeks, then take 2 - 3 tbsp. l. 3 - 4 times a day for at least a month.
Recipe 4. Peel one medium pomegranate and squeeze out the juice, then mix with 200 - 300 ml of dry red wine. Use the resulting solution 2 - 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. l. within a few weeks.
Recipe 5. You should take lungwort officinalis 30 - 50 g and leave it in 200 ml of alcohol for 2 - 3 weeks in a dark, cool place. Then strain and drink 2 tbsp. l. several times a day.
Anemia after childbirth is a fairly common occurrence. Sometimes women feel a loss of strength, weakness, drowsiness, skin changes for a long time and do not know what caused this condition.
Anemia can only be detected in conjunction with clinical tests prescribed by a specialist. This pathology has no obvious symptoms, so it is almost impossible to determine it on your own. Grade 1 anemia after childbirth can be corrected with nutrition, but moderate and severe anemia can only be overcome with the use of medications and sometimes even blood transfusions.
Prominent representatives of iron-containing preparations are Totema, Maltofer, Sorbifer Durules, Ferrum Lek.
The listed products are available in the form of solutions, drops, syrups and chewable tablets. The drug Maltofer is a universal remedy for the treatment of this disease in both mother and child. However, the use of this remedy for anemia not caused by iron deficiency is highly discouraged.
Ferrum Lek is available in tablet and syrup form, and is a very effective remedy for combating anemic symptoms in pregnant and lactating women. The use of Ferum Lek is contraindicated in other types of anemia.
Sorbifer Durules is combined and contains an iron component and ascorbic acid. Close attention should be paid to the dosage of this substance, which is selected by the doctor individually. In the presence of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, the use of the drug is not recommended.
Totem is considered to be the drug of choice for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in pregnant and lactating women. The release form of the drug is a solution. The use of Totema is contraindicated in the presence of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
How to increase hemoglobin after childbirth for a nursing mother: causes of deviations
During the period of bearing a child and breastfeeding, the mother's body's need for iron increases. With its deficiency, iron deficiency anemia may begin to develop.
In order to prevent the development of the disease, you need to monitor the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
For nursing mothers, there are different ways to increase the amount of hemoglobin - from medications to special diets and herbal infusions.
Symptoms and signs of decreased hemoglobin
Clinical signs of anemia do not have clearly defined boundaries. The most common symptoms of low hemoglobin are:
- hair loss;
- brittle nails;
- feeling of coldness in the feet and palms;
- headache;
- low pressure;
- drowsiness and loss of strength.
If a nursing woman experiences 3 or more signs from the above list, then she needs to see a doctor to make or exclude a diagnosis.
In severe cases, fainting, short-term loss of orientation in space, a decrease in heart rate to 40 beats per minute, and visual hallucinations may occur.
Laboratory indicators
In the last trimester of pregnancy, the hemoglobin level decreases by 10-15 units from the norm for a healthy, non-pregnant woman. When breastfeeding, reference standards are also reduced by no more than 20 units. If there was a large blood loss during childbirth, then hemoglobin may drop to 90 g/l, but these indicators should return to normal by 10 days after birth.
| Laboratory indicators of hemoglobin levels in the blood of women | |
| Healthy non-pregnant woman, 18-65 l | 120-150 g/l |
| 32-45 weeks of pregnancy | 110-115 g/l |
| Difficult birth | 90-100 g/l |
| The first three months under guards | 110-120 g/l |
| 4-12 months guards | 120-130 g/l |
For laboratory testing of hemoglobin levels in women after childbirth, a capillary (from a finger) or venous method of blood sampling is performed. In both cases, the test should be taken on an empty stomach, and medications containing iron and animal blood serum should be avoided.
Causes of anemia in a nursing mother
Rarely does a woman in labor avoid the problem of iron deficiency in the blood. For 9 months, all vitamins, minerals, macro and microelements were spent on the formation and gestation of the fetus, which caused a deficiency of nutrients.
Also, birth factors and injuries to the genital tract lead to heavy blood loss, which reduces the total amount of blood in the body, and as a consequence, the number of red blood cells. The number of red blood cells is directly related to the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
If there is a lack of the former, the latter also decreases.
Low hemoglobin in a nursing mother may occur due to the following reasons:
- blood loss during childbirth;
- postpartum vaginal discharge;
- immunity weakened by pregnancy and childbirth;
- high consumption of iron in breast milk;
- diets to eliminate allergies in a child;
- rapid pregnancy immediately after childbirth or during guardianship.
In some cases, a newborn baby is allergic to foods that are familiar and even necessary for the mother. Women sacrifice their health and go on strict mono-diets so that allergens do not pass into breast milk.
Such sacrifices can lead to low hemoglobin, calcium, potassium and magnesium deficiency.
If a child is found to be allergic to the foods that the mother eats, then the best solution would be to switch the child to artificial formulas, and for the woman to eat nutritious food rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals.
How can you increase hemoglobin?
You can increase hemoglobin after childbirth using both medications and traditional methods. If iron deficiency is slight, doctors most often recommend enriching the diet with foods that increase hemoglobin levels. If anemia has developed into a chronic form, the deviation from the norm exceeds 20% or more, then medications that increase hemoglobin are prescribed.
Diet and healthy foods
To increase hemoglobin in a nursing mother after childbirth, you can use a protein diet, the main product of which will be red meat (lean beef, veal) and liver. The daily calorie intake of the diet should be adjusted upward by 10-20%, since the calorie intake of such a diet is not designed for a nursing woman.
You can also increase the hemoglobin level of a nursing mother with the help of beets, carrots, pomegranates, potatoes and grapes. It is also good to consume milk and fermented milk products daily. Freshly squeezed unpackaged juices are diluted with water in a 2:1 ratio, best apple, pear, grape and tomato. A nursing mother should always have fruits and vegetables in her diet.
Traditional methods
In ancient times, a nursing mother was able to increase hemoglobin after childbirth. Low hemoglobin is well cured by nettle tea. 1 tbsp. dry nettle leaves are poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 9-12 hours. Drink on an empty stomach in the morning for 14-21 days. Then a break in the course for a month, after which the use of the infusion is resumed again.
St. John's wort helps with low hemoglobin. This decoction can only be treated by women who are protected by barrier methods of contraception, since hormonal pills can fail with this herb. After childbirth, hemoglobin will return to normal within 1 month.
To prepare the decoction you need 100 grams of dried St. John's wort, 20 grams of dried dandelion and 0.5 liters of boiling water. The herbs are mixed and poured with boiling water. After cooling, the steamed herb is squeezed out, and the decoction is infused in a cool, dark place for 12 hours. Take 5 tbsp morning and evening.
, diluted in half a glass of warm water.
Diagnostics
Hemoglobin levels are checked repeatedly during breastfeeding. While a woman is in the maternity hospital, this test is taken at least three times (on the day of birth, the next day and upon discharge).
In the future, the schedule for taking tests is prescribed by the local doctor or visiting nurse. A nursing mother should undergo examinations and donate blood on time to prevent the development of chronic anemia.
The hemoglobin level is determined during a general blood test. In front of it, you cannot eat, smoke, or drink iron-containing medications 12 hours before donating blood.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of acute anemia, you need to follow simple rules:
- If there is prolonged bleeding, consult a doctor. Minor but long-term blood loss can lead to iron deficiency.
- Avoid blood donation in the first year after childbirth and for 6 months from the date of the end of the guard.
- Eat right - your diet should be rich in foods that contain a lot of iron.
- Avoid stressful situations, try not to get nervous.
- Boost your immunity and avoid getting sick.
Important!
Low levels of ascorbic acid in the body can lead to problems with iron absorption, so it is recommended to take preventive courses of vitamin C during breastfeeding.
A nursing woman should take care not only of the child, but also of her body, because the condition of the baby will depend on her health. When the first symptoms of anemia appear, you need to take a blood test and consult a doctor. The diet of a nursing mother should be rich in red meat, beef and rabbit liver, eggs, grapes, cabbage, tomatoes and red peppers.
Source: https://krovinfo.com/kak-podnyat-gemoglobin-kormyashhej-mame/
Low hemoglobin in infants: causes of pathology
Hemoglobin is a complex blood protein that contains iron. The lack of this protein certainly affects the supply of oxygen to internal organs.
The causes of anemia in infants are not always obvious, but the consequences of such conditions are in most cases predictable - first of all, the baby’s brain structures will suffer, they will cease to function adequately, which will ultimately lead to severe developmental delays.
In hematology, each age and gender has its own norm for quantitative hemoglobin indicators. And if the analysis reveals strong deviations from the norm, then they speak of the presence of anemic syndromes, and in most cases the child is urgently hospitalized in a hospital.
As soon as the baby is born, this reserve begins to gradually be used up and is completely exhausted by the age of six months. Provided that the child is breastfed. At this point, responsible parents introduce the first complementary foods to the baby’s menu, which allows them to fully replenish the iron supply.
In case of prematurity, this period is reduced in proportion to the severity of the baby’s general condition, but complementary foods are never introduced earlier than three months. Mothers of such children should pay special attention to the quality and composition of infant formula.
Therefore, when answering the question - why is low hemoglobin in an infant, doctors often point to underfeeding or an incorrectly formulated diet.
- While carrying the child, the mother herself also suffered from anemic syndromes.
- The course of pregnancy was complicated by blood loss or impaired placental circulation was noted.
- The baby inherited an infectious intestinal disease from his mother.
- Accelerated growth rate of a child during the first months of life.
- Imbalance in the composition of milk formulas that are fed to artificial babies.
- A small percentage of iron content in complementary foods given to children under 12 months of age.
- Prematurity, developmental defects, genetically acquired pathologies.
Iron deficiency in newborns has certain specifics, and primarily depends on the reasons that caused it. And in some cases, from clinical symptoms and diagnostic methods.
Anemia in an infant has quite complex causes that affect the formation of the fetus even in the prenatal period. As you know, the stored iron reserve begins to be used up immediately after birth, but the child is not yet able to replenish it on his own.
All the factors due to which the baby does not receive or absorb iron are the causes of anemia.
And yet, most often the problem is faced by parents of children who are bottle-fed. If low hemoglobin is detected in a 10-month-old child, the reasons may lie in various infectious diseases that provoke massive internal bleeding.
In this case, anemia is determined according to the same generally accepted principle, that is, by assessing the results of a biochemical blood test. Pay attention not only to the level of hemoglobin itself, but also to its relationship with other components.
Anemia is said to occur when the protein level is below 110 g/l.
Low hemoglobin in a nursing mother: how to increase levels with diet and folk remedies
The first thing to do when anemia is diagnosed is to adjust the diet of the nursing mother. Food is a natural source of both heme and non-heme iron. That is, the menu must include not only meat, but also vegetables, herbs, cereals, and dairy products. You need to eat not only when you feel hungry, but without fail: at least five times a day, but in small portions.
The main sources of natural iron: red meat, organ meats, sea fish, egg yolk, all types of nuts, cocoa, seafood and cereals. The daily requirement of a nursing mother is within 20 mg of iron. An overdose is detected when more than 210 mg is consumed.
What does traditional medicine offer? Firstly, decoctions from black currants, rose hips or chokeberry. They are brewed like regular tea, infused in a thermos for at least 12 hours and taken half a glass three times a day. Secondly, a nursing mother can purchase a special herbal mixture at the pharmacy that helps stabilize hemoglobin levels and increase the number of red blood cells. It is brewed in the same way.
However, these are just auxiliary methods, and they will not be effective if traditional treatment is abandoned.
Iron cannot be adequately absorbed if the body does not receive adequate amounts of vitamin C, vitamin B and folic acid. But only a doctor can determine the correct dosage. Self-treatment is contraindicated, as it leads to altered conditions not only in the mother, but also in the child she is feeding.
They talk about the need to increase it when a mother is diagnosed with anemia. The woman feels it with headaches, drowsiness, and lethargy. Even fainting occurs. Hemoglobin is a protein that binds oxygen and carbon dioxide in red blood cells. Thanks to this protein, oxygen is transferred from the lungs to all the cells and tissues of our body. And when hemoglobin is low, oxygen starvation occurs. So, how to properly increase the amount of hemoglobin in the blood of a new mother?
How to increase hemoglobin after childbirth for a nursing mother: reasons, what to do
Some women who have given birth notice a deterioration in their health. They get tired quickly, feel weak and lethargic. One of the likely causes of malaise in a nursing mother is low hemoglobin.
Due to a lack of iron-containing protein, the natural process of gas exchange in tissues is disrupted and lactation worsens.
To increase the level of hemoglobin after childbirth in a nursing mother, the doctor prescribes a special diet and the use of special iron-containing drugs.
Postpartum anemia
Iron is an essential trace element for the normal functioning of the body. It is found in the blood in the form of the complex protein hemoglobin.
It ensures gas exchange in tissue cells, transferring oxygen to them and removing carbon dioxide. In a healthy woman, the hemoglobin concentration in the blood ranges from 120 to 150 mg/l.
A decrease in the indicator indicates the development of a disease called anemia.
Symptoms of anemia
An insufficient amount of hemoglobin during breastfeeding is felt especially acutely by a woman. With anemia, the following symptoms develop:
- constant weakness and general malaise;
- frequent dizziness;
- headache;
- decreased concentration;
- problems with sleep due to constant drowsiness;
- low performance;
- reluctance to move.
If the hemoglobin level is significantly lower than normal, the listed symptoms are accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and possible fainting. Then you need to immediately seek medical help. Sometimes the problem is not insufficient hemoglobin levels, but in other dangerous diseases with similar symptoms.
Laboratory test results
The development of anemia occurs in several stages. They depend on the results of laboratory tests of the patient’s blood:
- if the hemoglobin level is from 90 to 110 mg/l, they speak of a mild disease;
- when iron-containing protein levels drop to 70-89 mg/l, a moderate degree of anemia is diagnosed;
- if the amount of hemoglobin is below 70 mg/l, the disease has reached a severe stage.
In case of anemia, a general blood test reflects the following changes:
- low levels of hemoglobin, hematocrit and red blood cells;
- increased ESR;
- the appearance of microcytes - underdeveloped red blood cells resulting from a lack of iron;
- violation of volume distribution.
Important!
The treatment plan for anemia and restoration of normal hemoglobin concentration in the blood depends entirely on the stage of the disease. If at the initial stage a simple correction of diet and lifestyle is sufficient to achieve positive dynamics, in a serious condition hospitalization and a course of special medications are necessary.
Causes of anemia
Many women after childbirth have hemoglobin levels significantly below normal. Some people mistake alarming symptoms for fatigue and do not seek medical help. Such carelessness is dangerous, since anemia is a serious disease and requires proper treatment. A decrease in the concentration of iron-containing protein during breastfeeding occurs for the following reasons:
- increased consumption of iron in a woman’s body for the normal development of the fetus and placenta;
- neglect of the attending physician's recommendations about taking iron-containing medications;
- large blood loss during natural childbirth or delivery by cesarean section;
- prolonged bleeding in the postpartum period;
- multiple pregnancy;
- lack of meat in the diet of a nursing woman;
- chronic diseases;
- infectious inflammation accompanied by significant blood loss;
- bad heredity;
- lack of vitamins in the female body.
If left untreated, anemia takes a chronic form. Then the body is forced to constantly fight the lack of iron-containing protein. In the chronic form of the disease, the symptoms are smoothed out and the woman feels relatively well. But in any case, anemia requires treatment, since a lack of iron does not allow providing the child with adequate nutrition.
Ways to increase hemoglobin after childbirth
After diagnosis, the doctor offers a nursing mother several ways to restore normal iron protein levels.
First, a special diet is prescribed, which involves eating foods high in iron. Traditional methods of treatment are also possible.
If a woman’s hemoglobin level is significantly lower than normal after childbirth, drug therapy with drugs that replenish the daily lack of iron-containing protein is recommended.
Diet that increases hemoglobin levels
To eliminate anemia, a nursing mother must follow a diet with special foods that increase the amount of hemoglobin in the body. Strict restrictions for breastfeeding women are unacceptable. The menu should not consist only of cereals. Various foods are allowed, but in moderation, so as not to provoke allergic reactions in the baby.
In the postpartum period, the consumption of meat, offal and other products of animal origin is recommended. They contain iron in divalent form and are easily absorbed by the body. Plant foods also provide the supply of this microelement. But legumes and grains contain ferric iron. Therefore, its absorption occurs worse.
To increase hemoglobin, it is recommended to include the following foods in the diet:
- red meat and fish;
- nuts, especially walnuts;
- egg yolk;
- asparagus;
- spinach;
- buckwheat;
- seaweed;
- potato;
- dried fruits;
- black currants;
- honey;
- apples;
- pomegranate.
Important!
Many children often develop allergies to the introduction of new foods into their mother's diet. Therefore, new food is introduced gradually, in small portions.
By following a diet that normalizes hemoglobin levels, reduce the consumption of milk and products made from it. They contain calcium, which reduces the absorption of iron. To quickly achieve the desired result, include foods rich in ascorbic acid in your diet.
In addition to the diet, a nursing mother is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air to restore hemoglobin levels. Walks in the park or other places with a lot of vegetation are especially good.
Additionally, it is necessary to organize regular ventilation of the apartment, since being in a stuffy room is harmful if there is a deficiency of hemoglobin.
Medications
Drug therapy is started when folk remedies and diet fail to correct hemoglobin deficiency. Treatment is carried out under the guidance of a doctor. The specialist selects the dosage of drugs and the duration of their use separately for each case. To do this, he takes into account the results of blood tests.
Possible medications prescribed to treat anemia in breastfeeding women:
- Ferrum Lek;
- Aktiferrin;
- Sorbifer Durules;
- Fenyuls;
- Maltofer.
Important!
Before prescribing the drug, the doctor compares the expected beneficial result with the possible risks to the baby’s health. Most medications pass into breast milk and are a potential threat to the baby. Iron-containing preparations lead to digestive problems and cause constipation. Therefore, when consuming them, it is important to monitor the health of the woman and child.
Prevention of anemia
Due to anemia, some doctors recommend that breastfeeding women switch their baby to artificial nutrition. In reality, such actions are harmful to both mother and baby.
Through breast milk, iron enters the child's body and is absorbed by 75%. Only 5% of this microelement is absorbed from artificial nutrition.
Therefore, it is recommended to continue breastfeeding even with low hemoglobin.
Lactation is a good way to prevent the development of anemia:
- the absence of menstruation during lactation relieves a woman of monthly blood loss and a decrease in hemoglobin levels;
- a nutritious, healthy diet during breastfeeding increases the concentration of iron-containing protein;
- lactation improves the absorption of iron in the intestines;
- Breastfeeding immediately after childbirth helps the uterus contract, reduces blood loss and prevents the development of complications.
For breastfeeding women with anemia, the doctor offers several ways to restore normal hemoglobin levels. Usually, a special diet is recommended for this, including foods with a lot of iron. In severe cases, medications are prescribed under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Source: https://sosud-ok.ru/polza/kak-povysit-gemoglobin-posle-rodov-kormyashhej-mame.html
About nutrition
How to organize nutrition if there is anemia after childbirth? It is recommended to increase the share of meat products in your daily diet; they are a kind of “record holder” for the amount of iron.
Note: our body receives 6% of iron from meat products, 3% each from fish products and eggs, and only 2% from plant foods.
- Meat products from 120 g to 200 g per day.
- Fish products from 150 g to 250 g.
- Vegetables and fruits about 800 g (turnips, carrots, cabbage and apples in particular).
- Nutritionists also recommend eating porridge, cereal and bread. It would be an ideal option to combine porridge with a meat side dish.
About restrictions: milk should be consumed separately from other foods (especially those rich in iron). It is advisable to adhere to an interval of 1-2 hours. Tea and coffee should also be consumed less frequently; you should not drink these drinks immediately after meals, so as not to interfere with the absorption of iron. Coffee can be replaced with cocoa.
To eliminate iron deficiency, it is often recommended to eat peas and beans. However, if a woman is breastfeeding, the baby’s intestines may “protest.” If the food is artificial, please, peas and beans have a very beneficial effect on the level of iron in the body. It is also recommended to combine iron-rich foods with foods rich in vitamin C - this will improve the absorption of iron.
However, a specialized answer to the question “What to eat after childbirth with low hemoglobin?” The doctor can give it, taking into account the individual characteristics of the woman.
As you already know, the more severe the anemia, the sooner you will need medical help. You should take medications strictly according to your doctor's recommendations.
Complications
With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the prognosis for iron deficiency anemia during lactation is favorable. However, in some cases a number of complications are possible:
- heart failure,
- high risk of injury associated with frequent fainting,
- skin diseases due to excessive dryness,
- appearance problems (split ends of hair, broken arched legs, chapped lips and flaky skin),
- loss of milk, which in turn can cause (problems with children's digestion, baby's allergies, emotional disorders of mother and baby).










