Both children and adults enjoy the amazing taste of salmon. The popularity of salmon continues to grow. Therefore, its variety (most often it is cage salmon) from the 20th century. began to be bred in fish farms and fish farms. Buying salmon just got easier.
Parents try to treat their child with all the delicious foods, so they are interested in at what age can a child be given salmon, and how to properly and tasty prepare it for children.
Salmon is a predator fish from the salmon family that lives in the cold northern waters of the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. This fish continues to be studied by scientists; its lifestyle is not entirely common.
Salmon spend most of their time in the salty waters of the ocean, and in the fall they swim into mountain rivers, where they lay eggs in fresh, shallow water. The fry grow up in cold fresh water, then the fish find their way to the ocean. During these journeys, salmon are easy prey for fishermen.
The growing popularity of salmon has led to the fact that some unscrupulous farmers, in the interests of obtaining maximum income, may sell a low-quality product:
- This may be due to the use of feed with dyes to achieve the desired color of the fillets or to the pollution of fish ponds.
- By the way, every tenth farmed salmon contains an increased concentration of heavy metal salts or pesticides.
- To obtain large specimens, genetically modified salmon breeds can be grown.
Choosing fish for baby food
What kind of fish can you cook and offer to your baby? The baby's pancreas is not able to cope with fatty foods, so complementary feeding for a child under 12 months of age begins with low-fat varieties.
What quality of product should you avoid? Fish grown in private reservoirs can be dangerous for children. To speed up growth, the fry are fed special hormones. Consuming such a product is harmful.
It is better to use fresh or chilled fish, which retain as much nutrients as possible.
How to determine how long a product has been on the store counter and what is its freshness? The following signs indicate good quality:
- The scales fit tightly to the fish and shine.
- The eyes are bulging, without cloudiness.
- The gills are quite hard, bright red or pink.
- When you press on the abdomen, the dent quickly disappears. Abdominal bloating is a sign of spoilage!
How long can the product be stored after purchase? You can keep fresh fish in the cold for up to 2 days, and if you freeze it, then up to 3-6 months.
What to do when there is no fresh product on sale? What kind of fish, in this case, is permissible to give to a child under one year old? You can purchase frozen fish fillets or whole fish in stores.
When purchasing, you should ask about the date of capture and freezing. It is important to consider how much time has passed since the day of freezing: the fresher the product, the more microelements it contains. A smooth, transparent crust of ice indicates that the product has not been defrosted.
To preserve the maximum amount of microelements, fish should be thawed in lightly salted water. After defrosting, you can conduct another suitability test: pay attention to the condition of the product. When the pulp falls apart, does not hold its shape and resembles a rag, this means that the product is damaged. You shouldn't cook this fish for kids. Any suspicion of poor quality cannot be ignored, because the health of children is more important than the money spent.
Proper complementary feeding - how and at what age?
Children under one year old need to boil or steam fish. You should not give your children fried foods, especially salted or smoked ones.
It is important to consider that fish is an allergen. According to statistics, fish products cause an allergic reaction in 2% of young children. The risk increases when a parent or older child has a similar problem.
When the body responds to complementary foods with allergies, it is better to take a break for two weeks and then try other types of fish. Persistent non-acceptance of any fish products indicates that complementary feeding should be delayed until the age of one.
If there is no allergy, you can give your baby fish from 9-11 months. You need to start complementary feeding with 0.5 parts of a teaspoon in the first half of the day, carefully observing what reaction the body gives to the new product. It is advisable not to combine fish and meat complementary foods on the same day; it is better to arrange “fish” days 2 times a week. At 12 months, the child should receive a portion weighing 60 grams, after a year it is gradually increased to 100-150 grams.
It is better to start feeding infants up to one year old with one type of fish for 3-4 weeks, then you can add other types to the diet.
It is recommended to boil the fish fillet, remove the bones, grind it in a blender and give it to the child in this form. Later, by 12 months, when the baby has developed chewing skills, you can prepare fish soufflé or meatballs for him, and after a year, give fish in pieces and cook soups in fish broth from medium-fat varieties.
One of the important products necessary for feeding infants is low-fat sea and river fish, which contains fish oil, amino acids, vitamins F, A, D, E, B-12, which are very beneficial for the body, and minerals that promote proper metabolism: iodine , manganese, zinc, copper, boron, iron, fluorine, etc.
The choice of fish for a child's diet should be taken very seriously: if possible, use fresh fish; when buying whole fish, you should pay attention to the scales (high-quality fish have shiny ones), gills (without mucus), when buying fillets - to the color (white or pale -pink). Sea fish is safe and very healthy, as it is rich in minerals (primarily iodine and fluorine), as well as omega-3 fats; but it can usually only be bought frozen. Of river fish, which is more accessible and easier to digest by the body, nutritionists give preference to trout (it lives only in clean water and, therefore, does not contain harmful substances) and fish grown in artificial reservoirs.
When to introduce fish to an infant
Fish is introduced into the diet of infants later than other foods, as it can cause allergies. Nutritionists advise giving your child fish only after he has become accustomed to eating meat - at 9-10 months. You need to introduce fish into your baby’s menu gradually: start with 5-10 grams per day and increase the daily intake to 70 grams by 12 months. It must be remembered that fish broth contains substances that are harmful to the child’s body and are released during the cooking process, so fish soups are recommended to be given to children from 1.5-3 years old. You should also not feed infants fried, smoked, salted fish or fatty fish (all salmon, sturgeon, herring).
In order not to overload the child’s digestive system, you should alternate fish and meat days during the week, avoiding preparing these dishes on the same day; cook fish dishes no more than 2 times a week.
If eating fish has caused an allergy in a child, you should exclude it from the diet for two weeks, then try to cook a different type of fish (an allergy to both all fish and a specific type is possible).
Harm and contraindications
Predisposed children may develop an allergic reaction after eating salmon.
Despite its valuable composition and beneficial properties, salmon can cause an allergic reaction in a child. Particular care should be taken when:
- the baby's tendency to be allergic to fish;
- presence of fish intolerance in parents.
Fish from polluted waters can accumulate harmful substances in the skin and fat layer that can have a negative impact on the child’s body. To reduce the risk of harmful effects, it is recommended to remove the skin from salmon before cooking.
To avoid negative consequences, you need to carefully remove fish bones from the meat before giving it to your child.
It is undesirable to eat salmon:
- obese children;
- those suffering from liver and biliary tract diseases;
- for gastrointestinal chronic pathology.
In any case, the introduction of this fish into the diet of such children should be agreed upon with a pediatric gastroenterologist or nutritionist.
How to cook fish for babies
Until a child is one year old, it is preferable to cook exclusively white fish, at least until 10 months.
If you are boiling fish, then after freezing it and rinsing it in cold water, immediately place it in boiling water, remembering to reduce the gas to minimum.
How to cook fish for babies
When preparing fish for infants, several rules must be followed:
- defrost the fish in salted water (this will prevent bacteria from forming on it), and immediately begin heat treatment;
- Before cooking, rinse the fish well;
- be sure to check the fillet for bones;
- cook fish in two ways: in a double boiler or boiling in a large amount of water (cooking time for small pieces - 10-15 minutes, for whole fish - 20-25 minutes).
What is the best way to cook fish products for your baby yourself?
For it, you can give fish puree prepared with your own hands, which, depending on the circumstances and personal preferences, can be prepared in water or steam. During processing, immediately get rid of all bones and cartilage.
When you cook fish from the seas yourself, do not defrost it until the very end.
You can simply wash it thoroughly and cut it into small pieces, then calmly put it in boiling water. When the water boils, reduce the heat to low and cook the fish until cooked.
How to diversify the diet of a little gourmet if he already eats vegetables, fruits, and meat? Of course, fish. Let's talk about how to do it right.
In order for a child to grow healthy and strong, fish must be present in his menu.
Fish recipe for babies
Fish puree for babies
It is better to introduce fish into a baby’s diet in the form of puree. To prepare it, you need to boil 100 g of lean fish: hake, pollock, cod, haddock, flounder - and grind in a blender. Add 1 tsp to the fish. milk and vegetable oil. Mix the resulting mass well and boil for 2 minutes.
To the fish puree, especially during the first feedings, you can add a little ready-made potato or vegetable puree, to which the child is already accustomed.
Fish pudding
Boil the fillet, chop, then mix well with half an egg beaten with salt and mashed potatoes (ingredients: 1 potato, 2-3 tbsp milk, 2 tsp vegetable oil). Transfer the resulting mass into a mold and steam or steam for half an hour.
Fish meatballs
Grind (using a meat grinder or blender) 60 g of fish fillet and 10 g of soaked white bread, add ¼ of the egg yolk, 1 tsp. vegetable oil. Form balls from the resulting mass, fill them halfway with water and simmer for half an hour.
Children usually like these dishes because they can be held in their hands.
Sooner or later, the time comes when every mother wonders about including fish in her child’s diet. At what age and with what steps should you start introducing innovations in your baby’s nutrition? Find out in the article! In general, fish is a unique product by nature. The percentage of protein absorption by the body is, depending on the ingredients accompanying the dish and eating habits, about 98%. The beneficial properties from including this product in the menu are no less stunning.
How to cook salmon for children
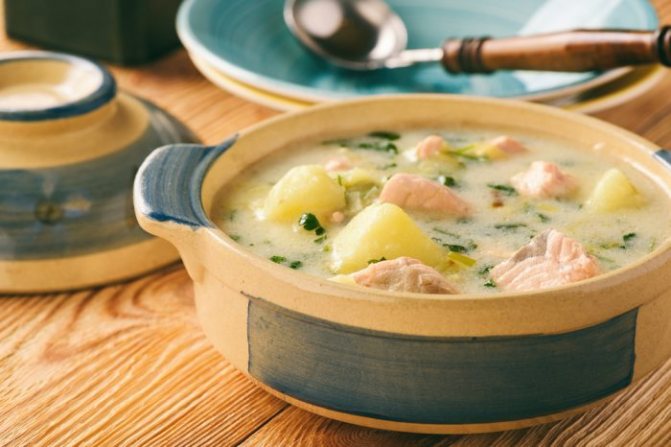

Salmon meat with its delicate aroma and pleasant taste is a delicious product with sufficient energy value. Fish can be boiled, stewed, baked, fried, steamed.
Thanks to the natural fat in the composition, the meat turns out juicy, does not fall apart and does not look like an unattractive mush.
Kids enjoy eating fish baked in the oven or steamed, delicious meatballs and cutlets. For older children, you can make a casserole or fish pie. But fried fish and rich broth are undesirable dishes for children.
Several recipes for children over 3 years old:
Salmon casserole
- You need to cut 250 g of salmon into cubes and marinate: sprinkle lemon juice (2 tbsp) on the meat, add salt and let it sit;
- Boil (but do not overcook) ¾ cup of rice, let cool;
- lightly fry the fish (2 minutes) in a frying pan in sunflower oil;
- add 150 g of asparagus green beans, salt and pepper to taste to the pan, fry for two minutes with continuous stirring;
- Break an egg into the rice, add 40 g of grated hard cheese, a little chopped dill and mix everything well;
- put the mixture with rice in a greased form, put fish fillet and beans on top and sprinkle with grated cheese (40 g);
- Bake in the oven at 170 0C for 15 minutes (until golden brown).
Salmon soup
- Pour water (1.5 liters) into a saucepan, place the tail of the salmon carcass in it, add 6 black peppercorns, a coarsely chopped onion and cook the broth;
- fish fillet (400 g) cut into pieces;
- cut 4 potatoes into small strips;
- remove the fish tail and onion from the broth;
- add potatoes to the broth and cook for about five minutes over low heat;
- add fish to the soup and let it simmer for ten minutes;
- 1 tbsp. l. add flour to 200 ml of 10-20% cream, mix thoroughly until smooth;
- pour the resulting mixture into the soup while stirring and bring to a boil;
- add salt (2 tsp), 30 grams of butter, chopped herbs (parsley with dill) to the soup.
What are the benefits of seafood?
The magnesium, zinc, copper, fluorine and iodine contained in fish predetermined its popular name - “food for the mind.” Protein, amino acids, enzymes have a positive effect on the human body. But its main advantage is the presence of Omega-3 fatty acids. Regular consumption of dishes containing seafood will help prevent the occurrence of various diseases. Such an ingredient will also be able to synthesize antibodies, form and maintain the body in a healthy state. A natural question arises: when and what kind of fish can be given to a child?
According to doctors, the optimal period for serving fish to the children's table is 10-12 months. However, it is worth noting that the inclusion of a product in a child’s diet is purely individual. For babies of brave mothers, purees, broths and cutlets with the addition of fish are not scary even at 9 months. Other parents remain on the side of specialists. They begin to feed the child with similar dishes at the recommended time or later. The allergenic nature of seafood and the experience of mothers have confirmed that a child should be protected from mussels, seaweed, shrimp and crabs for up to 3 years. Remember that such organisms act as biological filters for seawater!
Let's go shopping
Baby food requires special attention. At first it seems that the fish has only advantages, but this is not so. It also has significant disadvantages that reduce the frequency of its consumption by children. Firstly, the product can act as an allergen. Secondly, there is a danger of the fish bone getting stuck in the throat. Thirdly, not every adult will like the specific smell and taste of seafood. However, in toddlerhood, little attention is paid to the child’s gastronomic preferences. After all, his habits are just being formed. This means that you should focus on the quality and type of product served.
Must be served lean, low-fat, low-allergenic and fresh. Among the low-calorie representatives of reservoirs on store shelves you can easily find perch, hake, dorado or cod. By the way, it is rational to include the latter and its “family relatives” in children’s food once the child reaches the age of one year. Benign fish is distinguished by the integrity of its scales, fatness, carcass density or mobility of the animal. The gills should be pink or red in color. Be sure to pay attention to the shelf life of the product. The right decision would be to give preference to fresh or freshly frozen fish. Inspect the fins and eyes: there should be no films or damage!
What kind of fish should children serve? Preparing a meal for a little eater
So, we figured out what kind of fish to give to a child. Now let's figure out what to do with it. So, to prepare a delicious dish you need:
- Clean the carcass, rinse and, after chopping, send to freeze.
- Thaw before direct cooking.
- Place in water brought to 100 degrees.
- Boil for 30-40 minutes.
- After heat treatment, remove the bones from the fish. Be careful at this stage.
- Place the fillet along with the boiled vegetables into a blender, where the products are pureed.
Fish is suitable for a child who can chew if it is prepared in the form of meatballs or cutlets. It is better not to introduce broths made from seafood rich in extractive substances into the diet of a child under 3 years of age. This threatens to put extra stress on the young gastrointestinal tract.
Some information about river fish
The most serious representative of rivers is, of course, trout, since it is very picky about its own habitat and the surrounding ecological situation and cannot withstand the slightest cloudiness or pollution of the water in the reservoir where it lives. If you are well aware of where this or that fish was caught, you can without a doubt introduce pike perch, pike or trout into your child’s diet. You can add crucian carp, perch or bream to them.
However, these types of fish are very bony, and before giving them to a child, the fish must be carefully removed from all bones and cartilage. In addition to this diet, it is worth adding fish oil.
Children's canned fish
Special food in jars is a great option for busy moms. It is worth considering that feeding a child with such ready-made food cannot be considered a cheap pleasure. And this results in an additional financial burden placed on the shoulders of parents. In addition, a self-prepared lunch or dinner will never raise concerns about the quality and safety of the food consumed by the child. However, it is not worth slandering baby food manufacturers due to the following factors:
- Finished products are always certified and tested by specialists who know what fish is suitable for children and what is not.
- As a supplement, cereals and grains are added to the puree. This not only nourishes, but also strengthens the child’s body.
- Little gourmets will love filling the jars.
The fact that it saves time for always busy housewives is also attractive, so it’s worth a try.
Frequency of fish consumption
If your child is one year old and the green light is given to introduce fish into the diet, you should not overdo it. The first taste will be revealing. A child may simply not like fish or may lead to an allergic reaction. Carefully monitor the condition of the skin and mucous membranes.
Please note: allergies may apply to certain varieties. In this case, the child is no longer given unsuitable fish. It should become taboo: stop consuming the irritant for several weeks. After the “recovery” period, return to eating the product, giving preference to the new type.
Fish feeding starts with one teaspoon. If normal tolerance is observed, then the portion may grow to normal within a few weeks. For clean fish the figure is 20-30 g/day. The maximum dose of vegetable-fish puree reaches 100 g. It would be rational to add a “sea” or “river” ingredient to the weekly diet of a little gourmet with a frequency of 1-2 times.
How to choose and introduce into the diet
Fish is a dietary food product. It contains easily digestible protein (protein) and unsaturated fatty acids, as well as a balanced complex of vitamins and minerals.
Fish is an indispensable product in baby food, especially for children under one year of age who are bottle-fed.
Fish is also useful for older children with exhaustion of the body and significant physical and mental stress.
Comments
It is very difficult to find fresh fish here, even if it is not frozen, there is no guarantee that it has not been frozen previously. Therefore, for the first feeding we preferred fish from baby food, we took hake with potatoes from Heinz, another fact for the jars in the first feeding, there are 100% no bones, which is very important for babies!
- Complementary foods: meat, fish
Meat and fish are valuable sources of animal protein, minerals (phosphorus, potassium, iron) and vitamins. When and in what quantities can you start giving these foods to your child? And in what form are they better absorbed? Meat Meat is... - Fish and seafood in a child’s diet.
Girls!!! I asked myself this question and found this article. Maybe someone else will find it useful! Fish Fish is a very important protein product. The content of complete protein (it includes essential amino acids) varies in different types of fish from 10 to... - About complementary feeding!
I found some very interesting information about complementary feeding on the net. Everything about the timing of complementary feeding, and most importantly, how to prepare everything correctly. I’ve already printed it out for myself, maybe it will be useful for someone else.. HARD-BOILED CHICKEN EGG YOLK It is extremely undesirable to use it industrially... - Proper feeding.
I think this is a very relevant and important topic for all parents: when, what and how much to introduce, and how to do it correctly, without harming your child. I came across this topic when my baby was six months old. There is a lot of information on the Internet, and... - An article about complementary feeding, maybe someone needs it.
By the time your baby is 4-6 months old, it’s time to think about a feeding schedule. I am not a supporter of introducing complementary foods before the 6th month if the baby is breastfed and the mother produces enough milk. Introduction of complementary foods...
Fish is an excellent source of protein and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are very beneficial for a growing body. However, due to its high allergenicity, it is introduced into the baby’s diet gradually and in small portions. In this article we will talk about what kind of fish to start feeding your baby with.
The benefits of fish for the body
Fish is one of the most valuable foods and should be included in the menu of both adults and children. In addition to protein and polyunsaturated fatty acids (Omega-3 and Omega-6), it contains iodine, calcium, magnesium, potassium - all the microelements that a child needs for full development. But despite this, it is not recommended to choose fish for the first feeding. It should be introduced into the baby’s diet no earlier than he is 8–10 months old, that is, after the baby has tried vegetable and fruit purees, cereals, etc. Fish is considered one of the most powerful allergens. Therefore, after eating, it is necessary to carefully monitor the child’s condition. If he develops a rash or problems with the digestive system (diarrhea, bloating, etc.), the fish dish should be immediately excluded from the menu. If a baby has already had cases of food allergies to other foods, fish can be given to him no earlier than one year.
What should be the volume of one child's portion?
When introducing a new product into a child’s diet, the mother must follow the basic rules. The baby should try a new product if he feels well.
- No vaccinations should be scheduled at the time the fish are introduced.
- It is advisable to give the child a new dish in the morning once or twice a week, replacing it with meat puree.
- The first portion should be only 5 g, after which the child can be supplemented with vegetable puree. For the next feeding on this day, it is recommended to give meat puree, to which the baby is already accustomed. If the child tolerated the new product well, you can continue to introduce fish into the diet and increase the volume to 30–60 g (depending on age) and give him such food 1–2 times a week.
- After feeding the child a fish dish, the mother should monitor the baby’s condition for the next 2-3 days. Which fish is best for complementary feeding?
Which fish should be introduced first?
A question that interests many young mothers. To introduce your baby to this product, it is best to choose lean varieties of fish: flounder, cod, pollock or hake. They contain only 4% fat. In pink salmon, chum salmon and trout it is slightly higher - from 4 to 9%. The fattest varieties include salmon, mackerel and herring - in them the figure exceeds 10%. Fish of medium fat content and higher can be introduced into a child’s diet only after a year, so as not to cause problems with the digestive system. Your pediatrician will be able to give you an accurate answer about which fish for first feeding is right for your baby.
The benefits of fish for children
A growing body needs not only complete protein, but also vitamins and minerals, which are included in fish in optimal proportions.
“Fish” vitamins include:
- Retinol (vitamin A), which promotes the proper formation of the retina and prevents the development of vision defects.
- Ergocalciferol (a fat-soluble form of vitamin D), necessary for the growth of bones and teeth, including the formation of strong tooth enamel.
- B vitamins, without which the normal functioning of the central nervous system and brain is impossible. If they are deficient, the baby grows restless and may lag behind his peers in intellectual development.
Fish also contains the following macro- and microelements:
The fats in fish are polyunsaturated. They contain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which neutralize the harmful effects of excess free radicals and also balance the functioning of the child’s nervous system.
The calorie content of lean (lean) fish with a fat content of up to 2-3% is 75-100 kcal/100 g, and with a fat content of 4-8% this figure does not exceed 165 kcal. For this reason, the product is recommended for children with excess weight and metabolic disorders.
Beneficial features
If you regularly consume pollock, you can get the following benefits:
- blood sugar levels decrease;
- the functioning of the thyroid gland is normalized;
- the condition of the nervous and digestive systems improves;
- teeth and bone tissue are strengthened;
- the condition of bones, nails and skin improves;
- blood cholesterol levels decrease;
- blood pressure and metabolism return to normal.
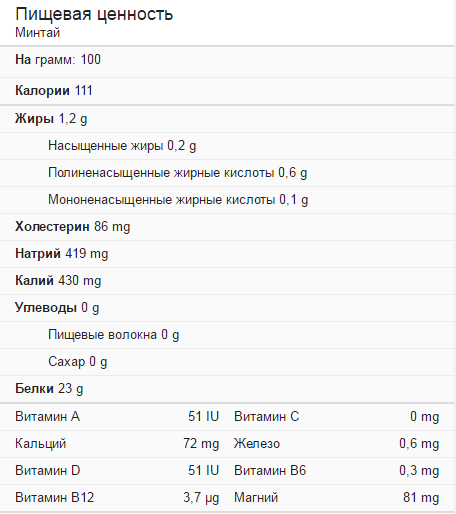
If you consume 100 g of this healthy product, you can fill the body’s daily need for iodine, chromium and cobalt. Iodine is necessary for the effective functioning of the thyroid gland, which ensures the normal functioning of all organs and the well-being of the person himself. Cobalt produces a hemostatic effect and regulates carbohydrate metabolism.
It also promotes normal absorption of iron, which can prevent the development of anemia. Chromium is a necessary element to ensure normal carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in the human body.
The calorie content of this fish is low (70 kcal per 100 g), which allows you to include it in your diet without worrying about your figure.
Delicious Pollock in the oven with a crispy crust
Rules for introducing a child into a diet
To the question “At what age can you give fish to a child?” Pediatricians answer unanimously - no earlier than 8 months in the absence of allergic reactions to food.
If a child has a tendency to allergies, it is better to postpone fish feeding until the immune system has stabilized.
From six months onwards, baby fish puree (without salt and other additives in the form of vegetables and cereals) is given only on the recommendation of a specialist in exceptional cases to children who are bottle-fed if rickets, anemia and some other diseases are suspected.
You should start complementary feeding with a minimal amount - at the tip of a teaspoon, before lunch or daytime breastfeeding.
If absorption is favorable (no allergic rashes, diarrhea and nausea), the portion is gradually increased to 10 g.
The frequency of feeding fish is twice a week.
After a year, the portion is increased to 30 g, and after three - to 50 g. It is not advisable to give fish to your baby more than twice a week: the diet should be varied.
Types of fish for baby food
The product is divided into types according to habitat and fat content.
By location
fish are divided into:
- freshwater (river and grown in artificial conditions);
- marine, which are considered the most preferable for children's diets due to their high content of iodine and unsaturated fatty acids.
However, kids themselves determine with their taste preferences which fish will be healthy. Usually the palm is given to navaga, hake, pollock and pink salmon, which contain large amounts of phosphorus and calcium, which stimulate bone growth.
By fat content
fish are classified into:
- skinny (lean) - no more than 2% fat in the composition (navaga, pollock, hake, cod, river perch);
- medium fat content - from 2 to 8% (pink salmon, trout, pike perch, catfish, low-fat herring, carp, sea bass, horse mackerel);
- fatty - from 8% or more (salmon, mackerel, chinook salmon, nelma, eel, sterlet, saury).
What kind of fish can be given to a child under one year old?
Pollock and navaga are recommended for babies: these species have a very delicate texture, a weak nutty taste and no specific smell that can forever turn a baby away from a healthy product. Pollock and navaga are varieties of fish without small bones, which facilitates the process of preparing a delicate puree.
The first fish for feeding a child should only be boiled or steamed. After cooking, it is crushed with a blender and rubbed through a sieve to remove small bones.
Fish for a 1 year old child
Starting from the year you can switch to denser lean varieties - cod, hake. River perch is also healthy, but it contains a lot of small bones that are difficult to remove.
Fish for a one-year-old child does not have to be pureed. Fish meatballs, cutlets, casseroles and souffles pleasantly diversify the diet and will only bring health benefits if consumed in moderation (2 times a week).
Fish for a child after one year
From the age of two, in the absence of allergies, red varieties are introduced into the diet - pink salmon, trout and similar ones.
Children's nutritionists recommend offering fish broth and soups based on it for lunch no earlier than three years, and fatty fish varieties no earlier than five.
Salmon can be given to a child after five years of age and only in boiled form. To prepare children's lunches, it is better to use the tail part of this fish - it contains less fat.
Flounder and mackerel are rarely liked by children because of their specific smell. If children have a persistent reluctance to eat these types of fish, you should not insist - switch your attention to the more traditional cod, navaga, hake and pink salmon.
Eel, salted herring and canned fish are not used in baby food. These foods can be eaten by children only when the digestive system is fully formed, that is, after 10 years.
Choosing fish by blood type
As useful information. Will it come in handy?
- 1 - sturgeon, salmon, cod, mackerel.
- 2 - cod, mackerel.
- 3 - flounder, halibut.
- 4 - sea bass, tuna, pike perch.
The child will eat more willingly if the food has an unusual appearance.
Fish for first feeding
When should you introduce fish into your child’s diet? In what quantity? How to cook? Which fish to choose for the first feeding? What is the difference between sea and river fish? You will find answers to all these questions in this article.
About the benefits of rolling fish
Fish contains high-quality protein, which is digestible by 93-99% (meat proteins are only 87-88%). Fish is also rich in vitamins A, B2, B12, PP1, D, it contains iron, zinc, copper and magnesium, and sea fish also contains iodine and fluorine. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish help keep your heart healthy. These acids are also beneficial for brain function. The human body does not produce omega-3 fatty acids, so it must obtain them through food. This is why fish occupies such an important place in a child’s diet.
When to introduce fish?
Fish is introduced into a child’s diet closer to the age of one year (at 10-12 months), because this is a very allergenic product.
How to cook?
As a rule, fish puree is made. Preparing fish for your baby is very simple: fillet boiled in water or steamed should be rubbed through a sieve or chopped in a blender, and then mixed with dishes that the child is already familiar with - porridge or chopped vegetable puree. For an older child, you can offer fish soufflé, fish casserole, fish balls or cutlets.
How many?
For the first time, it is enough to limit yourself to one teaspoon of puree (5g), preferably in the first half of the day (for breakfast or lunch), in order to monitor possible manifestations of allergies in the child. Gradually increase the portion, by one year - 60 grams, by 2 years - 100 grams of fish. It is better to cook fish for your baby no more than 1-2 times a week.
Which fish to choose?
It is better to start complementary feeding with low-fat varieties: hake, cod, river perch. These fish varieties are low allergenic.
Depending on the fat content, fish can be divided into 3 groups:
Group 1: low-fat varieties (up to 4% fat) - hake, cod, pollock, flounder;
Group 2: moderate-fat varieties (4-8% fat content) - pink salmon, sea crucian carp, chum salmon, pike perch, trout, herring, sea bass;
Group 3: fatty varieties (up to 20% fat content) - halibut, salmon, mackerel, herring.
Fish is also divided into sea and river.
Sea fish is rich in iodine, fluorine and zinc - minerals that are practically absent in river fish. The only disadvantage of sea fish is that it arrives on the shelves of our stores in frozen or canned form.
Marine fish varieties - hake, cod, pollock, flounder, sea crucian carp, sea bass, salmon, pink salmon, halibut, mackerel.
If your child is allergic to sea fish, do not be upset; offer river fish; it is quite possible that river fish will not cause an allergy. Some types of river fish are considered no less valuable than sea fish, and are not inferior in their taste characteristics.
River fish varieties - pike perch, trout, carp, haddock.
And finally, when choosing fish, try to give preference to fresh fish rather than frozen.
Criteria for choosing fish for home cooking
Fish can be purchased in stores, supermarkets and other retail outlets both fresh and frozen.
When purchasing fresh fish, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- smooth, well-fed back;
- shiny, tight-fitting scales;
- transparent, convex eyes;
- the product must have a fresh smell without any admixture of mustiness, mud and decomposition;
- the carcass should be elastic to the touch.
Dull scales that fall away from the skin, cloudy eyes and an unpleasant odor are signs of a low-quality product.
Frozen fish can be purchased as fillets, which is very convenient for cooking, or as a whole carcass. In this case, it is worth paying attention to the thickness and general appearance of the ice glaze, which should be smooth and no thicker than 2-3 mm.
Broken, uneven, thick azure indicates that the fish was defrosted: after re-freezing, it is not suitable for consumption.
In stores, you can also ask the administrator for a certificate for a batch of products. The shelf life of frozen fish should not exceed six months.
Precautionary measures
It is not advisable to purchase fish from random sellers, since in this case you can buy a product grown in an ecologically unfavorable area.
Nutritionists also warn against eating marine fish that live at the bottom of water bodies, where salts of heavy metals and mercury accumulate.
These include:
- tuna;
- pangasius;
- tilapia.
Despite the fact that sea fish is preferable to freshwater fish for children, it is better to exclude the above varieties of fish from the shopping list.
Some information about sea fish
Sea fish can also be given as complementary food, but it should not be too fatty. Hake, cod and perch are best suited for this. When purchasing seafood products, pay attention to their quality and freshness. If the fish is far from being fresh, this can lead to the possibility of food poisoning, which can critically affect the baby’s health.
Also remember that in no case should you introduce semi-finished fish products, such as cutlets or fish nuggets, into complementary foods. Such products are prepared from low quality raw materials.
Recipes
The success of fish dishes and the benefits from them depend on how to prepare fish for a child. The rules for preparing delicious juicy fish are as follows:
- Before cooking, soak the fresh carcass in water with lemon juice (10 ml/1 l) for half an hour;
- Do not defrost frozen fillets completely;
- When cooking, immerse portioned pieces only in boiling water;
- While baking, place a small piece of butter on each portion.
How long to cook fish for a child depends on its type. Lean varieties are cooked over low heat for 10 minutes, and medium-fat varieties - 15-20 minutes.
Meatballs
For preparation you will need:
- pollock or navaga fillet - 300 g;
- boiled carrots - 30 g;
- potato starch - 5 g.
Grind the fish with a blender along with carrots, mix with starch. Form meatballs from the resulting mass and freeze them in the freezer.
As needed, take out the required quantity, immersing it in boiling water for 10 minutes, avoiding boiling.
The dish is perfectly balanced. It can be offered to children from one year old, either separately or with a vegetable side dish.
Casserole
Baked fish is especially attractive to children because of its delicious crispy crust.
To prepare the casserole you need to take:
- 300 g of any fish fillet;
- half a glass of boiled rice;
- 1 raw chicken egg white;
- 30 g of hard grated cheese with a fat content of no more than 40%.
Cut the fillet into pieces, mix with rice, and place in a glass or ceramic dish.
Beat the egg whites, mix with the prepared fish and rice mixture, and sprinkle with cheese on top.
Bake at a temperature of 150-155 degrees for 20-25 minutes. The dish is recommended for children over three years old.
Fish baby food
Canned baby food is very convenient at the dacha or on trips, as well as when parents don’t have enough time. Recommended for use from 8 months.
Domestic
launched baby food with fish, packaged in 100 g glass jars:
- “Chum salmon and vegetables”;
- “Sockeye Salmon and Vegetables”;
- "Pike perch and vegetables."
In addition to fish, it contains zucchini and potatoes. The product does not contain sugar, preservatives or GMOs.
Baby food “Pink salmon with potatoes” from the manufacturer in question includes only fish and mashed potatoes.
The average price is 65 rubles.
Italian manufacturer Heinz
offers “Vegetables with trout” for children weighing 120 g in a glass container. In addition to minced fish, the puree contains:
- potato;
- zucchini;
- onion;
- rice flour;
- sunflower oil;
- fish fat;
- lemon juice (acidity regulator).
The manufacturer declares that the food contains no GMOs, sugar, or preservatives.
The average price is 70 rubles.
The benefits of fish for children are undeniable when consumed in doses and without allergies.
The introduction of this product into the diet will help develop healthy eating habits in children, as well as strengthen bone tissue and the nervous system.
The nutritional value of fish is not inferior to meat, and due to the smaller amount of connective tissue, it is more easily absorbed by the body. This product will provide children with the necessary nutrients for proper metabolism. Also, kids will receive one that is responsible for good vision, and one that is involved in the formation and strengthening of skeletal muscles. Fish contains a rich list of substances useful for children: phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, potassium, sodium, iron, fluorine, as well as iodine, the amount of which is important for stimulating mental abilities and neuromuscular development.
We prepare delicious and healthy fish dishes for your baby
Fish puree
- fish fillet without skin – 60 g;
- vegetable oil and milk - 5 ml each.
Preparation:
- Boil the fillet in a small amount of water for 15 minutes.
- Mash the cooled fillet with a fork or beat with a blender, first removing the bones.
- Add milk and butter to the mixture. Add salt.
- Stir and simmer over low heat for 1 minute.
- Serve warm.
Fish meatballs
- fish fillet – 60 g;
- wheat loaf (roll) – 10 g;
- yolk – ¼ pcs.;
- water – 1 tbsp. spoon;
- vegetable oil – 4 ml.
Preparation:
- Make minced meat from boneless fish fillet and pre-soaked bread
- Add yolk, butter, mix well.
- Form small balls from the resulting mass.
- Place the meatballs in a bowl and fill them halfway with water.
- Place on low heat for 25-30 minutes.
Fish pudding
- Fish fillet – 100 g;
- potatoes – 1 pc. (50 g);
- oil – 0.5 tbsp. spoons;
- egg – ¼ pcs.;
- milk – 30 ml.
Preparation:
- Boil the peeled potatoes.
- Drain the water and make mashed potatoes. Add milk.
- Boil boneless fish fillets in lightly salted water.
- Chop the pulp, add puree and melted butter - 1 teaspoon. Add the beaten egg. Add salt.
- Place the prepared mixture into a greased form and cover with a lid.
- Cook the pudding in a water bath for 25-30 minutes.
- Cool.
Finally
Fish is a unique product, the consumption of which provides many benefits. By receiving fish dishes at an early age, the baby will grow up healthy and develop properly.
It might be useful to read:
- Doctor allergist-immunologist: who is he, what does a specialist doctor treat and in what cases is it necessary to consult a specialist;
- Immunologist job description Release form, composition and packaging;
- Geneticist where to study;
- Where do they study to become a geneticist?
- What does a reproductive specialist do? ;
- Prices for reproductologist services Approximate duration of treatment;
- Dogs have the strongest jaws;
- Who is an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and what does he do? ;
Choosing fish for baby food
What kind of fish can you cook and offer to your baby? The baby's pancreas is not able to cope with fatty foods, so complementary feeding of a child under 12 months of age begins with low-fat varieties:
- Lean (skinny)
- cod, pike perch, hake, pollock, river perch, flounder, navaga. They have a fat content of up to 4%. Can be introduced into the diet of children from 9-11 months. - Medium-fat
- sea bass, sea crucian carp, trout, pink salmon, herring, sturgeon, chum salmon. They have a fat content of 4-8%. Suitable for feeding children from 1.5-2 years old. - Fatty
- salmon, mackerel, herring, eel, omul. They have a fat content above 8%. Introduced into the diet of children no earlier than 3-4 years.
What fish should you not give to your child?
What quality of product should you avoid?
Fish raised in private waters may be dangerous for children
. To speed up growth, the fry are fed special hormones. Consuming such a product is harmful.
It is better to use fresh or chilled fish, which retain as much nutrients as possible.
How to determine how long a product has been on the store counter and what is its freshness?
indicate good quality :
- The scales fit tightly to the fish and shine.
- The eyes are bulging, without cloudiness.
- The gills are quite hard, bright red or pink.
- When you press on the abdomen, the dent quickly disappears. Abdominal bloating is a sign of spoilage!
How long can the product be stored after purchase?
You can keep fresh fish in the cold for up to 2 days, and if you freeze it, then up to 3-6 months. When there is no fresh product on sale, you can purchase frozen fish fillets or whole carcasses in stores.
When purchasing, you should ask about the date of capture and freezing. It is important to consider how much time has passed since the day of freezing: the fresher the product, the more microelements it contains. A smooth, transparent crust of ice indicates that the product has not been defrosted.
To preserve the maximum amount of microelements, fish should be thawed in lightly salted water.
.
After defrosting, you can conduct another suitability test
: pay attention to the condition of the product. When the pulp falls apart, does not hold its shape and resembles a rag, this means that the product is damaged. You shouldn't cook this fish for kids. Any suspicion of poor quality cannot be ignored, because the health of children is more important than the money spent.
Proper complementary feeding - how and at what age?
Children under one year of age must have fish boiled or steamed.
. You should not give your children fried foods, especially salted or smoked ones.
It is important to consider that fish is an allergen
. According to statistics, fish products cause an allergic reaction in 2% of young children. The risk increases when a parent or older child has a similar problem. When the body responds to complementary foods with allergies, it is better to take a break for two weeks and then try other types of fish. Persistent non-acceptance of any fish products indicates that complementary feeding should be delayed until the age of one.
If there is no allergy, you can give your baby fish from 9-11 months
.











