What does a baby's coated tongue mean?
A tongue on which a white coating has formed may be a harbinger of certain problems with the body.
- Viral stomatitis. Most often it manifests itself with measles, chickenpox or other infectious diseases.
- Dysbacteriosis. In this case, everything in the mouth and lips is covered with a white coating.
- It is possible that the baby has intestinal problems. In order to diagnose them on time, it is necessary to undergo regular tests.
- If the white coating has the consistency of cottage cheese and cannot be removed, it is a thrush.
- If the newborn has been treated with antibiotics, the formation of plaque in the mouth and lips is a manifestation of an allergic reaction.
How to prevent the appearance of plaque on the tongue in children?
Normally, a newborn's tongue is light pink, as are the gums, palate and inner surface of the cheeks. He is wet, his movements are not hindered in any way. When examining the oral cavity, parents should pay attention to plaque or specks. The color of the mucous membrane should be uniform. If you notice bright red or whitish spots or plaque, you should be wary. Also causing concern is a uniform, but too bright or pale color of the tongue.
Is it possible to prevent the appearance of whitish plaque in a baby? Prevention recommendations:
- Monitor the child's hygiene. You need to clean your mouth from birth. Wash bottles, nipples, toys thoroughly and, if the material allows, boil. Caring for the oral cavity of a newborn should be carried out with products intended for children under one year of age.
- Taking care of your health. If the baby is breastfed, the woman needs to carefully monitor the cleanliness of the nipples. Thrush is transmitted from mother to child; it is useless to treat the baby if the mother herself has not been cured of the fungal infection.
- Do not contact sources of infection. You should not take your one-year-old baby to places with large crowds of people or to visit people with acute respiratory infections. The immunity of infants is much weaker than that of adults, so they can easily get sick.
If white spots, cheesy plaque, dirty gray film and various rashes appear in the oral cavity, you should not self-medicate. Unknown and frightening symptoms are a reason to immediately visit your pediatrician.
Observe how often a white coating forms on the tongue of a newborn. If it turns out that plaque comes and goes, appears after feeding, it may simply be milk residue.
The milk residue can be easily wiped off the child's tongue with a soft, dry or damp cloth.
If the skin of your child's tongue is pink and appears healthy after the residue has disappeared, no further treatment is required.
Thrush
If white spots appear on the baby's cheeks, lips, and tongue, the baby may have thrush. The fungal infection Candida albicans often invades the mouths of newborns or children younger than two months of age.
In a newborn baby, oral candidiasis develops when passing through an infected birth canal and in case of infection from contact with surrounding objects - untreated pacifiers, feeding bottles and toys.
Poor maternal breast hygiene may be another reason. Although formula fed babies are more likely to be exposed to thrush.
The acid reaction of saliva in newborns and the increased sensitivity of their mucous membranes, which are easily injured, are important factors in the development of candidiasis.
In a baby, fungal stomatitis appears due to a weakening of the body as a result of previous infectious diseases, prolonged digestive disorders and taking antibiotics or corticosteroids.
Thrush on a child’s tongue resembles yogurt or cottage cheese. Wiping may result in raw, red, or even bleeding areas. Babies with thrush often show persistent signs of discomfort during feeding.
The tongue should be cleaned regularly to reduce the risk of infection by fungi, bacteria or germs. Infants' immune systems are not fully developed and therefore not ready to fight infections.
There are three ways to clean a newborn's tongue from milk or anything else. For babies who don't yet know how to rinse their mouth, these cleaning methods can be very helpful.
Wash your hands thoroughly with soap. Take a piece of sterile gauze or cotton cloth.
Wet it in a glass of warm drinking water.
Wrap a piece of cloth around your finger and gently place it in your baby's mouth.
Wipe the surface of the tongue, the upper and then the lower gums. The ideal time to do this is when the child is playing or in a good mood.
It is not recommended to clean your baby's tongue immediately after feeding.
This toothbrush should not be used to clean a newborn's tongue. You can also choose a special gum cleaner.
Avoid using fluoridated products as they may be swallowed by your child.
Wash your hands thoroughly with soap. Take a sterilized baby earmold and dip it in a glass of warm drinking water. Now gently squeeze it onto your baby's tongue. Rub the upper and lower gums. Don't forget to clean your tongue itself.

Hold the earmold firmly.
Each child is individual. Some children may become irritated during the tongue cleaning procedure. In such cases, you can ask your pediatrician what other effective solutions to this problem are available. In addition, it is not recommended to give any medications to a child without consulting a doctor.
Prevention
- Make sure that the room in which the newborn is most often found is well ventilated: if the room is too hot, the oral mucosa will dry out, and this already provokes the appearance of this condition.

- If it is not possible to provide the necessary humidity, periodically give the baby a little water to moisten the oral mucosa. It is also advisable to give a couple of sips of water after each feeding to rinse the mouth.
It is also important to organize the necessary sanitary conditions: wash toys, especially if the baby actively puts them in his mouth, wash bottles and pacifiers well. Monitor breast hygiene if the baby is breastfed.
- The condition of the tongue directly depends on the condition of the whole organism, so it is important to periodically check the functioning of the internal organs to exclude possible diseases.
Causes of plaque
The reasons for the formation of white plaque on the tongue of a small child can be different. A pediatrician should answer the question of why exactly the plaque appeared in the mouth on the roof of the mouth.
Main possible reasons:
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, it is very important to do a full examination of the baby’s body as quickly as possible.
- Disorders in the nervous system.
- Presence of infections.
- Avitaminosis.
- Failure to comply with oral hygiene rules.
- Possible diabetes.
Sometimes the reasons why a child has a white coating in his mouth and spreads to his lips are not as terrible as those listed above.
- If the baby is bottle-fed, the rash on the tongue may be the remains of baby formula. The situation is similar with breastfeeding.
- After eating, the child burped and leftover food remained in the mouth.
- White plaque can be a harbinger of the appearance of baby teeth in children.
Among the reasons that influence the change in color of the mucous membrane in the baby’s mouth, one can distinguish safe ones (due to feeding with milk or formula) and dangerous ones.
Dangerous reasons include:
- Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (diet changes, improper introduction of new foods);
- Diseases of the oral cavity (stomatitis, thrush, herpes);
- Diseases caused by viruses or infection (ARVI, influenza, bronchitis, tonsillitis);
- Neurological diseases;
- Decreased protective function of the body, taking antibacterial drugs;
- Poor hygiene;
- Diabetes.
We suggest you read: Treatment and causes of bitterness in the mouth in the morning, after eating. What does it mean
Dysbacteriosis
Quite often, in infants, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted due to the incomplete formation of the digestive system. Dysbacteriosis is accompanied by abdominal pain, colic, and diarrhea. Therefore, if a gray coating appears on the tongue, you should immediately visit a doctor to prescribe the correct treatment.

Dysbacteriosis is often accompanied by severe abdominal pain and diarrhea
A white coating on the tongue of a newborn may be a sign of more serious diseases. For example, enterocolitis or gastritis. With intestinal inflammation, you may notice the presence of blood in the stool, an increase in temperature, and white spots appear only on the root of the tongue. With gastritis, the plaque may have a brown tint; you can notice it in the central part of the tongue, and there will be cracks along the edges.
Quite often, failure to maintain oral hygiene against the background of reduced immunity provokes the formation of white plaque in the mouth, which indicates infection of the oral cavity with infections, viruses, and fungi. Diseases such as stomatitis, herpes, and thrush develop.
If a child puts dirty toys, unwashed pacifiers, and bottles into his mouth, then various foreign microorganisms cannot be avoided. Against the background of weakened immunity, they develop and provoke the development of stomatitis. This is a disease of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by the formation of white spots throughout the oral cavity (on the gums, cheeks, palate, uvula), which, when subjected to mechanical action, bleed and transform into wounds. The baby feels a burning sensation, discomfort, lethargy, refuses to eat and sleeps poorly.
A viral manifestation of oral infection is herpes. In addition to white spots on the uvula, the child's body temperature rises and general weakness appears. The cause of herpes can be a sudden change in climate, poor oral hygiene and mechanical damage to the mucous membrane against a background of weakened immunity.
Thrush

The most common cause of white coating on the tongue is thrush (candidiasis). This is an infectious disease that occurs in children due to the proliferation of Candida fungi. The fungal infection starts from the tongue and spreads throughout the entire oral cavity. Candidiasis develops most often in babies under 3 months, since the body’s protective functions are not yet fully formed.
Thrush causes the baby to feel discomfort, burning, and dryness in the mouth. The child does not feel well, sleeps poorly, and in rare cases, candidiasis is accompanied by vomiting. It is impossible to remove plaque mechanically, since any damage to the mucous membrane can bleed and provoke the formation of wounds and ulcers.
It is worth noting that the causes of thrush, in addition to decreased immunity, can be:
- Mechanical damage to the oral mucosa;
- Diseases of the digestive system;
- Long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- Poor oral hygiene, dirty hands, toys, pacifiers;
- Infection of the child during childbirth (if the mother had thrush).
Other reasons
Also, infectious diseases, the consequence of which is a change in the color of the child’s tongue, can include influenza, sore throat, ARVI, pharyngitis, bronchitis. In this case, accompanying symptoms of the disease in the oral cavity may be a red or swollen throat, plaque on the tonsils. The cause of a white tongue may be bronchial asthma (the tip of the tongue is damaged) or diabetes.
A doctor's examination will help identify the cause of the appearance of a white coating on the tongue.
Reasons for the appearance of white plaque on the tongue
Normally, the tongue of a healthy baby is evenly colored pink, velvety to the touch, the oral mucosa is without light or red spots, ulcers, the gums are light pink and dense. A white coating on the tongue in the morning is normal for both children and adults; it gradually disappears during the day. If it remains all day, thickens and spreads to the palate, inner surface of the cheeks and lips, you need to consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Traces of breast milk or artificial formula and remnants of undigested food that entered the newborn’s mouth during regurgitation are the most common causes of plaque in a newborn baby; they are absolutely natural and do not affect his health.
Reasons that require treatment why a baby may have a white tongue:
- thrush - infection of the mucous membranes by a fungus;
- colds, especially those accompanied by a bacterial infection, often stain the tongue: with bronchitis, the tip of the tongue becomes white, pharyngitis leads to reddening of the papillae and the appearance of a thick white coating, with tonsillitis it forms on the root of the tongue and tonsils;
- scarlet fever turns the tongue white-yellow with red spots;
- diphtheria gives a white and gray coating, spreading to the tonsils;
- for intestinal problems, the film is brownish and lasts all day.
In all cases except thrush, coating on the tongue is not the decisive symptom when making a diagnosis; there are more characteristic manifestations - fever in infectious diseases, frequent loose stools in gastrointestinal diseases.
Why does white plaque occur?
What to do if, during the next examination, parents find a white coating on the child’s tongue? You definitely need to pay attention to the nature of the plaque, its shade, frequency of appearance, and smell. Perhaps its occurrence is due to natural causes and does not pose a danger to the baby’s health. Why does a whitish coating form on a child’s tongue?
Leftover food
What does white plaque mean in children in the morning? This whitish, almost transparent film is formed as a result of the active reproduction of bacteria and their death.
What does the film come from? Dairy food fed to newborns is an excellent breeding ground for microorganisms. The body fights foreign and harmful microbes with the help of white blood cells - leukocytes. When bacteria accumulate in the oral cavity, leukocytes begin to actively fight pathogens.
The whitish film may also be leftover milk after feeding. 3-4 month old babies often burp after eating. Artificial mixtures leave a dense yellowish coating. These marks are easily washed off with water; mom can wrap her finger in gauze, moisten it in warm water and wash off the film.

Stomatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the oral mucosa. The causes may be different, it all depends on the type of disease:
- Candidal stomatitis. Thrush is a fungal disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida. Often found in newborns who become infected with candidiasis while passing through the birth canal. The situation is aggravated by insufficient care and the use of dirty bottles. White plaques appear in the baby’s mouth, which gradually cover the entire tongue, pharynx, and tonsils. The plaque has a cheesy, flaky consistency, as if the child had just eaten cottage cheese or drank milk. The smell is unpleasant, slightly sour.
- Aphthous stomatitis. It is characterized by the appearance of gray spots (aft) on the mucous surface. At first these spots are few, but over time the aphthae grow, turning into deep ulcers covered with a gray fibrin film.
- Allergic stomatitis. When an allergen enters the oral cavity, the tongue swells and becomes covered with blisters that contain purulent fluid. These pimples burst and the tongue becomes covered with a whitish coating.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract
Often a white or orange coating indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Based on the location of the film, doctors can determine the source of the problem. If the central part of the tongue is covered with a film, this indicates problems with the stomach. A coated root indicates a malfunction of the intestines. You can see what a coated tongue looks like in the photo.
Diseases that are characterized by the appearance of a whitish coating:
- Gastritis. In the acute form, a dense white film appears in the center of the tongue, the mucous membrane is dry, and the child often asks to drink. With chronic gastritis, the entire tongue is covered with a yellowish coating.
- Ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. It is characterized by the appearance of a dense grayish coating at the root of the tongue.
- Pancreatitis. The mucous membrane of the mouth and the entire tongue are covered with a gray-yellow coating.
We suggest you read: The child has white pimples on the palate
When the digestive system is malfunctioning, the appearance of a white film in the mouth is often accompanied by other characteristic symptoms. The child suffers from colic, constipation or diarrhea, attacks of nausea and vomiting. Orange plaque indicates pathologies of the esophagus.
Whitish plaque is a symptom of many infectious diseases. As a rule, it appears at the beginning of the development of viral and bacterial diseases and is explained by the accumulation of leukocytes at the site of concentration of pathogenic microorganisms. Some infections, such as scarlet fever, are very dangerous for children aged 2-3 years. Having seen the characteristic plaque and smelled an unpleasant odor, parents should immediately go to the hospital.
The table presents a list of infectious diseases characterized by the appearance of white plaque.
| No. | Name | Pathogen | Symptoms |
| 1 | Scarlet fever | Group A streptococcus | In the first days of scarlet fever, the tongue becomes crimson in color (this is the so-called “scarlet tongue”), then a thick white coating appears at the root. The child develops a fever and a rash appears on the cheeks and groin. |
| 2 | Diphtheria | Loeffler's bacillus | A dirty white film covers the tonsils and the root of the tongue and is very difficult to remove. The throat hurts, the mucous membrane is swollen. The temperature is high (38-39 degrees), the baby is lethargic. |
| 3 | Angina | Streptococci, staphylococci, less commonly viruses or fungi | The tonsils are covered with purulent mucous exudate, the tongue is coated with a dense coating. The baby has a sore throat, it is very painful for him to swallow, and the temperature is elevated. |
| 4 | ARVI, CMV | Parainfluenza, adenovirus, rhinovirus, reovirus | With CMV, the tongue is coated, but dry. Accompanied by cough, runny nose, sore throat. |
Other reasons
A whitish film is a symptom of many diseases. In addition to the above diseases, it appears in the following diseases and disorders:
- Caries. Bacteria accumulate in carious cavities and spread throughout the oral cavity. They form plaque on the tongue, gums, and palate.
- Dysbacteriosis. It often appears after a course of antibiotic treatment, due to poor nutrition, or after severe poisoning.
- Iron-deficiency anemia. It often manifests itself in the form of a white tongue and a jam in the corners of the mouth (more details in the article: jams in the corners of a child’s mouth: causes and methods of elimination). In addition, the following symptoms are characteristic of anemia: weakness, pale skin, dizziness, fatigue, poor appetite, moodiness.
- Dehydration. With a lack of fluid in the body, the amount of saliva decreases and the secretion becomes thicker. This means that it cannot cope with the disinfection function.
- Smoking. In teenagers, white plaque with orange spots can form from smoking.
Causes of white plaque
- Leftover milk after feeding. If the plaque is easily removed from the surface, forms in specks rather than in a dense layer, and is washed off well with water, most likely there are particles of milk or remnants of regurgitation left on the tongue. A whitish tongue in infants under one year of age is absolutely normal.
- Fungal infection. Popularly this disease is called thrush, in medicine - candidiasis. If you have thrush, the coating on your baby's tongue will be thick and cheesy in appearance. This disease is caused by yeast-like fungi Candida. Please note that with true thrush, plaque can be not only on the tongue, but also on the cheeks, palate, and gums. Candidiasis can also spread to an unhealed umbilical wound and the mucous membranes of the genital organs. Candida fungi are considered opportunistic. They are present in the microflora of the vagina, intestines, and oral cavity. The rapid growth and reproduction of these microorganisms leads to disease.
The main reasons for the rapid growth of Candida fungi
These include:
- weak immunity;
- gastrointestinal microflora disorders;
- hormonal imbalances;
- taking antibiotics.
Pediatricians say dry mouth is one of the main reasons.
When to see a doctor
New parents carefully monitor the health of their newborn. If a white coating forms on your baby’s tongue and it doesn’t go away after a few days, it’s not a big deal. You should consult a doctor if your baby exhibits the following symptoms:
- excessive worrying and moody behavior for no reason;
- the baby does not take the breast because it hurts him to suck milk on his own;
- the inner surface of the cheeks and gums are severely inflamed.
If these symptoms occur, parents are advised to consult a pediatrician. He will have to examine the baby, take tests if necessary and identify the cause of plaque formation in the mouth and tongue.
If you need to go to the hospital, you shouldn’t refuse because the doctor won’t just suggest it. Necessary means necessary. This means it will be better for the child.
Diagnosis of diseases characterized by the appearance of plaque
Impaired regeneration of the epithelium of the papillae covering the tongue also occurs due to the presence of tonsillitis (angina), gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis and other diseases of the digestive and immune system.
A white tongue in a newborn is also a distinctive symptom used to differentiate between tonsillitis and pharyngitis, since the viral infection of the tongue that occurs with pharyngitis is usually not accompanied by the appearance of a coating on the tongue. In the case of diphtheria, it may have a grayish tint.
The method of treating tonsillitis should be determined by an otolaryngologist. In addition to the local use of antiseptic drugs, antibiotic therapy is used.
The formation of plaque on the tongue during intestinal diseases is very typical, since the tongue is part of the digestive system.
In the case of diseases of the liver and pancreas, these spots may have a yellowish color, while the condition of the papilla undergoes a number of changes in accordance with the level of intragastric acidity.
These facts indicate a close relationship between the tongue and other organs of the digestive system.
To remove plaque from the tongue, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease. This process should be entrusted to a gastroenterologist after all necessary examinations have been carried out.
Thus, a white coating on a child’s tongue is almost never associated with exclusively local pathology. After examining the pediatrician, you should also consult with an ENT doctor, dentist, allergist and immunologist (depending on the suspected cause of this condition).
If parents find a white coating on the baby’s tongue, they need to contact their local pediatrician. The doctor will examine your mouth and, based on the color, smell, nature of the film, as well as accompanying symptoms, make a diagnosis or refer you to other specialists for diagnosis:
- dentist - for diagnosis and treatment of caries and stomatitis;
- gastroenterologist - for the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- immunologist-allergist - in case of allergies.
To confirm the diagnosis, the pediatrician writes a referral for tests (general blood and urine tests). If necessary, plaque scraping is done. If a child is found to have blue plaque, a consultation with a cardiologist is required. A blue tongue is often a sign of cardiovascular pathologies.
Treatment: subtleties and nuances
Before you start treating white plaque in a child’s mouth, you need to understand why it appeared. Only an experienced doctor will help with this. It is worth noting that it is not always necessary to resort to treatment. In some situations, the plaque goes away on its own. Let's consider the main subtleties and nuances that parents should know about.
- In case of gastrointestinal diseases, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease first. After this, the tongue will clean itself. The main thing is to quickly find out what exactly the problem is in your child’s body.
- If your baby has problems with the nervous system, only a neurologist can help. With proper treatment, the plaque will go away on its own within a few days.
- If the disease is viral or infectious in origin, drug treatment may be required. You cannot buy pills for your baby yourself - this will only worsen the situation. The required treatment and prevention are prescribed only by a competent doctor after a thorough examination of the child.
- For thrush, the main treatment can be accompanied by cleaning the palate with a soda solution.
The first thing to do when a white tongue appears in an infant is to ensure that the mucous membrane is moisturized. To do this, it is necessary to ensure room humidity (about 50-60%) and temperature conditions (no more than 20-22 degrees). When white spots begin to appear, they can be washed off with a weak solution of water and soda several times a day.
We suggest you read: Why the tip of the tongue is red and stings
If you are dealing with an infectious or fungal infection of the oral cavity, doctors prescribe special medications.
The color of the tongue can tell about the child’s health and the presence of certain diseases. Therefore, it is recommended to check the condition of the oral mucosa (tongue, gums, inner cheeks, palate) from time to time. Inspection of the tongue should be carried out from above and below, examining the tip of the tongue and its root.
If it is found that the change in the color of the tongue is not associated with food intake and does not disappear after rinsing, then treatment must be carried out with the help of medications. In the case of thrush, in addition to local effects on the mucous membrane, in advanced cases it is necessary to take a course of internal antifungal drugs.
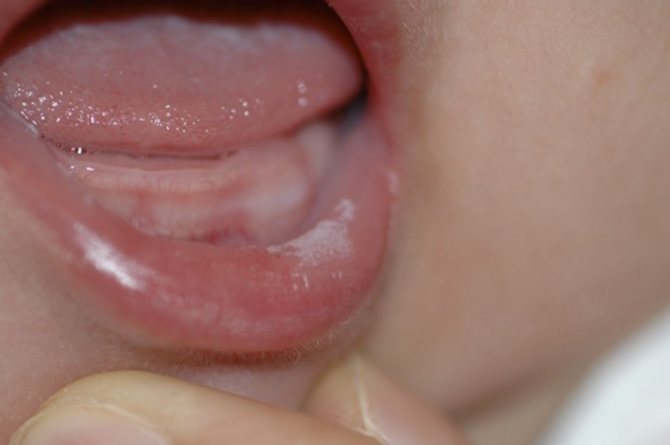
These are medicines that contain nystatin or clotrimazole (Candida solution). The dosage and duration of taking the drug are prescribed by the doctor based on the degree of complexity of the disease and the age of the child. For infectious diseases of the oral cavity, antibiotics are prescribed, and there are cases of treatment in a hospital setting. Physician supervision is especially necessary during chronic stomatitis.
If a doctor discovers thrush in a baby, then, depending on the stage of the disease, he can prescribe safe antifungal drugs and procedures for local action. For example, a weak solution of boiled water and soda helps fight thrush. Moisten sterile gauze with this mixture and wipe the tongue with light movements several times a day.
Pediatrician Komarovsky, regarding the white coating on the tongue of a baby, says that if this does not bother the child, then there is no need to worry. If the baby’s behavior has not changed and he does not feel discomfort, then this plaque is most likely the remainder of the milk. If, along with a change in the color of the tongue, there are other symptoms and the child feels unwell, you should definitely consult a doctor. He does not recommend using soda solution because of its unpleasant taste.
At home, it is recommended to use honey or lemon juice in addition to soda to remove white plaque from a baby’s mouth. Honey is used along with turmeric for better effect. This combination has good antibacterial properties, but must be used with caution, as it can cause allergies.
A popular method of combating plaque is also rinsing the mouth with lemon juice. But doctors do not recommend using this method as the main method of combating plaque. It is quite acidic and can burn the delicate skin of a child, and citrus fruits can also cause an allergic reaction.
If a nursing mother is worried about a white coating in her baby’s mouth, she should show the baby to a pediatrician. After the examination, the doctor will reliably determine whether treatment is required. If there is no reason for concern, then the mother and baby are sent home. In other cases, therapy is prescribed, and sometimes a preliminary examination of scrapings from the tongue is required.
If the cause of the plaque is viral stomatitis, then the child is prescribed antiviral drugs in the form of suppositories or syrups. Symptomatic treatment is also recommended - anesthetic gels, antipyretic suspensions. For bacterial stomatitis, you cannot do without antibiotics. Drugs are selected individually; usually penicillin drugs or macrolides are used for infants.
With thrush, many mothers try to remove the white plaque on their own. However, a single cleansing of the mucous membrane does not eliminate the infection. Alternative medicine recommends using soda solution, honey, and chamomile decoction to treat the mouth. But only a doctor can tell you what to do in a particular case.
Mild forms of candidiasis, on the recommendation of a pediatrician, are treated with antiseptic solutions. It is important to treat not only the baby’s mouth, but also the breasts of the nursing mother.
What to do if white plaque is detected
Firstly, it may not be thrush at all. And secondly, even if it is candidiasis, you can cope with this disease at home.
- Traces of milk. They can be eliminated with boiled water. After feeding, give the baby one or two tablespoons of water, and the plaque will usually wash off. There is no need to clean off traces of milk mechanically and once again disturb the child.

Mild form of thrush. The doctor prescribes local treatment, which the mother carries out at home. It is necessary to treat the oral cavity with a soda solution. An alkaline environment prevents the growth of fungi. You can treat pacifiers and bottle nipples with a soda solution. Plaque can also be treated with bactericidal aniline dyes and iodinol.- Severe form of thrush. In this case, in addition to mandatory treatment of the oral cavity, the doctor may prescribe treatment with antifungal agents, immunostimulants, and a vitamin complex. Under no circumstances should you use medications for thrush on your own, without a doctor’s prescription. It is also important to know that a 5% borax solution, which used to be so actively used to treat thrush in children, is prohibited due to its toxicity.
Usually mild forms of candidiasis can be easily treated at home within 5-7 days. In severe cases, the child’s temperature rises, plaque spreads to the throat, is difficult to remove, and after removing the plaque, painful bleeding wounds form. To prevent this condition, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the baby and regularly examine the oral cavity.
What to do and how to remove plaque on the tongue?
If the film is the result of poor care or food residue, you can remove it yourself; you do not need to use special tools for this. In the case of some diseases, it is difficult to remove, leaving bleeding wounds. Any manipulations to cleanse the oral cavity of a sick child should be carried out after consultation with a doctor.
Depending on the disease, the doctor prescribes medications that remove white plaque from the tongue. Most often these are topical preparations - rinsing solutions, ointments, gels.
The table below provides a list of medications.
Folk remedies
White plaque in a baby’s mouth can be removed very easily if there is no serious damage to the body. Try to do this with proven folk remedies. If there is no result, then you should consult a doctor.
- Honey. This is an excellent remedy for fighting bacteria and germs. The only downside is that honey is an allergen. You must first make sure that the baby does not develop a rash after consuming it. If there is no allergy, a cotton swab is moistened with honey and the plaque is removed with it.
- If the child has not previously shown an allergy to citrus fruits, the plaque can easily be removed with pure lemon juice. In addition, it copes with fungal formations, if any.
- Soda. Try getting rid of plaque with a baking soda solution. It does not taste very pleasant, so for a small child it is better to use one of the methods listed above, and resort to soda only as a last resort.
How to treat thrush
Treatment of an infant should be treated with extreme caution. The baby has very delicate skin and mucous membranes. Some drugs can cause allergies. You can start treating thrush yourself at home. Carefully, without damaging the skin of the tongue, remove the white coating with a cotton swab. Then treat your baby's mouth with an unsaturated baking soda solution. To do this, dilute a teaspoon of powder in a glass of warm water. Not hot - this is important! Soak a cotton swab with baking soda and wipe your tongue, cheeks and palate.
In addition to soda, experienced mothers advise wiping the affected areas with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or hydrogen peroxide. The frequency of the procedure is every 2-3 hours for a week. It is better to use cotton swabs for treatment, since a child can swallow or inhale a cotton ball.
The procedure must be carried out a quarter of an hour after feeding. Otherwise, irritation will cause vomiting and the baby may vomit what he ate.
If home treatment is ineffective, it is worth showing the child to specialists and getting tested. Based on them, the doctor will prescribe antifungal drugs. A series of such medications for small children includes Fluconazole or Diflucan. If the components are intolerant, a suitable drug will be selected individually for the baby.
In addition to the syrup, if the tongue is severely affected by plaque, the doctor prescribes ointments or local gels. Miconazole, slightly less often Nystatin. They are applied with a cotton swab or a finger to the fungus-affected areas in the child’s mouth.
You should not stop treatment if clinical manifestations in the form of plaque have disappeared. After all, the causative agent of the disease may remain, and the coating on the tongue will appear again. The course must be completed.
Rules for mom
The mother of an infant with thrush must follow some rules.
- Even if the mother does not have signs of the disease, she needs to undergo treatment, which must be prescribed by a doctor.
- Before and after each feeding, the breasts should be rinsed with warm water.
- If the child is artificial, the nipples are also treated with soda solution each time.
Preventive measures
White plaque on the tongue and lips of a baby is a phenomenon that in most cases can be prevented. You just need to follow basic preventive measures.
- All feeding devices (bottles, pacifiers) must be sterilized as often as possible.
- Sterilize toys that your baby comes into contact with most often.
- Bed linen must be boiled to kill bacteria.
- If the baby is breastfed, the nipples must be washed with warm water before feeding.
- Make sure your baby consumes enough vitamins. Add a little lemon juice to your water if you are breastfeeding, and eat healthy fruits and vegetables.
- Pay special attention to your child's oral hygiene.
A white coating on a baby's tongue is not always a symptom of a serious illness. Try to remove it, and if that doesn’t work, then make an appointment with a doctor to identify the cause and begin treatment.
Relationship between feeding and plaque
Before looking for pathology in a baby, it is worth remembering that all the food he consumes is white. In babies under 4 months of age, the salivary glands are underdeveloped, the tongue's functioning is imperfect, and the oral cavity is poorly cleaned of food debris. The coating formed from food is uniform, slightly transparent, taste buds are visible through it, and does not cause discomfort. Such a white coating on the tongue of a newborn does not require treatment.
Breast-feeding
During breastfeeding, plaque occurs more often than during artificial feeding. Its difference is that it affects exclusively the tongue, the rest of the oral cavity remains clean. It usually disappears half an hour after eating, but in children who frequently suckle it can persist throughout the day.
If the white coating is natural, it can be easily removed with a cotton swab or bandage, the surface underneath is pink, without redness. There is no need to get rid of such plaque, since it does not harm the child in any way. Moreover, the desire to clear the tongue of the white film can lead to damage to the mucous membrane and its further infection.
Artificial feeding
When feeding a child with infant formula, white plaque may also form in the mouth. Due to the fact that bottle-fed babies feed by the hour, its intensity is less and it usually disappears by the next feeding.
The coating from the mixture can cover not only the tongue, but also other places in the mouth, most often the inside of the lips. Not all mixtures leave a white coating. To find out whether the mixture consumed by a baby can cause a colored tongue, you can do a test: put it in your mouth, hold it for a few minutes, and then examine the tongue.
In a baby, a white coating due to thrush occurs more often when he is bottle-fed, since the sugar in formula promotes the development of fungi. To find out whether the film on the tongue is due to the mixture or is it the work of fungi, you need to clean part of it and examine the mucous membrane. If it hasn't changed color, there's nothing to worry about.










