Can pregnant women and nursing mothers take Espumisan?
Espumisan during pregnancy is the drug of choice for women with increased gas formation, pain and discomfort in the abdomen. The active component, simethicone, transforms and removes gases from the intestines in a natural, physiological way. While carrying a baby, women face problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to:
- changes in hormonal levels;
- growth and pressure of the uterus on surrounding organs;
- nutritional errors: excessive consumption of simple carbohydrates (baked goods, sweets, confectionery products made from white flour), carbonated water, legumes causes bloating, discomfort and heaviness in the stomach.
The German medicine Espumisan helps to cope with unpleasant symptoms, improves the well-being, psycho-emotional state and quality of life of the expectant and nursing mother. The medicine is taken in the early and late stages of pregnancy, during lactation. It is allowed to use the medicine immediately after childbirth. The doctor decides how much simethicone to take.
Foods that cause gas in the intestines
Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract are known to all people. However, if for most patients such disorders bring only minor troubles, then for a nursing mother these problems can become a cause of serious concern.
In medical practice, there are quite a lot of medications that help reduce intestinal turmoil in a baby, but the use of such drugs is far from harmless, so it is best for a young mother to adhere to a certain diet.
Prohibited products include:
- First of all, these are any leguminous plants. Peas, beans, beans, and even soy, which is popular after childbirth, can increase fermentation in the intestines of mother and baby.
- Many foods, including pears, grapes, are contraindicated for a woman in the first few months of breastfeeding.
- Not all plants grown in one’s own garden can be eaten by patients if they are bothered by the urge to produce excessive gases in the intestines. Turnips, onions, celery and even should be excluded from the diet.
- It is prohibited to drink any sweet carbonated drinks, fresh white and.
- Concerning vegetable oil, debate continues among experts: many are against its use as food, others recommend this product as a way to combat intestinal and stomach disorders in mothers and children.
- Doctors consider it the most dangerous vegetable for a young mother. Many nutritionists offer a nursing woman cauliflower or a variety of broccoli almost from the first days after childbirth. However, recent studies have confirmed increased gas formation in the intestines of mother and child after eating this vegetable.
Flatulence during breastfeeding is a fairly serious problem. And it is the use of the listed products for the daily diet of a nursing woman immediately after childbirth that can lead to a similar problem. A nursing mother should limit herself to lamb or veal and potatoes in the first few months of lactation. Such products do not lead to the formation of excess gases in the patient and child; a dietitian should recommend such a diet to the young mother.
Instructions for use of Espumisan during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Espumisan is produced in the form of capsules, emulsions and drops for internal use. The capsules are small in size and do not need to be washed down with water. This dosage form is convenient to take with you to work, on trips, and travel. The medicine is used during meals or before going to bed. The drug is effective and safe, but is not intended for self-medication. Before starting use, you should consult your doctor.
Can pregnant women take Espumisan?
The active substance of Espumisan, simethicone, is of natural origin. The substance does not penetrate the placental barrier and is quickly eliminated from the body. It is not able to influence the growth and development of the child, regardless of the month of gestation, since it acts locally.
Safe for pregnant women and babies from the first days of life.
- prescribed by doctors to reduce gas formation, pain, eliminate psychological discomfort caused by flatulence;
- the drug acts locally, does not penetrate the systemic bloodstream and does not affect other organs;
- well tolerated, indicated for women in all 3 trimesters of pregnancy, as well as after the birth of the baby;
- The medicine contains no sugar, so it can be used for diabetes.
The product can be used as first aid, for symptomatic treatment of pain, bloating, and heaviness in the abdomen. The drug is also suitable for long-term treatment in combination with other groups of drugs.
Indications for therapy during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Taking Espumisan is indicated for women with the following pathologies:
- functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by hiccups, belching, and dyspeptic disorders;
- flatulence at any stage of pregnancy, including during gestosis;
- anemia, which is corrected medically using ferrum-containing medications;
- accumulation and stagnation of feces;
- chemical poisoning: simethicone in this case acts as an antifoam.

Capsules are used in the process of preparation for ultrasound, endoscopic, and x-ray examinations. Taking the drug allows you to get more correct results.
Symptomatic treatment
Most new mothers do not have enough time to visit doctors, so they try to get rid of a delicate problem on their own. You should start with your diet. It is also necessary to ensure that bowel movements are regular.
As symptomatic emergency medications, it is permissible to use the following drugs: Espumisan, Sab Simplex, children's Bobotik or dill water.
Such products are allowed during breastfeeding; they will also have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the baby’s digestive system. Anti-flatulence medications will break up the accumulations of gases and gently remove them naturally.
Experts note that the birth of a baby can sometimes provoke unpleasant changes in the mother’s body, such as increased gas production after childbirth. Often this disease is accompanied by bloating, rumbling and seething in the stomach. Sometimes stomach cramps and other eating disorders are possible. All this affects the already changed routine of life. What is the reason? What will help to cope with this phenomenon without harming the child and when is a doctor’s help needed?
The condition of the stomach is inextricably linked with nutrition. If a woman eats irregularly and in large portions, intestinal problems cannot be avoided.
The choice of products itself is also important. Some foods can cause flatulence during the postpartum period:
- Brown bread and other yeast-based flour products, fresh milk and ice cream have these properties.
- Vegetables at risk include potatoes, cabbage, radishes, turnips, onions and all legumes.
- Fruits that cause flatulence include pears and grapes.
- Mushrooms, cereals with the exception of rice and sparkling water close the list.
If any of this is regularly or in large quantities present in the diet of a nursing mother, increased gas formation can be expected.
Other causes of flatulence are associated with physiological changes in the mother's body.
Before birth, the grown fetus actively puts pressure on the organs, squeezing them or moving them to the side. Therefore, within several months after the birth of the child, it is necessary to restore the entire body to a normal state.
In some cases, bloating may indicate serious health problems, such as dysbiosis. We need to consider what a young mother can do at home.
Having determined the causes of this disease, you need to understand what to do to eliminate them. Firstly, it is worth reviewing your diet. It is necessary to minimize or eliminate the consumption of foods that increase flatulence.
They can be replaced with something that, on the contrary, will alleviate your condition:
- Instead of milk, you can eat fermented milk products with almost no restrictions.
- The main products in the diet will be lean meat and fish.
- Citrus fruits will help you in moderation (you shouldn’t get carried away with them, as they can provoke allergies in either mother or baby).
- Pumpkin porridge, rice, sweet peppers, muesli, and tea with fennel seeds prevent increased gas production.
Even though breastfeeding takes up most of your time and energy when caring for your newborn, it is still worth making an effort to take care of yourself. You need to eat small portions 5-6 times a day. With the permission of the attending physician, it is necessary to take walks and exercise. This way, it will be easier for the body to recover after childbirth.
If the mother has made every attempt to change her lifestyle and diet, but the problem remains, you should consult your doctor. This could be a therapist or gastroenterologist. If bloating persists, it may indicate a more serious digestive problem. Before starting treatment, a specialist may prescribe an ultrasound or other type of diagnostic to most accurately determine the cause of this phenomenon.
If a caesarean section was used during childbirth, this circumstance can also lead to increased flatulence, since during this operation drugs are introduced into the body that temporarily block the activity of the digestive system. In this case, the doctor will recommend one of the types of moderate physical activity to quickly restore organ function.
In case of dysbiosis or active activity of harmful microorganisms in the intestines, drug treatment is necessary.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the following drugs may be prescribed:
- The drug Linex is aimed at enhancing the improvement of intestinal microflora. Since this product is based on herbal ingredients, it is safe for women who have recently given birth to children.
- Espumisan allows you to stop the production and painless removal of excess gases. This is facilitated by simethicone, the main active ingredient of the drug.
- The action of Hilak-Forte is aimed at reducing gas pressure on the intestinal walls, which reduces spasms caused by flatulence. The drug is also aimed at restoring microflora, so it can not only eliminate pain, but also heal.
Remember that the use of any medications is possible only after they have been prescribed by a doctor, so as not to cause harm to the baby’s delicate body during feeding.
Flatulence can occur in a woman after the birth of a child for various reasons: due to cesarean section, poor nutrition or dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
To restore stomach function, a young mother needs to reconsider her diet and meal times, and engage in physical exercise.
If the situation is serious, you need to contact a specialist so that he can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
The joy of motherhood is not the only thing a young mother may face after giving birth. Thus, a woman often faces a very delicate problem that is kept silent about - gases and fecal incontinence after childbirth
. As a rule, a young mother, faced with similar problems - frequent flatulence and gases with minor feces - simply does not talk about her embarrassment, considering it indecent.
But experts talk about the forced and timely need to consult a doctor, since incontinence after childbirth is a very common complication that can be quickly and easily treated. A young mother should be wary of frequent intestinal bloating, characteristic pain syndrome and farting with feces. In most cases, this is associated with improper nutrition of the nursing mother, and fecal incontinence is explained by weakening of the sphincter muscles, which is a fairly common phenomenon after pregnancy. But women simply close themselves off with their problems alone, exclude any visits to friends and relatives, and refuse intimacy with their husbands. The problem with gases and feces can be solved, which is described in detail in the article.
Flatulence and stool incontinence after childbirth can develop due to the following reasons:
- Improper nutrition of the mother - for example, a woman constantly wants to consume whole milk or kefir. These are exactly the foods that are beneficial for the baby and the production of breast milk, but provoke bloating in a woman. Therefore, it is important to exclude such products from the menu.
- Flatulence is a consequence of a combination of incompatible products - for example, proteins and starch, when combined, provoke bloating. Therefore, after giving birth, you should not eat meat with potatoes or pasta - here it is better to use the nutritional rules (grains and proteins are separately combined with vegetables).
- Overeating is also a cause of bloating. After childbirth, a young mother is recommended to eat fractional meals - up to 5-7 times a day, but in small portions.
- Eating fruit after the main course is always prohibited, since fermentation begins in the intestines, causing bloating to take on harmless turns.
Intestinal bloating in a woman in labor is a completely understandable phenomenon due to the displacement of internal organs during pregnancy. Immediately after childbirth - within a month - flatulence may appear. But farting here happens without excreting feces - otherwise, it is considered a pathology that requires timely treatment at the initial stage.
Rules for using Espumisan
At any stage of pregnancy, as well as after its end, the medicine can be used only with prior agreement with the doctor. The dosage, frequency and duration of therapy are selected taking into account complaints about emerging symptoms, the course of pregnancy, and the presence of concomitant diseases. Each of the dosage forms has its own application features:
- You can skip the capsule with water or take a few sips of liquid after taking it;
- Shake the bottle of emulsion thoroughly, measure the required dose using a measuring spoon;
- shake the container with drops, measure out the required amount using a dispenser.
The dose for a woman during the first, second and third trimesters of pregnancy is in most cases similar.
Treatment regimens for pregnant women
To reduce gas formation, a single use of the medication is sufficient. The drug is also used in courses, on the recommendation of a doctor:
- capsules: 2 pcs. up to 5 times a day;
- emulsion – up to 5 times a day;
- drops – 50 pcs. 3-5 times a day.
Caesarean section and gas formation
A separate group includes women who developed severe flatulence after surgery. Often the complaint of increased gas formation is associated with the fact that the child is born by caesarean section. This procedure requires the use of drugs that temporarily shut down the digestive tract. Recovery does not occur immediately, and decreased peristalsis leads to temporary constipation and gas formation.
Symptoms of flatulence after a cesarean section disappear within a few weeks. If the abdominal pain continues to bother you or the incision is healing poorly, then you should definitely contact a gynecologist with these complaints.
Are there any risks for the child if the mother takes Espumisan: doctor’s answer
Doctors note that there are no risks for the child when using Espumisan. However, the FDA (American Drug Administration) has not yet determined which category simethicone falls into. There have been no reliable, strictly controlled studies regarding the safety of its use in pregnant and lactating women.
The drug has been on the market for 16 years. During this time, no information was provided regarding adverse effects on women or the fetus. However, it is worth taking responsibility for your own health and the health of your children. The possibility and advisability of using carminative drugs with unproven safety is recommended to be discussed with qualified, experienced specialists.
How to properly give ESPUMIZAN to a breastfed newborn
- Cleaning your face at home from acne and blackheads – 04/17/2019
- Which formula is best to choose for a newborn with mixed feeding: advice from mothers! – 06/16/2017
- How to get SNILS for a newborn child: list of required documents – 06/09/2017
Increased gas formation and colic are common problems faced by parents of newborn babies. This happens due to the physiological characteristics of the body: the baby’s digestive system is not yet fully adjusted . During feeding, the child captures air bubbles, which, penetrating into the intestines, stretch its walls and cause discomfort. The baby begins to tuck his legs in and cry hysterically, thereby aggravating the situation. You can help your baby in different ways. One of them is taking the drug Espumisan. Parents are interested in whether the medicine will harm the baby, in what dosage it should be taken, and how to do it correctly. We will try to answer all questions in the article.
How can a pharmacy help with flatulence in mother and baby?
Most often, a young mother copes with intestinal bloating by changing her diet and selection of foods. However, there are situations when medical intervention is required to solve such a problem.
In such situations, doctors advise:
- The most common drug allowed during breastfeeding is Linex. This medicine enhances the growth of intestinal microflora of both mother and child, thereby preventing the formation of gases. It should be noted that this product is created on the basis of natural plant components.
- As one famous advertisement says: “There’s a hurricane in your stomach - take Espumisan.” This product really reduces the formation of gases in the intestines of a woman and baby thanks to its active ingredient - simethicone.
- And, of course, the well-known drug “Hilak Forte”. This medicine is indispensable if the patient has a disruption in the production of beneficial bacteria in the intestines caused by a malfunction in the diet of a nursing woman. This drug helps reduce gas pressure on the intestinal walls of the baby and his mother, thereby reducing the severity of pain and intestinal colic.
Flatulence in newborns during breastfeeding is most often caused by inconsistency between workers in the postpartum department and children's wards. Naturally, childbirth and the associated loss of calories cause a burning appetite in a young mother, which can lead to disturbances in the mother’s diet.
Not all foods are allowed in the first days after the baby is born. It should be borne in mind that even ordinary ones can provoke intestinal colic and bloating in a little person.
The coordinated work of the neonatal and postpartum wards is the key to reducing digestive problems for mother and baby. This is reflected in the latest protocols for the work of perinatal centers and maternity hospitals.
How to give espumizan to a newborn while breastfeeding
Espumisan has a wide spectrum of action . Its peculiarity is that the drug can be used even by newborns. Although it is available without a prescription, you should consult your doctor before using it. Indications may be the following:
- Bloating, gas, colic;
- Flatulence, heartburn;
- Poisoning;
- Preparing for an ultrasound.
As a rule, doctors prescribe the drug if colic torments the baby every day ; dill water, massage and warm diapers do not help. In severe cases, pediatricians recommend not waiting for the situation to worsen, but giving medicine at every feeding (up to five times a day) for several weeks.

It is also worth noting that Espumisan acts as a sedative, after which the child quickly falls asleep.
Required dosage
Before giving the drug to a baby, you need to understand the dosage . It doesn’t matter whether the child is breastfed or bottle-fed, the scheme should be as follows:
Espumisan 40
- Children from birth to 6 years – 5 ml;
- From 6 to 14 years – 10 ml;
- Adults – 10–15 ml.
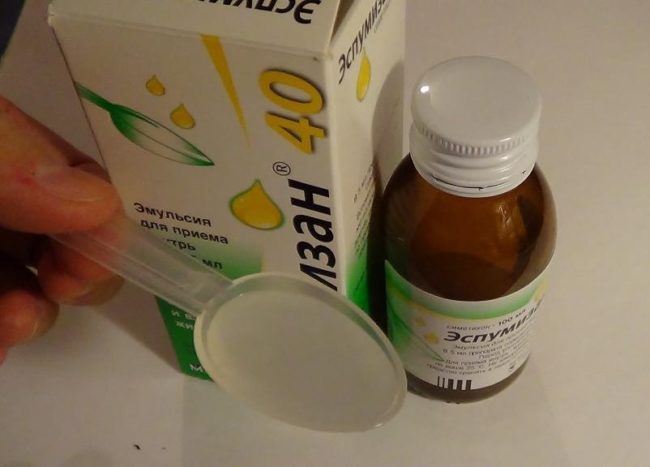

The maximum dose at one time is indicated above. Doctors do not recommend using the drug more than 5 times a day.
Espumisan L
- Children under 6 years old – 1 ml (this is 25 drops of the drug);
- Children from 6 to 14 years old – 2 ml;
- Adults – 2–2.5 ml.

If the child is breastfed, Espumisan should be given using a measuring spoon or syringe. If the baby refuses to take it, you can mix it with milk. But adding the product to water is not recommended.
For bottle-fed children, the drug is added to the mixture. As a rule, these children have more pronounced problems.
Composition of the drug
Liquid suspension for internal use is milky-pastel in color, slightly viscous, with a sweet odor.
The active substance is simethicone 40 mg. Additional components: glycerin (MZ = 3.0), Sorbic Acid, E952, E954, flavoring agent, filtered water.
Price: 260 rubles.
Enterol capsules: instructions for use for adults and children.
How to properly treat dysbiosis in a baby? Read our article at the link.
Which is better - Festal or Mezim? https://vashjeludok.com/lekarstva/tabletki/festal-ili-mezim-chto-luchshe.html
Contraindications and adverse reactions
Espumisan is a practically safe drug . But you still need to know about its contraindications:
- Intestinal obstruction. In this case, it simply will not work;
- Individual intolerance to the drug;
- The presence of allergic reactions to the components included in the product.
You also need to be aware of the adverse reactions that may occur:
- Rash all over the body . It is necessary to take an antihistamine immediately;
- Itching ;
- Dysbacteriosis . Happens extremely rarely. You need to start a course of taking prebiotics;
- Constipation . Quite a common occurrence. If a child, after taking Espumisan, cannot go to the toilet at all, then its use should be discontinued.
conclusions

Many parents experience colic in their newborns. Even if the baby is breastfed, he may be tormented by gases. Espumisan will help cope with the problem. This drug is allowed to be taken from infancy; it is not absorbed into the blood, thereby not harming internal organs. The article presented a regimen for taking the drug. Remember, if the remedy does not work, consult a doctor; there is no point in increasing the dosage, this will lead to poisoning.
Folk remedies for fighting gases during lactation
Treatment of intestinal bloating in nursing women and their children is best started by stabilizing the diet of the young mother. For this purpose, modern medicine has enough developments, which a nursing woman will be introduced to with great pleasure at the antenatal clinic.
However, there are also folk remedies to solve this problem. Traditional healers consider fennel decoction to be the most effective. This well-known plant, in addition to other positive qualities, has a good effect on gas formation in the intestines. The subtlety is that all healthy drinks based on this gift of nature destroy gas bubbles in the intestines, thereby facilitating the passage of feces and relieving pain.
To prepare a folk medicine, 150 grams of dry plant are poured into 0.5 liters of water and brought to a boil. The solution is boiled for 30 minutes, after which it is diluted with running water in a 1:1 ratio.
The recommended dose of the drug for patients is 30 grams 20 minutes before meals at least 2 times a day. After achieving the result, use of the decoction should be continued to consolidate the effect. Usually 2 weeks are enough.
Young mothers immediately after childbirth face a lot of problems, and bloating in the baby or woman is not the worst. However, any disruption of the natural state of a nursing woman during this period can lead to various diseases in the child.
Therefore, the main recommendation if a gastrointestinal disorder occurs in a young mother is to immediately seek help from a doctor. Any self-medication during lactation is fraught with problems not only for the woman, but also for the baby.
Flatulence is a condition in which gas formation in the intestines increases. Typical signs are bloating, rumbling, and gurgling in the stomach. In addition, this condition is accompanied by intestinal spasms.
Lactating women often suffer from digestive disorders. Flatulence occurs due to the fact that mothers do not follow a diet and consume gas-forming products. The woman feels discomfort and awkwardness. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, you need to adjust your diet and take special medications.
Espumisan is a drug that is used to eliminate flatulence. The components of the medication penetrate the intestines and destroy the gas bubbles that have formed there. Espumisan is also used before diagnostic or surgical procedures. Women are interested in the question of whether the drug can be used by nursing mothers. According to doctors, this is permissible if the rules of admission are followed.