Jaundice in newborns due to physiological reasons is considered normal and does not require treatment. It usually disappears within a week after birth.
If a baby who is breastfed continues to have yellow skin for a month, then he has developed breast milk jaundice.
This is due to the properties of milk to prevent the breakdown of bilirubin, causing it to return to the blood. This condition is not dangerous if there are no other pathologies. With physiological jaundice, there are no objective reasons for refusing natural feeding.
What it is?
Pregan jaundice belongs to the category of physiological jaundice. Occurs in approximately 5% of infants fed breast milk and continues for 2-3 months. This syndrome was first discovered and studied by scientist Arias in the mid-20th century. Pathology was named after him.
This condition is caused by the presence of large amounts of estrogens in breast milk. They prevent the processing of bilirubin and provoke its reabsorption in the baby’s intestines. The underdevelopment of the child’s digestive system, in which the excretion of bile pigments is slowed down, is also important.
Typically, children with jaundice do not have other pathologies. The babies eat well, gain weight, and their development is appropriate for their age. Their liver and spleen are of normal size, feces and urine are not dark, unlike children with gastrointestinal pathologies.
With Aries syndrome, there is no toxic effect on the brain, since conjugated bilirubin has low toxicity. Therefore, the mental development of children is within normal limits.
Watch in the video what Komarovsky says about breastfeeding jaundice:
What is the reason for the occurrence
While in the womb, the baby's body contains an unusually high level of hemoglobin.
After birth, hemoglobin, synthesized with oxygen, begins to slowly decrease and return to normal. But it is not it that gives yellowness to the skin, but bilirubin. Bilirubin is a substance that helps to synthesize hemoglobin. It is formed as a result of the destruction of red blood cells and is fat soluble. In fact, this same process occurs every day in the body of every person, but the skin and whites of the eyes do not turn yellow. The thing is that in newborns, some organs, including the liver, which is responsible for receiving and processing bilirubin, are not able to cope with such a large amount of this substance.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
The body of a newborn, not accustomed to such active work, does not process the nth amount of bilirubin. And it is for this reason that the baby turns orange. As a rule, doctors call such jaundice physiological, that is, completely normal.
Causes
The cause of jaundice is an excess of the level of conjugated bilirubin in the child’s blood. The provoking factors of hyperbilirubinemia are:
- Prematurity. In premature babies, the condition occurs 3 times more often than in those born at term.
- Untimely passage of meconium (after 12 hours). This happens for 2 reasons: the umbilical cord was clamped untimely, labor was stimulated with oxytocin.
- Prolonged fasting of the newborn due to late breastfeeding Bilirubin levels decrease with early and frequent feeding, which promotes weight gain.
- Difficult labor resulting in fetal asphyxia.
- Chronic maternal diseases associated with endocrine disorders (diabetes, hypothyroidism).
- Heredity. If a similar condition occurs in the mother, then the likelihood of manifestation in the baby increases.
- Lack of nutrition. The baby does not have enough mother's milk, so the intestines have difficulty emptying.
Symptoms
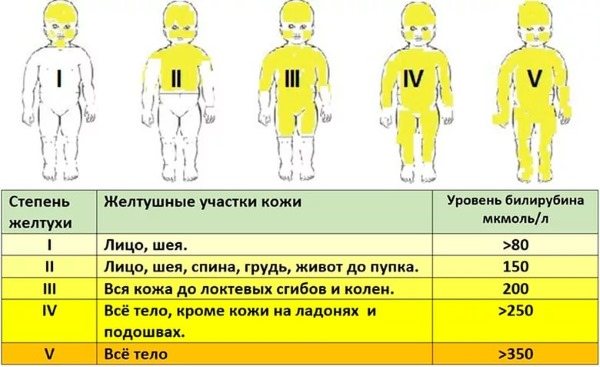
The first signs appear 7 days after birth and disappear by 3 months. Sometimes Aries syndrome is a continuation of physiological jaundice that developed on the 3-4th day of life. The skin and sclera of the newborn become yellow.
In the child’s blood, the level of conjugated bilirubin increases to 450 µmol/l, and indirect (toxic) bilirubin increases slightly, to 55 µmol/l.
The child is no different from his peers, he suckles well, is actively developing, and his weight is appropriate for his age. After about a month, the manifestations of jaundice weaken and disappear by 2.5-3 months. If this does not happen, then they speak of a pathological condition.
Main causes of the disease
Breastfeeding jaundice develops in the presence of a number of specific substances in the composition. They negatively affect the production of bilirubin and prevent it from being excreted normally from the body. The situation is dangerous due to the accumulation of the substance, which manifests itself as a change in skin color. After a certain period of time it turns yellow.
Scientists have been able to establish that the development of the disease is also influenced by a genetic factor. Therefore, if close relatives were previously diagnosed with this disease, then the baby’s risk of developing it increases. In this case, parents should be extremely attentive to the child’s condition and, if the first symptoms appear, seek advice from a pediatrician.
Breast milk jaundice is a disease characterized by a number of features:
- The clinical condition is diagnosed in the baby 7-10 days after birth.
- If the physiological condition worsens, jaundice may show its first signs three days after birth.
- Breast milk jaundice begins to appear only in the third week after the baby is born. The difference between this type of pathology is that in addition there are no disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems in the baby’s body.
Yellow skin color is the first sign of illness
Breast milk jaundice cannot negatively affect the functioning of the digestive and genitourinary systems. The baby does not refuse food, and his growth and weight gain are within the required range. The condition negatively affects only the content of bilirubin in the blood. Due to this, the skin and urine do not change their color, although this symptom is characteristic of other types of jaundice.
The second week of the disease is considered the peak. During this period, the maximum content of bilirubin in the blood is recorded. Additionally, it should be noted that the situation does not negatively affect the brain, since there is no toxic effect at all. Bilirubin at this point is bound to glucuronic acid.
This jaundice cannot negatively affect the psychological and emotional development of the baby. You should also be aware of this feature when making a diagnosis.
The disease decreases in severity as the child grows older. It usually goes away by the end of the third month. Only in some cases can one notice a long course of the disease. In this case, throughout the entire lactation, the baby experiences an increased level of bilirubin in the blood.
If jaundice from breast milk persists for a long time, then the baby may have a constantly poor emotional state, insufficient weight gain and breast refusal. In this case, you should consult a pediatrician. He will be able to carefully analyze the situation and prescribe adequate treatment.
Diagnosis requires blood testing
Diagnostics

Determining whether jaundice is related to drinking breast milk is very simple. It is necessary to stop breastfeeding for several days and transfer the child to artificial nutrition. If the yellow color of the skin turns pale and the bilirubin level decreases by 25%, this indicates pregan jaundice.
The level of a substance is measured in two ways:
- Using a biochemical blood test.
- Using a transcutaneous bilirubinometer. This is a portable device that uses directional white light to measure the spectral properties of the skin and calculate the bilirubin content.
Causes and mechanism of development of Arias syndrome
Can jaundice come from breast milk? Yes. The condition of an infant who is breastfed and suffers from jaundice for a long time was described by I. M. Arias. The doctor identified the correlation back in the 60s of the last century. That is why another name for the physiological phenomenon is Arias jaundice.
The yellowness of a baby's skin during breastfeeding is due to an increase in the woman's concentration of pregnanediol, a component that gives milk the ability to absorb bile pigment from the baby's digestive system and promotes its entry into the bloodstream.
In addition, the etiology is based on an underdeveloped digestive system and difficulties with the natural removal of bilirubin from the body. In such a situation, a change in skin color is observed even against the background of consumption of cow's milk.
The occurrence of milk jaundice occurs due to late excretion of meconium, which is caused by the following factors:
- Stimulation of labor with drugs.
- The umbilical cord was clamped incorrectly.
To accurately diagnose Arias syndrome, the child is weaned from the breast for several days. If the yellowness of the skin becomes less, then this is jaundice due to lactation.
How does jaundice develop in babies?
During intrauterine development, the child’s body has an increased concentration of hemoglobin. After birth, the component enters into a special reaction with oxygen, which over time helps to normalize the level. But it is bilirubin, which is responsible for the transformation of hemoglobin, that is responsible for the yellow color of the skin.
Thus, bilirubin is formed due to the breakdown of red blood cells. The liver, which processes bile pigment, is not sufficiently developed in infants, so it cannot cope with its increased content.
Etiological factors and causes
The development of breast milk jaundice is detected rarely, in approximately 1-2 children out of 100. Factors that contribute to the occurrence of jaundice syndrome:
- Starvation of the child or a sharp decrease in body weight. Rare bowel movements due to lack of milk provoke a disorder in the excretion of bilirubin. To prevent problems, the baby needs to be put to the breast at least 8 times every 24 hours.
- Having a baby prematurely.
- Prolonged asphyxia during labor.
- Gene disorders that developed in utero.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Hereditary pathologies.
- Drug intoxication of a baby.
Breast jaundice in an infant is the only symptom. As a rule, children eat well, gain weight steadily, and development is fully appropriate for their age.
How to distinguish Aries syndrome from pathology
If yellowing of the skin is the only symptom, then there is no need to worry. The following signs indicate diseases:
- lethargy and poor appetite of the child;
- restless sleep, screaming;
- disturbance of stool, regurgitation;
- decreased reflexes;
- convulsions.
The main differences between the two states are shown in the table:
| Sign | Aries syndrome | Pathology |
| Start | 3-4 days after birth | On the first day or after 20 days |
| Development | Uniform | Uneven. Symptoms disappear and appear |
| Child's condition | good | Lethargy, poor appetite, regurgitation, restless sleep |
| Duration | Up to 60 days, then declines | More than 90 days, symptoms continue unabated |
| Indicators of direct bilirubin | Normal or slightly increased, 5 µmol/l | Several times higher than normal (up to 25 µmol/l) |
| Indicators of conjugated bilirubin | Up to 202 µmol/l | Above 230 µmol/l |
| Liver and spleen | Normal | Increased |
| Color of urine and feces | Fine | Dark |
Physiological jaundice should be differentiated from such serious diseases as:
- Pathologies of the endocrine system (hypothyroidism).
- Cholestasis, in which little bile enters the duodenum.
- Hemolytic syndrome.
- Congenital liver dysfunction.
- Crigler-Nayjar disease.
- Congenital fetopathy arising from maternal diabetes.
- Gilbert's syndrome.
The most dangerous consequence of increased bilirubin is encephalopathy. The substance has a toxic effect on the baby's brain. Because of this, intracranial pressure increases, the signs of which are: convulsions, decreased reflexes, night screams, poor sleep.
At this moment, irreversible processes begin in the central nervous system, which lead to cerebral palsy, hearing loss, and delayed mental development.
To exclude the above pathologies, additional studies are prescribed:
- Liver tests.
- Study of thyroid hormones.
- Ultrasound of the liver.
- X-ray of internal organs.
Treatment methods
If the bilirubin level is more than 240-300 µmol/l, the baby is prescribed phototherapy. It is carried out in a hospital setting. Thanks to the radiation of the blue lamp, it is possible to destroy excessive amounts of bilirubin and facilitate its removal from the child’s body. This procedure does not harm the baby and does not cause pain.
The application of this technique is based on the use of a special lamp. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, bilirubin is transformed into a safe isomer, which leaves the body in a normal way.
To carry out the procedure, perform the following steps:
- They completely undress the child and put him in the incubator;
- They cover their eyes with a blindfold; boys need to additionally cover their genitals;
- They place a lamp - this is done at a distance of 50 cm from the baby;
- The duration of the procedure is 2 hours - with a high bilirubin content, irradiation can last up to 4 days with feeding intervals;
- Every hour the little patient is turned over - on his back, stomach, sides.
The procedure must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. The child's temperature should be measured every 2 hours. If the baby overheats or red spots appear on the body, the manipulation should be stopped. This is also done if the total bilirubin level has decreased, but unbound bilirubin has not increased.
In rare cases, you need to use the method of stopping lactation for 1-3 days. During this period, the baby must be fed with artificial formula, and the mother maintains lactation by pumping. After normalization of the level of bilirubin in the blood, you can return to breastfeeding.
In some situations there is a recurrence of jaundice. In this case, the procedure must be repeated. Sometimes the manipulation is carried out many times. During this time, the child should drink a lot.

With minor abnormalities in the functioning of liver cells, it may be necessary to use phenobarbital. This medicine has the following properties:
- Stimulates metabolism in the liver;
- Accelerates the elimination of excess bilirubin.
For this purpose, the milk must be expressed and heated to 60 degrees, then cooled to 36. Through heat treatment, bilirubin can be deactivated.
In severe forms of pathology, which develops against the background of genetically determined hyperbilirubinemia, the following manipulations are recommended:
- Plasma transfusion;
- Albumin administration intravenously - these substances help dilute bilirubin;
- Plasmapheresis.
How to feed your baby
Until recently, it was believed that with pregan jaundice one should stop natural feeding and switch to formula. Modern medicine has abandoned this practice. If the newborn’s condition is normal, bilirubin does not exceed 215 µmol/l, then breastfeeding can and should be done.
For severe symptoms, breaks in natural feeding are practiced. For several days, the child is given formula and plenty of fluids, this promotes the rapid elimination of bilirubin. The mother conserves milk by pumping. Then the baby is breastfed again. The symptoms return again, but are less pronounced.
Watch a video about breastfeeding jaundice and feeding rules:
Signs of breastfeeding jaundice
The main sign of breastfeeding jaundice is yellowing of the skin of the newborn. With a slight increase in bilirubin, the child does not experience discomfort, and nothing threatens his health. This condition is a variant of the norm. It gradually stabilizes and the jaundice goes away.
If jaundice persists for approximately 2 months, this is a sign that hyperbilirubinemia has developed. This disease is associated with dysfunction of the endocrine system. Along with a yellow tint to the skin, the baby develops symptoms such as:
- problems with stool (frequent constipation);
- lethargy, irritability;
- decreased heart rate;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- swelling.
This is interesting: Lamp for the treatment of jaundice in newborns: indications, contraindications and treatment process
Common signs include:
- skin pigmentation;
- enlarged spleen and liver;
- overestimation of bilirubin levels;
- development of anemia;
- drowsiness;
- tearfulness;
- irritability;
- colic in the abdomen;
- breast rejection.
These symptoms appear while milk is entering the baby’s body.
Treatment
If the baby’s health indicators are within normal limits, then no treatment is performed. Until the 90s of the 20th century, phenobarbital therapy was practiced. It was believed that it accelerates metabolic processes in the liver and promotes the excretion of bilirubin.
The drug is not currently prescribed due to its toxic effects. In extreme cases, infusion therapy is carried out, that is, the baby is given droppers with saline solutions and glucose to accelerate the clotting of bilirubin.
If the manifestations are pronounced and the level of the substance in the blood is exceeded, the newborn is given phototherapy. The baby is placed under an ultraviolet lamp; under the influence of its rays, bilirubin is destroyed. Treatment is carried out in a hospital. Foreign clinics practice home treatment, but not all clinics have the necessary equipment.
If the symptoms are associated with pathological conditions, then more serious treatment methods are used:
- plasmapheresis;
- droppers with albumin, which dissolves bilirubin;
- purification of blood from toxic products (hemosorption) or hemodialysis.
How to treat
As noted earlier in the article, there is no need to treat jaundice of the physiological type, since the body stops reacting with “yellowness” after the first week. As for pathological jaundice, it is a little more complicated.
- If you and your baby have negative Rh factors, doctors, even during pregnancy, are required to monitor and regulate the level of certain substances that affect the development of severe jaundice in the fetus, leading to death. As a rule, therapy is carried out in the form of injections and medications.

Phototherapy is recognized as the most common method of treatment after birth. How does this happen? Continuously. That is, the child is placed in a special box with light rays that affect jaundice and help completely get rid of it. The baby is removed from the box only during feeding. Possible complications: minor burns, lactose intolerance and hemolysis.- The following are used as additional therapy to phototherapy:
- infusor therapy necessary to restore the water balance of the skin and body;
- introduction of enzymes that improve liver function;
- introduction of enterosorbents, such as Smecta, Enterosgel.
- Exchange blood transfusion is used in emergency cases when there is a risk of developing kernicterus.
- Fat-soluble components that can eliminate bilirubin can be introduced as excipients.
Prognosis and prevention

If pregan jaundice is diagnosed, the prognosis is favorable. By 3 months, the child’s digestive system reaches its maturity, metabolic processes are normalized and symptoms disappear.
The prognosis of pathological jaundice depends on the detected disease and timely treatment. Infants with jaundice are monitored by a neurologist and gastroenterologist.
It is possible to prevent the occurrence of Aries syndrome with proper management of pregnancy and childbirth. The development of fetal hypoxia should not be allowed. It is recommended to put the baby to the breast immediately after birth. Pregnant women with thyroid pathologies and suspected diabetes should be under special medical supervision.