What does normal stool look like in a child?
In the first day or two after birth, the newborn begins to pass the original feces - meconium.
It is black in color with a greenish tint, viscous consistency and has no characteristic odor. The appearance of meconium is proof that the baby's intestines are working normally. On the third or fourth day, the baby’s stool takes on a different color and consistency. Usually at this time the mother and baby are discharged from the maternity hospital home. So, by this moment the meconium should completely leave the child’s body. By the second week of a newborn's life, his stool turns yellow or mustard. It has a liquid, mushy consistency. The smell of the stool is faint and sour. It is acceptable to have white grains or a small amount of mucus in the stool. The main thing is that the stool is not too dense or, conversely, watery.
At each diaper change, its contents should be inspected in order to identify pathology in time. It should be remembered that the nature of the stool is an important indicator of the baby’s health.
What does the color of mucus mean?
Mucus in stool can look different. Its shade depends on the reason that caused the deviation. Here's what the discharge colors say:
- Green. Indicates the rapid proliferation of pathogens in the intestines. A small amount of such mucus occurs during dysbiosis. Abundant inclusions may indicate enteritis or bacterial colitis. The smell of feces is particularly foul.
- Yellow. It speaks of progressive inflammation. The mucus takes on this color due to the large number of leukocytes in it. Sometimes pus impurities are responsible for the yellowish color.
- Pink. Very bad color. The mucus contains streaks of blood. This symptom may indicate Crohn's disease, erosion, or ulcers in the intestines.
- White. The mucus contains exfoliated epithelial cells. Similar processes occur when the inner lining of the intestines is irritated due to allergies. This color also occurs with worms.
- Red. Explained by a large number of blood impurities. Often, mucus of this color becomes the result of mechanical trauma to the rectum due to frequent use of enemas or gas tubes. A bloody tint may indicate Crohn's disease or allergic colitis.
- Red-brown, black mucus colors occur when internal bleeding has opened.
Infant feces - color and disease
The consistency of the mucus also matters. Thick discharge, similar to a dense “jelly” lump, is characteristic of parasite infestations. Liquid - for conditions associated with pancreatic dysfunction or lactose intolerance in a child.
If, instead of stool, only watery mucus is released, an acute intestinal infection is most likely present.
The color of the mucus indicates the nature of the process:
- Transparent slime. Most often it appears during viral inflammation, against the background of physiological causes.
- Green slime. Indicates the addition of a bacterial agent, or the passage of snot in transit through the entire gastrointestinal tract.
- White streaks of mucus. They talk about the presence of fibrin effusion and most often occur with fungal invasion (candidiasis, intestinal damage by Mycobacterium tuberculosis). Also, white streaks occur during helminthic infestation or during the healing of ulcers and erosions against the background of an autoimmune process.
- Streaks of blood. Appear when the capillary network is damaged or excessive permeability during intussusception or amoebic infection.
Pathological causes of blood in the stool of an infant
It is worth noting that this problem can occur in both breastfed and bottle-fed babies. The appearance of blood in the stool can be caused by a number of factors. One of the most common causes of this condition is cracked nipples in the mother. In this case, namely during breastfeeding, blood in the baby’s stool is more normal than pathological.
In general, blood in a baby's stool can come from two sources:
- From the upper parts of the digestive system. In this case, blood in the stool is explained by pathological processes in the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum.
- From the lower intestines. The reason for this condition lies in diseases of the colon and rectum, as well as the anus.
It is quite difficult to determine on your own why a child has scarlet streaks in his stool. For this purpose, a comprehensive examination is carried out in a medical institution. But parents should know the reasons why feces with blood streaks most often appear in infants:
- Anal fissures. This pathology is typical for children of any age, and not just for infants. In this case, the blood is located directly on the surface of the stool and remains on the toilet paper or napkin. The child experiences discomfort during bowel movements, grunts, writhes in pain, and sometimes cries a lot.
- Allergic reaction. This problem is most often encountered by children on artificial or mixed feeding. Blood in the stool occurs due to an allergy to the milk protein that is part of the mixture.
- Intussusception. The pathology most often occurs in children from 4 months to 1 year. The disease begins acutely, with severe abdominal pain and vomiting. In this case, the feces resemble the consistency of jelly with admixtures of mucus and blood.
- Intestinal infections. Infants are extremely rarely affected by diseases such as dysentery, typhoid fever, botulism, salmonellosis. But parents should be wary of such dangerous symptoms as diarrhea streaked with blood, nausea, and fever.
- Polyps. The disease is accompanied by constant constipation, difficulties with defecation and streaks of blood in the stool. This pathology can only be treated surgically.
- Helminthiases. It is quite difficult for an infant to become infected with worms, but for children under 5 years of age this problem is very relevant. In this case, the baby is bothered by itching in the anus, diarrhea, and interrupted sleep.
The following factors can trigger the problem for both guys on breastfeeding and artificially trained ones:
- Introduction of complementary foods. Often, diarrhea and mucus in the stool are explained by the introduction of new foods into the diet, for example, vegetable puree. To reduce the manifestation of a negative reaction, it is worth giving up the problematic product for a while or reducing its share in the diet;
- Diseases of the digestive system. In such cases, it is necessary to analyze the intestinal microflora;
- The natural formation of mucus in newborns is explained by transient dysbiosis. No treatment is required here;
- Diseases of the respiratory system (very rare). For example, when you have a runny nose, part of the mucous secretions that form in the nose is swallowed and then ends up in the feces.
- Taking certain medications (most often these are anti-bloating drugs, such as Espumisan, Bobotik);
- Gluten deficiency.
Interesting. At birth, the gastrointestinal tract of infants is sterile. Soon the baby begins to drink mother's milk, then various microorganisms enter his intestines. In the first month of life, a certain microflora with a predominance of lacto- and bifidobacteria should form. During the period when there is a “fight” between beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms, the child experiences transitional stool. The greenish color of stool and the presence of mucus in it are not signs of the disease.
Stool with mucus in a one-month-old breastfed baby most often indicates inappropriate nutrition. The baby most likely cannot digest the selected product normally for the following reasons:
- allergic reaction;
- any component included in the mixture is difficult to digest;
- a sharp transition to a new type of nutrition (from breastfeeding to IV) or a new mixture.
On a note. Often there is a cumulative effect: in the first weeks there are no visible negative signs, but then it becomes more difficult for the body to absorb the wrong product, and then it is simply impossible not to notice the problem.
Mucus in stool during breastfeeding
Mucus in the stool of a breastfed baby can be caused by the following problems:
- Mother's milk is not sterile. A special analysis helps to establish this fact. In this case, feeding is usually not interrupted, and mother and baby are prescribed a course of therapy.
- Lactase deficiency.
- Mother's diet. Mucus in this case is a sign of intolerance to certain foods by the child’s body. The baby may have an allergic reaction to one or another component (most often it is sweet, fatty, fried, flour). If normalization of the diet does not produce positive results, a blood test for the presence of allergens (MAST test) is recommended. Finding out which product caused a similar reaction in the baby will not be difficult with the help of a food diary.

This is the most common cause of problems with stool in newborns. This condition occurs when pathogenic bacteria (staphylococci, clostridia, etc.) begin to predominate in the microflora.
A mild form of dysbacteriosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Constipation;
- Flatulence;
- Colic;
- Mucus in stool.
In advanced situations the following are observed:
- Diarrhea;
- Lumps of curdled milk in stool;
- A large amount of mucus;
- The presence of blood streaks in the stool;
- In rare cases, pink or red mucus (indicates damage to the walls of the digestive tract).

Dysbacteriosis requires complex long-term treatment. The first stage is the sanitation of the baby’s intestines, the second is the restoration of microflora.
Important! To prevent relapse, it is necessary to provide the child with proper feeding and careful care.

Colic, abnormal stool and mucus in the stool may indicate dysbiosis
A newly born baby is not yet able to digest food in the same way as adults. The child's intestines are underdeveloped and do not have all the necessary enzymes to digest food. This is why there may be some mucus in the baby’s stool. This phenomenon is of a natural physiological nature, so parents should not worry. During this period, you need to be more careful with the introduction of complementary foods and carefully monitor the condition and reactions of the child’s body.
Advice. If the situation does not improve or, on the contrary, worsens, it is better not to rush into introducing new foods into the baby’s diet.
The lactase enzyme makes possible the fermentation of lactose contained in milk. In certain cases, babies have a congenital deficiency of this enzyme. Thus, milk cannot be properly absorbed by the body; when the product enters the intestines, fermentation processes begin. As a result, the child experiences symptoms such as:
- Stomach ache;
- Flatulence;
- Loose stools;
- The presence of lumps of milk and a small amount of mucus in the stool.
An accurate diagnosis can be made by testing for carbohydrate content in stool. Therapeutic therapy comes down to a special diet that completely excludes dairy products. A child on breastfeeding is prescribed a course of medications containing lactase. For artificial drinkers, a mixture is selected that does not contain lactose.
Mucus in the stool of newborns often becomes a sign of a viral or bacterial intestinal infection. The most common diseases of this kind are:
- Stomach flu;
- Dysentery;
- Salmonellosis.
With these and other similar pathologies, elements of mucus in the stool indicate inflammatory processes occurring in the intestines. To exclude dysbacteriosis and establish the presence (or absence) of a bacterial or viral infection, it is necessary to conduct a special analysis by stool culture.
Recommendation. Babies under one year of age who experience noticeable changes in their stool should be seen by an infectious disease specialist. If the doctor insists on hospitalization, it is better to agree to eliminate the risk of serious consequences.
If you suspect dysbacteriosis or infection, you must submit your stool for analysis.
What impurities can be in the stool of an infant?
Baby feces may contain impurities and are heterogeneous.
Bloody mucus during bowel movements
This situation requires immediate medical attention. The reason for this may be the following - the appearance of cracks in the anus. Bloody mucus means a manifestation of atopic dermatitis or an allergy to cow's milk proteins. Blood clots in the mucus indicate inflammation in the baby’s intestines, the appearance of polyps and their rupture, as well as an advanced form of helminthiasis.
Foam and slime
Mucus along with foam during bowel movements is a violation of the functionality of digestion with pathological changes. A latent disease that is identified during diagnosis may have similar symptoms.
Increased amount of mucus
Mucus should be present in the feces - this is explained by the physiological norm. This is the norm in the feces of an infant or an adult. But, when inflammation begins in the body, the normal volume of mucus increases.
Mucus with white lumps
White lumps when a baby defecates are particles of milk in a curdled state. When their number exceeds the norm, this means that the baby is overeating and his system is not able to cope with the incoming food. This process may be accompanied by clear discharge in the stool.
If certain changes in the baby's stool are observed, then strict monitoring of his behavior and condition will be required. If the process is accompanied by fever, the child may lose appetite and body weight. In this case, you will need to immediately contact a doctor.
When should you not worry?
When breastfeeding, there are several options for normal stool color and consistency. Even the absence of bowel movements for 24 hours is not considered constipation if the stool looks like a yellow, soft porridge. In fact, the color of stool may change for the following reasons:
- Products in the diet of a nursing woman. If the mother’s menu the day before included tomatoes, beets, and black currants, the baby’s stool may turn reddish. But this does not mean at all that the baby has bloody stool.
- Taking medications. If the mother takes antibiotics, medications containing iron, or tablets containing dyes, the color of the baby's stool will certainly change.
- Introduction of complementary foods. When a child is introduced to a new food, changes occur in his digestive system, including stool. This should not cause concern to the mother.
What should parents do?
If parents notice mucus in the baby's stool, it is recommended to visit a pediatrician. A specialist will help determine the cause and recommend a suitable solution. In most cases, parents are quite capable of coping with this problem:
- Change the mother's diet if she is breastfeeding (avoid flour, fried, smoked, spicy, sweet).
- If the child is bottle-fed, then choose the appropriate formula for him.
- Do not rush to introduce complementary foods.
- After the above measures have been taken, monitor the child’s condition for several days.
- If the mucus was clear and not white, the parents' actions may be effective and the problem will go away. However, in any case, it is recommended to visit a pediatrician for an examination and advice.
Important! You should not resort to self-treatment with medications and other means without consulting your pediatrician.
Norm of mucus in stool
Mucus protects the intestines from aggressive substances - acids and alkalis. Mucous discharge mixed with feces should not be noticeable when the baby leaves. The presence of large fragments of mucous formations that are visible to the naked eye should alert the mother.
If a child poops green mucus, there is more of it than usual, but the newborn is active and eats well - in this case there is no need to worry. A serious problem is considered if mucus is visible with every bowel movement of the baby. Call a doctor when the following symptoms are present in an infant:
- unpleasant pungent odor of excrement;
- regurgitation;
- cramps and colic in the abdomen;
- the baby does not sleep well and cries constantly;
- body temperature rises;
- lack of appetite;
- vomit;
- the baby is not gaining weight;
- poops more than 5 times a day;
- there is foam in the feces;
- blood in stool.
The process of formation of intestinal flora can be delayed when the baby is bottle-fed. The amount of discharge depends on the type of feeding: with breastfeeding there is more mucus. The introduction of complementary foods also affects the color and consistency of stool.
When should you see a doctor?
Blood streaks in the stool do not always require treatment. For example, if their appearance is associated with damage to the nipples of a nursing mother or cracks in the anal area. Such simple problems often go away on their own. The main thing is to try not to aggravate the situation and help the child get rid of constipation as quickly as possible.
If there is a lot of blood in the stool, it is dark, coagulated, or, conversely, liquid and scarlet, you should immediately seek medical help. In the first case, the cause may be internal bleeding, and in the second, it may indicate problems in the lower intestines, for example, the presence of a bleeding tumor.
In most such cases, parents do not need to worry. The appearance of mucus in the stool of an infant indicates a disruption of the digestive tract. Deviations may be caused by excessive stress on the children's intestines.
The presence of white mucus in the stool should alert parents. In this situation, a visit to the doctor is mandatory. The doctor can determine the following reasons:
- White mucus may indicate inflammatory processes in the infant’s gastrointestinal tract;
- Dysbacteriosis that has developed as a result of taking antibiotics or other drugs;
- Allergy to a particular food product;
- Lactase deficiency;
- Helminths.
Note! There is no way to avoid a medical examination if the presence of white mucus in the stool is accompanied by frequent colic, sleep disturbances, restless behavior of the child, and constant crying.
If a baby has liquid, green, foamy diarrhea with blood clots, urgent medical attention is needed.

Lactase deficiency often causes mucus to appear in children's feces
If a one-year-old baby or older child, in addition to mucus in the stool, experiences diarrhea and elevated body temperature, you must call an ambulance.
Yellow jelly-like mucus in a baby's stool indicates inflammatory processes. This shade is formed due to a large number of leukocytes and pus impurities.

In such cases, parents should pay attention to the following signs:
- The stool has a strong putrid odor;
- The color of the stool is unusual for this child;
- Mucous, heterogeneous stool in infants includes large fragments;
- Bloody impurities are noticeable in children's poop;
- A large amount of mucus.
Important! Dark, black or red-brown mucus in the stool indicates internal damage. Urgent medical attention is required.
Diagnostics

Abundant mucus in the stool is clearly visible to the naked eye. It is also easy to notice bloody, yellow, green, white, black masses. Before going to the doctor, it is advisable to take a closer look at the clot of mucus, determine its consistency, shade, and quantity, so that the specialist gets the most complete picture and chooses the optimal examination methods. You can take your baby's soiled diaper with you.

Stool analysis - a coprogram for diagnosing the disease
Most often, if there is mucus in the stool, a coprogram is performed. Also practiced are bacterial culture, macro- and microscopy of feces, a general blood test, studies to identify parasites, ultrasound, and x-rays. The use of certain methods depends on the symptomatic picture, medical history, age, and general condition of the patient.
To determine the reason why mucous stool appears in a baby, it is necessary to take tests for intestinal microflora. The doctor, based on the symptoms, prescribes tests for eggworm, dysbiosis, allergens, carbohydrates, and you will also have to do a coprogram. The technique for collecting baby stool is as follows:
- Prepare a special container, ensuring its sterility.
- In the morning (or the night before), use a spatula to collect feces from the surface of the diaper (not from the depths), trying to get into places with small patches of mucus. If the stool is too liquid, you can lay down a medical oilcloth and wait until the baby defecates on it.
- If the analysis took place in the evening, you should place the box of stool in the refrigerator, and in the morning, attaching a tag with the child’s name and surname, take it to the laboratory.
Taking medications
If it is not possible to visit a doctor immediately, the baby can be given Smeka or probiotics. Mucus in the stool is not a pathology, but only indicates a specific problem associated with a malfunction of internal organs. Therefore, it is not the effect that needs to be eliminated, but its cause. Treatment may be as follows:
- If the baby gets sick with bronchitis, ARVI, pneumonia, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs.
- Dysbacteriosis is eliminated with antiseptics and probiotics.
- If intestinal infections occur, a course of antibiotics or antiviral drugs is prescribed.
- Antifungal agents are used to eliminate thrush.
- For intestinal inflammation, glucocorticoids and sulfalazines are prescribed.
- Erosions and ulcers are treated with healing, painkillers.
- For pancreatitis, medications containing digestive enzymes are prescribed.
Symptoms of pathology
Blood streaks in a baby's stool are the main sign of pathological changes in the baby's body. They do not always indicate a dangerous disease, but you should not let the situation take its course. Depending on the specific disease that caused blood clots in the stool, your child may experience the following symptoms:
- diarrhea and mucus;
- constipation, difficulty with bowel movements;
- nausea, vomiting;
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- pain in the abdominal area (the baby cries, bending his legs).
If a child, along with bloody streaks in the stool, has at least one of the above signs, he needs additional examination to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe timely treatment.
When to sound the alarm
One-time diarrhea with mucus in a baby should not worry parents too much. But if such symptoms develop, you need to seek emergency help:
- diarrhea with mucus and blood;
- black and bloody impurities;
- nausea, vomiting;
- screaming, crying, constant worry;
- refusal to eat;
- acute reaction to touching the stomach;
- temperature;
- paleness or severe redness of the skin.
Diarrhea with blood and foul odor requires urgent help. Before the ambulance arrives, you should not give any medications. But it is necessary to ensure the restoration of water balance, to give more fluid, even if this ends in vomiting.
Doctor Komarovsky about intestinal infections
A well-known pediatrician believes that parents should not ignore the presence of blood streaks in their baby’s stool. Komarovsky believes that constipation is often the cause of this condition. He recommends that a nursing mother change her diet to include prunes, fermented milk products, and clean water. You should definitely use elements of therapeutic exercises with flexion and extension of the legs.
Pediatricians warn parents that blood in the stool is not normal for healthy children. Their advice boils down to the following:
- The presence of blood streaks in the stool, along with an increase in temperature, frequent loose stools mixed with mucus, vomiting, and abdominal pain, requires immediate contact with a pediatrician or infectious disease doctor.
- Late visit to the doctor if there is blood in the stool for a long time only aggravates the current situation and complicates treatment.
- Experts (gastroenterologists and proctological surgeons) do not advise self-medication and immediately consult a doctor if blood is detected in the stool of an infant. Komarovsky believes that a pediatrician should be visited even if no other symptoms of dangerous diseases are detected.
According to the famous pediatrician, Evgeniy Komarovsky, the appearance of mucus in the stool of an infant is a natural reaction of the body to the introduction of complementary foods and the addition of new products to the standard menu. The doctor does not recommend that parents worry too much about changes in the smell, color and consistency of stool, since in the first months of life the baby’s digestive system is just getting started. It is for this reason that symptoms may occur in the form of mucous discharge in a child’s stool.
On a note. In the first year of life, the main indicators of a baby's health are optimal weight gain, good sleep and moderate activity. If the baby’s growth and development correspond to the listed standards, then the mucus in the child’s stool should not bother the parents.
If suspicious situations arise, a reputable doctor recommends:
- Stop panicking.
- Carefully monitor the baby for 3-4 days.
- If the changes affected only the composition of children's feces, then nothing needs to be done. When the baby’s digestive system improves its functioning, the unpleasant symptom will disappear on its own.
- If the baby is not yet ready to accept “adult” food and is breastfed, it is necessary to adjust the mother’s diet.
- Call an ambulance immediately if you notice liquid, foamy, green diarrhea mixed with blood clots.
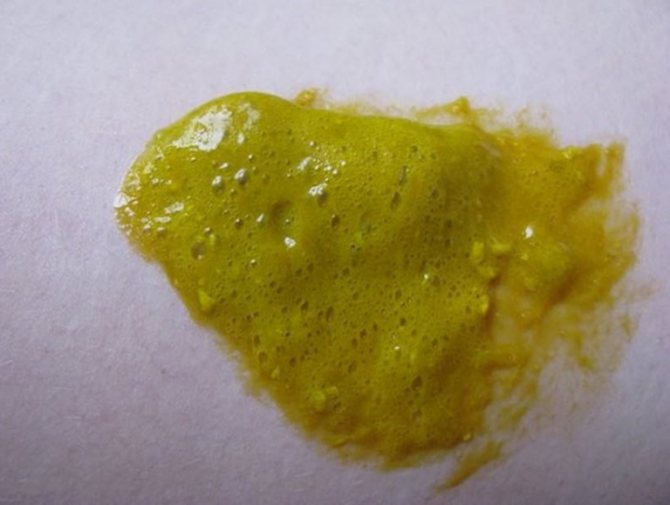

Green, foamy stool that has a liquid consistency is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
So, if a baby poops mucus, but there is very little of it, and it appears rarely, then there is no serious reason for concern. If an unpleasant symptom makes itself felt with every bowel movement, accompanied by a sharp unpleasant odor and other negative manifestations (sleep disturbance, diarrhea, bloody spots in the stool, frequent regurgitation), then we can talk about certain disturbances in the functioning of the child’s internal organs. In this case, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Characteristics of baby mucus and feces
It is worth noting that a child always has mucus in his stool. When mixing the contents of the large intestine, the passage of feces through the intestines improves.
If a baby defecates, the stool can be of different colors, ranging from dark green and orange to brown or black. All this “coloring” carries the necessary information for doctors and parents.
What does the color of stool indicate?
- If dysbiosis or an imbalance of intestinal flora occurs, the stool becomes lighter. It is worth noting that lightening of stool appears during teething.
- If the stool is white or discolored, hepatitis is suspected. This disease can be found in small children not so often, but it is dangerous.
- At first, when the baby is born, the stool is yellow, brown or orange - this is a reaction to the bile pigment. It's called bilirubin.
- Feces and its color are the body’s reaction to a medicine or antibiotic. The color change appears some time after consumption. If an infant feels normal, then black stools should not frighten parents.
- The color of the stool indicates what type of feeding the baby is having. If the baby is exclusively breastfed, the color will be yellow-green.
- With the introduction of complementary foods, the stool becomes greener. This can be explained by the appearance of increased bile content during the pickling process of food.
- Mother's milk is poorly digested (stools are green or orange).
When inflammatory processes occur in the child’s body, the mucous volume will increase. It manifests itself not only during bowel movements, but also during examinations and is observed visually.
What does a stool coprogram show?
Laboratory analysis of stool will accurately determine the cause of most internal bleeding. A coprogram is prescribed in order to identify hidden blood and make a correct diagnosis of blood streaks in the stool of an infant. When interpreting the results, the following pathological changes can be identified:
- the presence of impurities in the stool, including blood, is often a sign of internal bleeding in one of the intestinal sections;
- the presence of bilirubin - this bile pigment can only be in the stool of a breastfed child, and the test must be negative on artificial or mixed;
- the presence of red blood cells or white blood cells - an excess of their norm is observed with a polyp, ulcer, helminthiasis and various formations (tumors) in the intestines;
- the presence of protein indicates an inflammatory process in the intestines;
- change in the consistency of stool - foamy stool may indicate the presence of an intestinal infection in the body.
If the infectious nature of the disease is suspected, the child is tested for microorganisms.
Types and characteristics
A particular danger is whitish and liquid mucous stool in infants. Often you can notice blood impurities and fat in it. The child in such situations is very restless, he suffers from colic, and the temperature may rise. Let's take a closer look at when to sound the alarm and what the color of children's stool means.
Transparent
According to experts, small amounts of transparent mucous masses indicate inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract. They can also be triggered by enteroviruses that attack the walls of the large and small intestines.
White
Foamy or thread-like whitish discharge may appear in different cases. Most likely, the baby has pathologies in the digestive tract that require immediate examination by specialists. We are talking about the causative agents of dysentery and salmonellosis. It may also be an expression of the vital activity of helminths.
Did you know? A newborn baby's stomach can hold only 30 ml of liquid, and its size is equal to the volume of a baby's fist.
If white thread-like mucus comes out with hard feces, and the baby often suffers from constipation, this may be a sign of polyps formed in the intestines. In any case, when white mucus appears in the stool, it is important to conduct a timely examination and begin treatment.
Green
Mucus of all shades of green is a clear sign of dysfunction of the digestive organs due to the activity of bacteria. Often these stools contain particles of blood and undigested food. You should seek medical help immediately, since an intestinal infection is raging in the baby’s body.
Yellow
Regular yellow lumps of mucus in liquid baby stool also indicate intestinal dysfunction. If these discharges have an unpleasant, pungent odor, then the reason for their appearance may lie in an insufficient amount of enzymes, the presence of an intestinal infection or helminths. In all cases, you should not delay your visit to the doctor.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Thrush in a child’s vagina
Important! Yellow, non-loose stools with a small amount of mucus are normal for a child under one year of age, especially if we are talking about his artificial feeding with milk formulas.
Pink

This color of mucus is a clear sign of serious problems in the baby’s intestines. It appears as a result of blood impurities caused by a hemorrhagic inflammatory process on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Therapeutic measures
If blood streaks are detected in a baby's stool, self-therapy can be even more dangerous than the disease itself. It must be remembered that treatment is prescribed only after receiving the results of the examination and making the correct diagnosis.

Depending on the reason for the appearance of blood in the baby’s stool, the following types of therapy may be indicated:
- a diet that excludes allergenic foods;
- ointments, creams;
- antiviral and antimicrobial drugs, antibiotics;
- for constipation - a laxative (for example, Duphalac).
In particularly difficult cases, only surgical intervention can solve the problem.