What it is
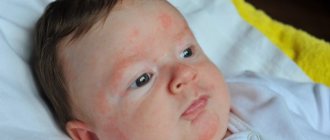
Food allergies are a common pathology among young children.
This is the starting point for the development of other allergic diseases.
The symptoms of this disease are varied, but the first and most significant manifestation is atopic dermatitis.
In addition, food allergies can cause other types of rashes, such as hives or swelling.
At the same time, following a special diet can significantly improve the baby’s condition and stop further progression of diseases.
Therefore, parents of children with allergies should know that there are products with different allergenic properties, namely low-, medium- and high-allergenic.
Based on this information, the child’s diet should be built.
What to do if your baby has allergies?
If your baby develops symptoms of the disease, it is recommended to consult a doctor. The pediatrician will rule out other problems and, if necessary, give a referral to a pediatric allergist.
A blood test is performed to identify the allergen. Based on the results obtained, it is easier to develop nutritional recommendations and select medications to alleviate the child’s condition.
To remove toxins from the body from eating foods that cause allergies while breastfeeding, mothers are advised to drink more clean water. It is also worth taking a sorbent.
If all the rules are followed, as the child grows older, the allergy in most cases goes away completely.
A nursing mother will more easily endure temporary dietary restrictions if she realizes their importance for the health of her baby. When creating the right menu, you can use a large number of recipes that allow you to eat deliciously using hypoallergenic products.
- Related Posts
- Humana lactation tea
- List of WHO recommendations on breastfeeding: methods and timing
- Mlekoin for lactation: homeopathic granules
« Previous entry
Kinds
There are several types of diets for allergy sufferers.
They all differ in the principle of product selection.
In any case, the doctor must propose a specific menu, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Hypoallergenic
This diet is the basis for the treatment of allergies, since it makes it possible to detect the causes of the disease, get rid of excess weight and normalize the functioning of the immune system.
The main indication for the use of a hypoallergenic diet is the food form of the disease.
It involves eliminating factors that cause undesirable reactions and helps reduce the allergenic load on the child’s body.
It is very important that nutrition is as gentle as possible and at the same time physiologically complete.
The amount of salt should be limited to 7 g per day.
All dishes are prepared boiled, and soups must be cooked in a third broth.
Meals should be fractional - at least 6 times a day.
If swelling occurs, it is recommended to limit free fluid intake.
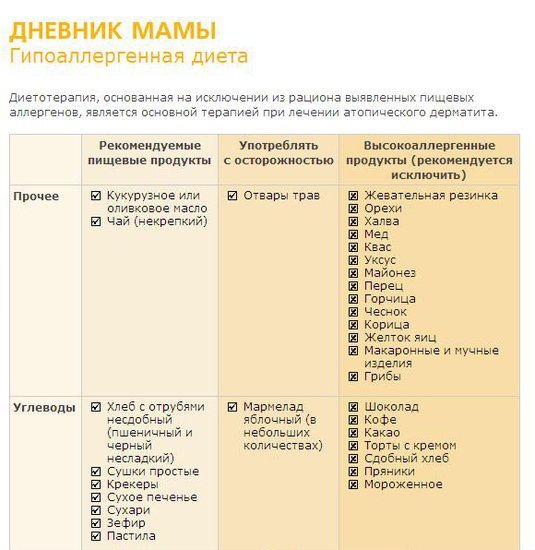
Photo: Example of keeping a diary
Elimination
This type of diet is also called an elimination diet because it helps identify allergenic foods.
The elimination diet is based on a nonspecific hypoallergenic menu.
Those foods that can provoke unwanted reactions must be removed from the baby’s diet for a couple of weeks.
If you have any doubts, you should first avoid the most common allergens:
- citrus fruits;
- nuts;
- wheat;
- dairy products;
- It’s also worth removing eggs and corn from your diet for a while.
During this period, you need to carefully monitor the child's condition.
After two weeks, you can introduce one product into the diet and monitor the reaction for three days.
Once an allergen has been identified, it must be excluded from the diet.
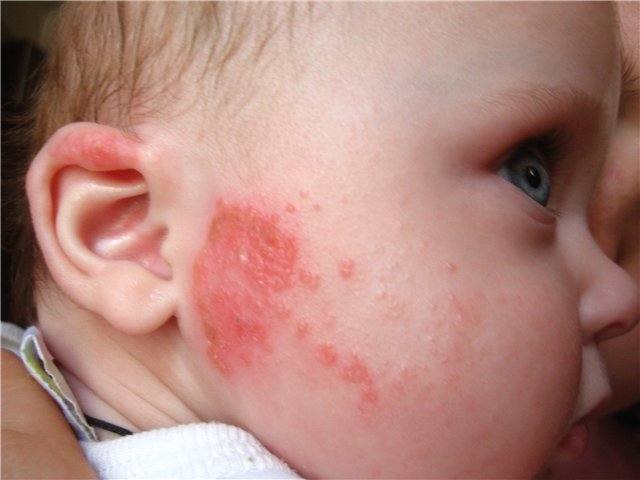
Photo: Food form
Alternating
If a child has a food-borne form of the disease, the cause most often lies not in the allergens themselves, but in their quantity.
If you follow a rotating diet, you will be able to provide your baby with all types of foods without causing high sensitivity to them.
Of course, if a product causes an acute reaction in a child, then it should be completely removed from the menu.
The basic principle of an alternating diet is that a child may not respond to certain foods if he only receives them once every three days.
Nonspecific
Products that can cause allergic reactions are called obligate allergens.
Depending on their nutritional value, they can be divided into two categories.
The first group includes allergens that can be removed from the diet without harming the baby’s health.
These include:
- chocolate;
- caviar;
- honey;
- raspberries;
- melon;
- fish, etc.
The second group includes products that cannot be completely removed from the menu, as they have high nutritional value.
These include chicken eggs and milk. However, the total volume of such food is reduced by 2-3 times.
In addition, it is very important to carry out thorough heat treatment.
A diet for food allergies in children involves excluding extractive substances, salty foods and hot spices.
Instead of meat broths, children should be given vegetable broths.
Fried vegetables or meat are replaced with boiled or steamed ones.
Products that have an enveloping effect are also very useful.
For example, oatmeal and rice porridge help prevent allergens from entering the bloodstream.
Be sure to exclude any products with food additives. These include smoked meats, mustard, and canned food.
Rules for feeding a child on breastfeeding
It often happens that allergy symptoms appear in children on breastfeeding even before the introduction of the first complementary foods. In this case, the cause of the negative state is the mother’s consumption of foods that provoke its appearance. In infants, the first signs of allergies are rashes on the skin of the face and various parts of the body. They may look like hives or a weeping rash. As a rule, these rashes flake and itch, causing great discomfort to the baby. In addition, in children under one year of age, allergens enter the blood more easily due to the fact that the gastrointestinal tract is still immature and does not produce enough enzymes to digest food.
If it is established that the baby's allergy arose from foods eaten by the mother, and not for other reasons, the main method of treatment will be for the nursing mother to follow a strict diet. Products that have the highest risk of causing allergies in the baby should be completely excluded from the diet. These include:
- all fruits and berries are orange and red;
- chocolate, coffee, cocoa;
- whole milk;
- chicken eggs;
- nuts;
- fried, spicy foods;
- hard cheese;
- smoked meats;
- fish, caviar, seafood.
A diet for allergies in children involves the nursing mother refusing to eat pasta and baked goods made from white flour. During this period, it is important for the child to continue breastfeeding and not to start feeding the baby with various mixtures, as this may cause an additional wave of reaction to the new product.
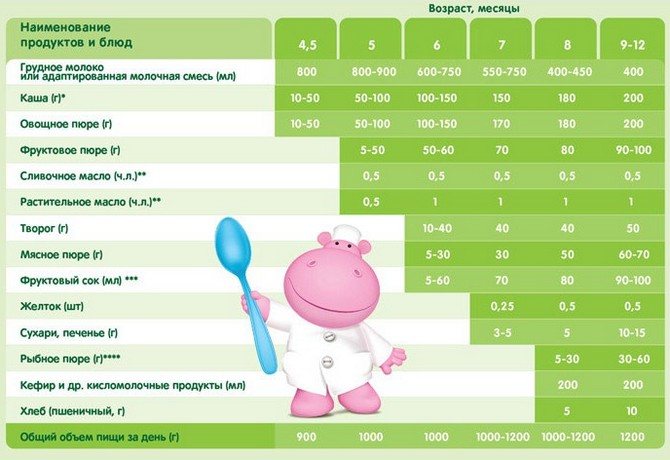
Recommendations for first feeding
It is better for a nursing mother to make up her diet from the following products:
- cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice);
- water soups;
- vegetables and fruits of white and green colors;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- lean meats (poultry, beef);
- weak tea, dried fruit compote, still water;
- sunflower or olive oil;
- bakery and pasta products from 2 grades of flour.

This diet must be followed for several months until all symptoms of allergies disappear. During the period of introducing complementary foods, it is necessary to fill out a food diary, which notes the reaction to the use of new products in the child’s diet.
Diets for allergies in children with intolerance:
Cow's milk
Reactions to milk in children are very common.
In this case, it is recommended to completely exclude from the diet all products that contain milk or are prepared with its addition.
Quite often, children who have a reaction to cow's milk tolerate goat's milk quite well.
In addition to milk, you need to remove from your diet:
- soups with added milk;
- cheeses, fish, poultry, eggs, and in some cases beef;
- baked goods with added milk;
- cereals with high protein content;
- cream, butter, sour cream, cottage cheese;
- yoghurts;
- condensed milk and milk powder;
- milk chocolate;
- milkshakes.
Young children should not consume artificial formulas made from cow's milk.
At the same time, cottage cheese and kefir are also contraindicated for some children, while others can eat these products in small quantities.
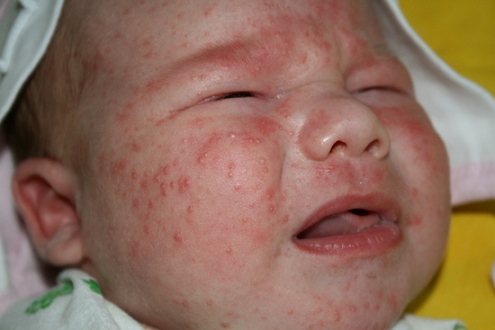
Photo: Small pimples as a reaction to red foods
Chicken and eggs
In this case, a fairly strict diet is assumed, since eggs are an integral component of baking.
They are also often found in pasta, mayonnaise and other products. In addition to eggs, you should not eat egg powder or albumin.
Quite often, allergies to chicken eggs are combined with reactions to chicken meat. In this case, it also needs to be excluded from the diet.
Beef and pork are allowed. You can eat any vegetables and cereals.
Suitable for child:
- homemade baked goods without eggs;
- unhealthy bread;
- butter and vegetable oil;
- milk.
Wheat
This type of allergic reaction is much less common.
In this case, you need to exclude wheat and any products that contain this ingredient from the menu:
- semolina porridge;
- flour;
- crackers;
- bran.
Also, children with such food intolerance are contraindicated:
- soups with pasta or dumplings;
- wheat bread;
- wheat flour pasta;
- pancakes, pancakes;
- wheat porridge;
- baked goods based on wheat flour.
Corn
This diet is significantly less restrictive because corn is much less common in processed foods.
Apparently, this is why intolerance to this product is not diagnosed so often.
Children with this diagnosis should not be given foods that contain corn.
In this case, reactions can be caused not only by the cooked product, but also by:
- flour;
- starch;
- flakes;
- butter and canned corn.
You need to carefully study the composition of ready-made vegetable mixtures.
It is also worth considering that some medications, vitamins and toothpaste can be dangerous. Therefore, it is so important to pay attention to their composition.
Read how to find out what your child is allergic to. Has your child become allergic to flowers? Read the article for what to do.
Soybeans
This pathology is quite rare.
In young children, it can be the result of prolonged feeding of soy formula.
It is also worth considering that this component is included in many food products.
Therefore, it is not recommended to give children products whose packaging contains instructions regarding vegetable protein content. Soy may also be hidden under it.
Soybeans and shoots, oil, flour, and soy-based sauces are also contraindicated.
This ingredient is often added to:
- ready margarine;
- ice cream;
- semi-finished meat products.
It can also be found in sweets, as well as seasonings for meat or fish dishes.
Hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers
A special diet includes a gradual expansion of the menu. Immediately after giving birth, they follow a strict diet. Potential allergens are removed from the menu during the first months of breastfeeding. Depending on the reaction of the infants, the woman is prescribed a nonspecific or specific diet. The first type of restrictions is suitable if reactions occur rarely or the child has a hereditary predisposition to allergies. A nonspecific diet is a prevention of increased sensitivity.
The second type of restrictions is prescribed when the baby reacts frequently.
A specific diet completely excludes highly allergenic foods. This diet is recommended to be followed throughout the entire period of breastfeeding.
Food is steamed, boiled, baked. During the first month, it is advisable to eat decoctions of cereals and vegetables as first courses. Then the soups are cooked in the second broth. It is advisable to soak cereals before cooking. Preference is given to natural products without preservatives or flavors. Dishes should not contain many components.
Allergies usually occur upon repeated use of the component. It should be noted that heavy foods (mushrooms, meat, legumes, etc.) take a long time to digest. Therefore, the allergen does not immediately enter the milk. To detect a reaction, the interval between the introduction of new products should be at least 2-3 days. Some types of allergens persist in milk for a long time. The baby may react to the stimulus after several feedings.
Highly allergenic foods
When monitoring your baby’s reaction, it is important to monitor the frequency of consumption of certain dishes and the volume of food eaten. A small portion may not cause allergies. But as soon as the mother exceeds the “permissible norm,” sensitivity increases. This situation often occurs when eating sweets.

An approximate list of the most allergenic (“red”) foods, experts consider the most dangerous during breastfeeding:
- chocolate,
- confectionery,
- cow's milk,
- honey,
- nuts,
- seafood,
- Strawberry Raspberry,
- tomatoes,
- eggplants,
- brightly colored peppers,
- fatty fish (especially red),
- salo,
- margarine, spreads,
- caviar,
- sharp, salty cheeses,
- marinades,
- smoked meats,
- canned food,
- spices,
- sauces,
- mushrooms,
- exotic dishes,
- tropical fruits,
- semolina,
- rich pastries,
- red fruits, citruses,
- carbonated drinks,
- chicken eggs,
- coffee,
- strong tea.
They are removed from the menu in the first months of lactation. Most often, young children are sensitive to proteins in cow's milk, eggs, and wheat flour (gluten).
Products of average allergenicity
This category is the so-called “yellow list”. Such food is introduced into the diet starting from the second month of breastfeeding. Use with caution:
- beef, veal,
- offal,
- rich broths,
- lean fish - cod, pollock, hake,
- chicken,
- Hercules,
- millet,
- pasta,
- wheat cereal,
- bananas, peaches, apricots, plums,
- blueberries, lingonberries, currants, cranberries, cherries, watermelon,
- pumpkin, cauliflower, turnips,
- Green pepper,
- butter,
- apple marmalade,
- peas, beans,
- herbal decoctions.
Sugar is limited to 40 g per day. During the diet, it is recommended to use melted butter and olive oils. They are less likely than others to cause negative reactions.
Menu and nutritional recommendations for children under 3 years old
The products included in a hypoallergenic diet may be different - it all depends on the type of reaction and the period of exacerbation.
Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor in a timely manner, who will draw up an individual menu.
Typically, children under three years of age are allowed to consume the following categories of foods:
- boiled beef, turkey, chicken;
- vegetable soups;
- oatmeal, rice, buckwheat;
- natural yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese;
- sunflower and olive oil;
- vegetables – potatoes, cabbage, cucumbers;
- green varieties of apples and pears;
- dried fruits and compotes from them;
- dried wheat bread, lavash without yeast.
What to eat for schoolchildren
After 4 years, the menu of a child with allergies becomes wider.
At the same time, dietary characteristics are preserved even at school age.
During this period, the diet should not be hypoallergenic, but elimination.
Products that previously caused allergies are excluded from the menu, but the range is becoming wider.
There are foods with a high risk of intolerance:
- mushrooms;
- honey;
- nuts;
- chocolate;
- fish.
In some cases, they should not be consumed until middle school age.
However, such prohibitions usually arise with the development of chronic forms of allergies and are agreed with a doctor.
Types of diets
There are three main types of dietary nutrition for children with allergies.
- The nonspecific hypoallergenic diet has already been mentioned above. Its principle is to exclude provoking foods from the diet and limit those that theoretically cause allergies;
- Elimination, its goal is to identify a specific allergen. First, they exclude foods that are most likely to provoke allergies, and then one by one they begin to introduce them into the child’s diet. When using an elimination diet, the product that provokes the allergy quickly becomes clear.
- Alternating diet. It is based on the following fact: both the allergen itself and the amount consumed by the child matter. Following an alternating diet, the child is given allergenic food, but not more than once every three days. This form of nutrition is prescribed in cases of non-acute allergies.
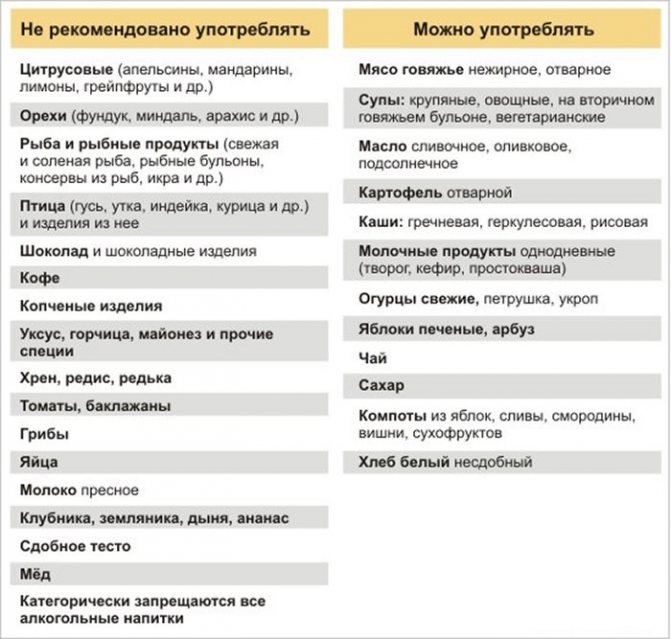
Menu for overweight allergy sufferers
To improve the child’s condition, it is imperative to cope with excess weight.
To do this, you need to follow a certain menu.
For breakfast you can offer your baby:
- oatmeal or corn porridge;
- cottage cheese;
- boiled eggs or omelet;
- fruit salad with yogurt.
Suitable for lunch:
- vegetable soup;
- buckwheat or rice porridge;
- salad.
Boiled chicken or turkey breast is also an excellent option.
If you are not allergic to fish, you can offer your child fish casserole.
For dinner you should cook:
- baked vegetables with meat;
- boiled potatoes with fish;
- carrot casserole.
Find out if your child has a fever due to allergies. What effective nasal drops for allergies are there for children? The answer is here.
How to cure allergies on the cheeks of a child? Details below.
Food diary for breastfeeding
A food diary involves recording all the foods eaten by the mother during the day, as well as a description of any unusual reactions of the child’s body to them (in this case, a hypoallergenic diet during breastfeeding must be followed).
Features of record keeping:
- The diary should be kept every day for a period of time determined by the pediatrician.
- It is better to keep records in the form of a table with columns: “date”, “meal time”, “type of product”, “quantity” and “changes”.
- It is imperative to write down not only the composition of the dishes, but also the method of their processing.
- Products purchased in a store are entered into a diary indicating the manufacturer in order to prevent the consumption of the entire line of foods that are obviously dangerous for children.
- Be sure to write down the amount of food eaten.
- It is advisable to divide the “changes” column into 4 parts, indicating the manifestations of allergies on the skin, through the respiratory and digestive organs, as well as the general condition of the child. The time of occurrence of any negative reaction is recorded.
- You should especially note in your diary the intake of certain medications, including vaccines.
- The introduction of new products should be coordinated with a pediatrician or allergist, recording this fact in a diary.
A hypoallergenic diet will help improve the child’s condition and prevent the occurrence of atopic reactions. This is the best way to avoid long-term treatment for the disease in the future.
Views: 422