Description of the drug
The name of the drug coincides with the active substance.
It acts quickly and aggressively towards the pathogen, is an imidazole derivative, and when ingested, it destroys ergosterol, an enzyme that is part of the cell membrane of the fungus. After oral administration, fluconazole easily penetrates tissues and organs, accumulates best in affected areas and completely kills the fungus in a matter of days, but remains active for some time, since the cumulative effect of the active ingredient occurs. It is prescribed for thrush, cryptococcus, nail and skin fungus.
Release form: capsules of 150 mg or 50 mg in packages of 1, 3 or 6 pieces for oral use. Despite its good effectiveness and speed of action, this drug is toxic to the liver, has a moderate load on the kidneys, and can cause tachycardia and arrhythmia, headaches, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. It is possible that part of the substance that reaches the baby during breastfeeding may cause negative side reactions.
Composition and effect of the drug
The main active component of the drug is fluconazole, an antibiotic that destroys strains of pathogenic fungi by destroying the cell membranes of the pathogen, as a result of which their vital activity is suppressed and death occurs. In addition to the mechanism of action, fluconazole has its own peculiarity - it has a destructive effect only on the enzymes of harmful fungi, without affecting similar compounds that are normal for the human body.
The drug also contains excipients - starch, calcium stearate, capsules are characterized by the presence of dye, preservative and gelatin. They help the drug to be absorbed quickly.
The active substance of Fluconazole has the ability to penetrate into all biological fluids, so the medication is very effective in the treatment of candidiasis. After taking the tablet or capsule, the product is actively absorbed and begins to act within an hour and a half.
How does breastfeeding affect lactation and the baby?
The medication has a significant effect on the quality of breast milk. The active component fluconazole penetrates through the bloodstream into milk in significant quantities. Such a high concentration has a different effect: a woman tolerates it easily, but a child may experience symptoms of an overdose and negative effects in the form of colic, severe allergies, anemia, and disturbances in the functioning of the digestive and central nervous systems.
A fragile child's body may not be able to process and eliminate the medicine. In addition, this is an extra burden on the baby's liver.
It is recommended to stop breastfeeding while taking the drug. The baby needs to be switched to adapted formulas or use pre-prepared frozen breast milk. At the same time, the mother must constantly pump so that painful lumps do not form in the mammary glands. In addition, this will preserve lactation.
On a note. Breastfeeding can be resumed 5-7 days after taking the medicine.
Can I take it while breastfeeding?
Fluconazole is able to pass through the bloodstream into breast milk, being in it in the same concentration as in blood plasma. This can negatively affect the baby's health. The instructions for the drug prohibit taking the drug while breastfeeding.
Important! There is an opinion among doctors that a single dose of 150 mg is safe for the child, but it is better to stop breastfeeding for 5-7 days.
During lactation, Fluconazole is prescribed strictly as directed by the doctor in compliance with all recommendations and dosage. A nursing mother must understand responsibility for the possible consequences and state of health of the child after taking the medication.
If possible, it is better to abandon Fluconazole and use alternative treatment methods using non-toxic and safe medications, as well as folk remedies.
How does Fluconazole work in the female body?
During breastfeeding, mothers are especially susceptible to various infections entering the body. This is due to a weakened immune system. The female body has not yet had time to recover from childbirth, and hormones have not yet stabilized. Against the background of various disorders and under the influence of various negative factors, a woman’s body becomes easily infected.
The drug is used for cryptococcosis, genital and vaginal candidiasis, fungal skin infections. Fluconazole can also be used to prevent fungus in people with reduced immunity.
In a woman’s body the drug:
- eliminates the activity of pathogenic microflora;
- blocks the spread of infection;
- suppresses oxidative processes in the liver;
- destroys the cells of yeast-like fungi and eliminates the infection.
As a result of exposure to Fluconazole, the activity of the fungus is eliminated, the clinical manifestations of thrush disappear - itching, burning on the mucous membranes. The use of the drug in treatment eliminates swelling of the vaginal walls, which often accompanies the inflammatory process. The medicine eliminates cheesy white vaginal discharge and eliminates genital rashes.
The drug includes the active drug substance fluconazole. The product is available in capsules and solution for injection. In the treatment of thrush, the tablet form of Fluconazole is taken. Sometimes the medicine can cause side effects. This fact must be taken into account when using the medicine.
There have often been cases where Fluconazole provokes:
- the appearance of a skin rash;
- dyspepsia;
- stool disorders;
- digestive disorders.
You should not take Fluconazole if you are hypersensitive or highly sensitive to the drug.
If side effects occur, it may be necessary to discontinue the drug or reduce the recommended dose. Most often, adverse reactions are caused by a high dose of the drug. If necessary, reduce the dosage of the drug. It is important to understand that when using the medicine, adverse reactions may occur in a small child. Therefore, it is not surprising that the baby developed a rash and diarrhea if the mother took Fluconazole.
Recommendations for use by mothers
- The dosage of the drug depends on the type and severity of the disease. For uncomplicated thrush, it is enough to take a single dose in the form of one capsule (150 mg) or drink 3 tablets of 50 mg.
- For a fungal disease, a diet that involves reducing the consumption of sugar, starch and flour products is important. At the same time, fermented milk products in the form of cottage cheese and kefir bring great benefits.
- Two weeks after treatment for thrush, you must come for an examination to a gynecologist and take a vaginal smear for laboratory testing. If a fungus is detected in it, the doctor will determine the tactics of further therapy.
- The fungus can pass to the child, so daily hygiene of the genitals and nipples, proper nutrition and careful examination of the child’s mucous membranes for the presence of thrush are important for the mother.
- You should refrain from sexual intercourse until symptoms are cured to avoid infecting your partner and worsening the situation.
READ MORE: Fluconazole during pregnancy in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd trimester, when planning
Diagnostics
A woman can treat thrush during lactation at home. Modern methods of eliminating this problem effectively and in a short time relieve itching and burning, while being safe for children undergoing breastfeeding.
Diagnosis of thrush is carried out by examining the affected area and taking a smear of the vaginal mucosa. If a woman has been diagnosed with thrush, then her sexual partner also needs treatment, since even without external signs of the disease, he also has Candida fungus. Unlike a woman, a man may well limit himself to a single use of an antifungal drug - for example, Flucanazole or Diflucan.
Alternative Treatment
Fluconazole is not the only antifungal agent. The medicine has several pharmacy analogues, in addition, many women successfully use folk remedies that help in the comprehensive fight against thrush.
During lactation, mothers are susceptible to various diseases. These include diseases caused by fungi. Many women wonder what products can be used to combat fungal diseases while breastfeeding.
In the treatment of this disease, drugs such as Fluconazole, Diflucan and Miconazole are often used. They all contain one active substance - fluconazole and have almost the same therapeutic properties.

How well do they help a nursing mother and are they harmful to newborns? This is discussed in our article.
Tablets and capsules for thrush
Typically, they try not to prescribe antifungal agents in tablets or capsules to nursing mothers. This is explained by their high toxicity. In modern medicine, there are examples of tablet medications for thrush, which are also applicable during lactation. These include tablets whose main active ingredient is fluconazole, namely “Fluconazole” and similar drugs “Miconazole” and “Diflucan”.
When prescribing Diflucan, there is no need to wean the baby from breast milk or adjust the feeding regimen. Such medications, in accordance with the international reference book of medications, are compatible with breastfeeding, however, despite this, their instructions clearly indicate that their use by nursing mothers is contraindicated. Therefore, a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist is mandatory!
Often after pregnancy, women are faced with an unpleasant phenomenon - a fungal disease. When the body, weakened by pregnancy, is unable to cope with the disease on its own, antifungal drugs will come to the rescue.
Doctors should prescribe Fluconazole during lactation in women, taking into account the fact that this drug is capable of:
- increase the half-life of drugs that lower blood sugar levels;
- slow down the excretion of zidovudine, theophylline, saquinavir;
- in combination with anticoagulants provoke bleeding;
- increase the degree of toxicity of NSAID drugs.
When taken simultaneously with hydrochlorothiazide, the concentration of the active substance Fluconazole in the patient’s blood increases significantly.
Contraindications for women who are breastfeeding
Candida fungus, the causative agent of the disease, belongs to the yeast-like fungi and lives in the microflora of the vagina, on the oral and intestinal mucosa, and is completely harmless if its level is normal.
However, if, under the influence of certain factors, its amount begins to increase significantly, thrush develops rapidly. Every second woman in the world suffers from candidiasis. Women who are breastfeeding are especially at risk for this disease.
Considering that many medications for the treatment of thrush during breastfeeding cannot be taken because of possible harm to the baby, then the young mother is lost and does not know what exactly to do.
The body of a nursing woman is very vulnerable under the pressure of various bad microbes and infections. Having discovered a relapse of thrush, you should not immediately run to the nearest pharmacy and buy the first medicine that comes to you, hoping for its healing power.
Such an action can cause aggravation of the disease, which is very dangerous for the woman and her child.
When a woman experiences symptoms of progressive candidiasis, which affects not only the genitals, but also the nipples, a natural question arises: how and how to treat the disease? Before answering this question, it is necessary to understand what triggers the activity of the candidiasis fungus.
The manifestation of thrush in a nursing woman can be caused by the following reasons:
- Reducing the protector of immunity properties.
- Hormonal imbalance, which is considered a common occurrence during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- The presence of infectious diseases of the genital organs, mouth and intestines.
- Use of antibacterial and hormonal medications.
- Avitaminosis.
- Too rapid restoration of sexual activity after childbirth, when the mother’s body is not fully restored.
- An infection with candidiasis occurred during sex. In this case, the man does not necessarily have thrush, he just may be a carrier of the Candida fungus.
- Failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene.

White, curd-like discharge from the vagina is the first symptom of thrush. But during breastfeeding, the disease can also spread to the nipples; they become bright pink, with the formation of painful cracks in which a whitish substance collects. Thrush in nursing mothers is accompanied by other obvious clinical symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- itching and burning in the genital area, nipples;
- lethargy;
- prostration;
- temperature (in acute form of thrush).
Timely treatment of thrush, especially with breastfeeding, is the key to the healthy condition of the child, who is the first to fall into the risk zone of contracting this disease. Treatment of the disease in young children is a lengthy, complex and painful procedure.
We suggest you read: How can a woman get thrush from a man?
Medications prescribed for thrush are divided into two groups:
- For internal use (capsules, tablets).
- For local use (suppositories, creams, ointments, vaginal tablets).
Many doctors consider oral medications to be harmful during lactation, so preference should be given to topical medications.
An antibiotic is an effective treatment option for thrush, which helps to get rid of the disease in a short time, but in case of breastfeeding it should be avoided due to the perceived danger to the child.
Various ointments and creams made on the basis of antibiotics are considered milder.
Hexicon
Suppositories with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. Absolutely do not show any side effects. Normalize the microflora of the mucous membrane, destroy harmful bacteria and fungi.
It is used immediately before bedtime, as the candle melts and turns into a gel, which is distributed over the entire problematic surface, thereby exhibiting its medicinal effect. The main feature of Gekskon is that upon contact with water and alkali, its medicinal properties are reduced.
Therefore, when using the drug, adhere to hygiene only of the external genitalia.
Zalain
The main component is sertaconazole, which inhibits the viability of yeast fungi and harmful microorganisms. Eliminates all conditions for the development of candidiasis. The duration of the treatment course is 14 days, and should not frighten nursing women. It has absolutely no harmful effect on the mother’s body and the quality of her milk.
Candide cream (ointment)
An antifungal agent with a broad therapeutic effect. Recommended for the treatment of thrush even during breastfeeding. It has antibacterial and antiprotozoal properties.
Clotrimazole
Has a wide range of influence. It is successfully used for the treatment of thrush, especially during lactation, since its main effect is local therapy, which does not require interruption of breastfeeding.
Lactagel
A popular and effective drug. Restores the natural healthy environment in the vagina.
Productively eliminates all painful symptoms: itchy discomfort, unpleasant odor and other symptoms of thrush. It has proven itself to be an excellent prophylactic agent.
Many gynecologists advise nursing women to take this particular medicine, as it is one of the best drugs for candidiasis.
Nystatin ointment
It has an excellent medicinal effect on Candida fungus. It has a destructive effect on its structure, which subsequently leads to its death. Very often prescribed as a prophylactic when there is a threat of thrush development.
Pimafucin
It is made on the basis of an active antibiotic and has an immediate healing effect. Already after the first use it reduces itching and burning in the vagina.
Relieves redness and swelling in affected areas. The main substances of the drug have a detrimental effect on all types of harmful microorganisms and fungi.
It is better for nursing women to use this product in the form of an ointment, which will protect the child from its medicinal influence.
Terzhinan
It has unique capabilities against fungus and bacteria. Pharmacological form – vaginal suppositories. The main active ingredient of the drug is prednisolone, which is completely harmless to the baby.
Fluconazole
An antifungal agent, recommended for diseases of fungal origin, including thrush. Although the annotation for it states that it is contraindicated in breastfeeding, international medical reference books note that the medicine is compatible with breastfeeding.
Conclusion
Any drug for the treatment of thrush during lactation, despite its gentle properties, has a number of contraindications. If side symptoms occur caused by taking the medication, you should contact a gynecologist for competent advice.
A woman who is breastfeeding, suspecting she has thrush, should consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis.
Treatment of thrush in women with breastfeeding should begin with a visit to the doctor, who will write out directions for the necessary tests, including culture for bacteria. The results obtained will become the main criterion for prescribing drugs.
Antifungal suppositories and ointments
Suppositories for thrush during lactation are the most common method of treating candidiasis. Vaginal suppositories and ointments produce a local effect, but not all popular suppositories are approved for use during breast milk production, so it is extremely important that they are approved by the treating gynecologist.
In the first time after childbirth, many women simply do not have the opportunity to see a specialist. What should she do in such a situation? Having decided to choose your own candles or ointment, you must carefully study the instructions for use, especially pay attention to points related to contraindications.
READ MORE: Can chronic thrush be cured with fluconazole?
Certain medications contain tiny substances that are unsafe for a fragile body - they can enter the mother’s bloodstream, being absorbed through the vaginal mucosa, and then into her breast milk. As a result, a mother who develops thrush during lactation should give preference to medications that cannot harm the baby. Otherwise, breastfeeding will have to be stopped, and this can also negatively affect the baby’s health.
Any antenatal clinic has a list of vaginal suppositories that are allowed to be prescribed to women to overcome candidiasis during lactation, according to the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. This list includes:
- Polygynax;
- Hexicon;
- Pimafucin;
- Ruvidon;
- Clotrimazole;
- Livarol;
- Betadine;
- Zalain.
Medicines can be divided into 2 groups. One includes suppositories that do not require stopping breastfeeding, the other includes those for the period of use of which it is better to refuse breast milk.
pharmachologic effect
The main antimycotic effect is blockade of the synthesis of protein enzymes of the fungus, which leads to increased permeability of the cell membrane, inhibition of reproduction, and then death of the pathogen.
Most pathogens of fungal infections are sensitive to Fluconazole.
The medicine dissolves well and is absorbed in the body. Food intake does not affect the rate of absorption of the drug. The maximum therapeutic concentration is reached 4 hours after taking the drug.
The active substance of the drug is distributed in the biological environments of the body in different ways. In saliva, sputum, in vaginal secretions, in periarticular fluid, in breast milk, the concentration corresponds to blood plasma, 90% passes into the spinal cerebrospinal fluid. It accumulates in the epidermis, stratum corneum, and sweat in larger quantities than in the blood serum. Half-life 30 hours, excreted from the body in urine.
Indications for use
The drug is effective for various fungal diseases, it reduces the activity of the fungus, quickly relieves itching and burning of the affected mucous membranes. The most common and common illness among nursing mothers is genital or vaginal candidiasis (thrush), which is the main indication for the use of Fluconazole. In addition, the drug is prescribed for the following diseases:
- Generalized candidiasis (fungal damage to the eyes, digestive and respiratory organs).
- Candidiasis of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose.
- Cryptococcosis – damage to the central nervous system, lungs, and skin.
- Mycosis is a fungus of the fingers, nails, and groin area.
Fluconazole is aimed not only at treating fungus, but also at preventing it. The drug can be used to prevent fungal diseases when the body's defenses are reduced or the immune system is malfunctioning.

A fungus is a microorganism that can cause serious illness. It can affect the skin (it especially loves the feet and palms), nail plates, mucous membranes and even internal organs.
A fungal infection causes a lot of inconvenience, so it is necessary to get rid of it and, preferably, do this at an early stage of the infection. One of the effective drugs that helps cope with this annoying disease is Fluconazole.
Since the active substance actively penetrates into all fluids and tissues of the body, it will easily penetrate into breast milk. If you rely on the information specified in the international reference book on the effects of drugs, then fluconazole can be combined with breastfeeding. The half-life of fluconazole in breast milk is 30 hours, and the maximum concentration of the active substance in the blood reaches 1-2 hours after use. It is believed that a safe dose per day is 50 mg - 200 mg of fluconazole.
However, not all experts share the information provided in the directory. Some believe that the maximum permissible daily dosage for breastfeeding should not exceed 150 mg, and if you need to drink more, then lactation is temporarily interrupted. Other experts even consider fluconazole to be a dangerous drug for breastfeeding and interrupt breastfeeding for about a week during therapy.
It is believed that when the drug enters a child’s body, it can cause the following negative side effects: colic, developmental delay, poisoning, allergies. In any case, this medication is a last resort and is prescribed for hepatitis B in especially severe cases, since there are other effective remedies for thrush for topical use that do not penetrate the systemic bloodstream.
READ MORE: Fluconazole tablets 50 mg No. 10: instructions for use
Fluconazole may be prescribed during lactation in women, including in the presence of diseases such as:
- genital or intestinal thrush;
- oral thrush;
- fungal infections of internal organs.
In addition, this drug can also be used to prevent fungal infections. But lactating women should still refuse to use this drug in this capacity, replacing it with a safer medication.
The dosage of this drug depends on the specific disease and is selected by the doctor individually. In any case, lactating women should not take more than 150 mg of this medicine at a time. Depending on the manufacturer, this dose of the active substance may contain one capsule or three.
After taking Fluconazole, it is still recommended not to breastfeed the baby for 3-5 days. To ensure that lactation does not stop during this time, milk should be expressed periodically. During this period, the child is transferred to artificial formula.
Take this drug in any form orally. At the same time, when taking Fluconazole at normal times or during lactation, like almost any other tablets and capsules, wash it down with water.
For some diseases, women may be prescribed larger dosages of the drug. The doctor chooses this treatment regimen with Fluconazole, for example, for candidiasis or cryptococcal meningitis. If a patient has such a problem, she can be prescribed up to 600 mg of the drug per day. In this case, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding altogether.
Permitted dosage for breastfeeding, as well as an alternative to Fluconazole during lactation
During lactation, fluconazole can be replaced with topical antifungal drugs in the form of suppositories or ointments for vaginal use. This:
- Butoconazole, two percent cream.
- Miconazole, suppositories.
- Pimafucin, suppositories.
These drugs, in the appropriate form, are almost not absorbed by the body through the vagina, therefore, do not penetrate the bloodstream and breast milk.
But in a complicated form with vaginal candidiasis with a chronic recurrent nature, Fluconazole is prescribed in three doses every 72 hours, one capsule. In this case, breastfeeding is stopped for this period until the drug is completely eliminated from the body. The baby is fed formula or frozen milk supplies. To continue lactation after treatment, the breasts are expressed while taking the drug, but the milk should be disposed of and should not be given to the child. This treatment is used in rare cases and only under the supervision of the attending physician. If there is a fungal infection in a woman’s body that requires intravenous administration of the drug, then breastfeeding is stopped and the baby is transferred to artificial feeding.
Analogues of the drug containing the same substance in their composition
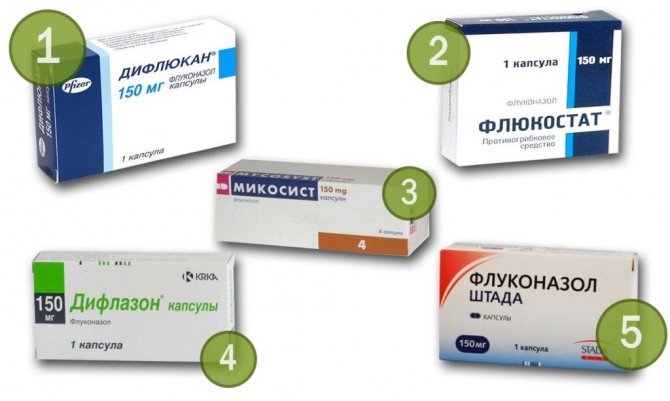
Today's pharmacology offers a large number of similar remedies for fungi containing fluconazole. The difference may be in price, manufacturer and concentration of the active substance. For example, it could be Russian-made Flucostat or French-made Diflucan, as well as Diflazon, Mikomax, Flucoside and others.
The price can vary from 9 to 50 rubles. for one tablet or capsule with a dosage of 150 mg. The composition of these drugs is distinguished by the presence of additional components that regulate the appearance and consistency of the product, but do not affect the effectiveness of the drug. The only thing that remains unchanged is the main active substance, fluconazole.
Remedies for fungus that are not so dangerous during lactation
Drugs with a similar effect, but with a different active substance, can also be prescribed to nursing women. Moreover, APILAM (Association for the Promotion and Cultural and Scientific Research of Breastfeeding) has allocated several funds with minimal risk to the baby. These include:
Products containing itraconazole
In this case, there are also several similar drugs, but with the same active ingredient, itraconazole. The effect of the substance is identical to that of drugs with fluconazole, the death of fungal cells by preventing their development through ergosterol in the membrane.
Itraconazole can eliminate systemic infections. Therefore, it is prescribed for histoplasmosis, aspergillosis, candidiasis, cryptococcosis at a time when similar drugs do not help or are not suitable for treating the diagnosed disease.
There is no clear answer about drug recommendations for lactation, since the annotations for drugs from different countries and manufacturers contain different information, for example, Russian analogues indicate that itraconazole is contraindicated during breastfeeding. Therefore, when prescribing such medications, you should consult a pediatrician.
Medicines containing ketoconazole
The action of a series of these products is identical; they destroy the fungus by acting on the membrane-forming elements of fungal cells.
Manufacturers of medicines in Russia still exclude lactation from the recommended period of taking the drug. But foreign colleagues still talk about minimal risk for the newborn.
Therefore, if you need to use products with ketoconazole, you should ask advice not only from a gynecologist, but also from a pediatrician. Moreover, the list of side effects of such analogues is quite significant.
Clotrimazole
This remedy is most often prescribed to women to treat fungal infections. It is based on an active substance called imidazole, which has a similar effect, destroying cell membranes.
Clotrimazole is prescribed in ointments, so when this drug is used during lactation, it enters the blood in a minimal concentration. Because of this, it is recommended for lactation by both Russian manufacturers and APILAM.
Varnish Mikozan
This is a remedy that is used to treat fungal infections on the hands and feet. Externally, the drug resembles ordinary nail polish. There is no main active component; Mikozan acts on the fungus mechanically, suppressing its growth. Most often you hear about this remedy that it is not a cure, but a means of prevention. This may be why APILAM does not comment on this drug in any way, since it deals only with medicinal products.
Indications for use
Fluconazole is prohibited in case of individual intolerance to the components of the drug and is not prescribed in the following cases:
- Pregnancy.
- Lactation.
- Taking terfenadine.
The medicine is used with extreme caution in cases of impaired absorption of lactose and renal failure. The drug cannot be used while breastfeeding, although doctors often prescribe it to nursing women for fungal diseases.
Reference. If treatment with Fluconazole is unavoidable, then breastfeeding must be stopped and the child must be switched to an adapted formula. After therapy, the baby can be put to the breast again.
If the dosage is observed, Fluconazole is usually well tolerated by the body; side effects appear in rare cases and are short-lived. Among them the following stand out:
- Dizziness, headache.
- Abdominal pain, flatulence, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea.
- Rash, itching, redness of the skin.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Deterioration of taste and loss of appetite.
- General weakness.
If negative consequences occur, discontinuation of the drug or dose reduction is required; this will be discussed at a consultation with the doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable and can negatively affect a woman’s health. We must not forget about the harm that the medicine causes to the baby if breastfeeding is not interrupted.
Side effects
Before taking Fluconazole, you should be aware of possible unwanted effects, such as:
- dyspeptic disorders: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, pain and bloating, diarrhea or constipation;
- drug-induced hepatitis, hepatonecrosis, increase in blood liver enzymes, bilirubin, cholesterol;
- allergic skin reactions;
- neurological disorders in the form of impaired consciousness: hallucinations, paranoid behavior, peripheral paresthesia, tremor, dizziness, insomnia;
- anemia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
Reviews about the drug
Why Fluconazole can help women during lactation is clear. The spectrum of action of this medicine is quite extensive. But what kind of reviews has this drug received from patients?
Both doctors and women themselves during lactation have a very good opinion about this medicine. Patients consider the speed of action to be the main advantage of Fluconazole, in comparison with many of its analogues. Also, consumers attribute its rather low cost to the undoubted advantages of this drug.
Many lactating women consider the advantage of this medicine to be its relative safety, as well as ease of use. Fluconazole tablets and capsules are quite easy to swallow.
As we found out, Fluconazole can also be taken during lactation. There are good reviews about it, but, of course, this medicine also has some disadvantages. These include, for example, toxic effects on the liver, the presence of contraindications and the ability, although quite rare, to still cause side effects.