Mother's milk is a product that has been specially created to be ideal for infants. It contains proteins and fats that are quickly digested in the stomach and intestines. The drink contains an optimal balance of vitamins and minerals. Not a single manufacturer has yet been able to create a composition that would have the full range of necessary properties. However, the mother is unable to insure her child against various health problems. Lactose intolerance in infants is an unpleasant condition. Parents should know its causes and symptoms, as well as possible solutions to the problem.
What is lactose intolerance?
Women's milk contains a special component - lactose. This is essentially sugar that a child needs to get energy. He is directly involved in the process of formation of the nervous system.
Sugar from milk must be completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Lactase is a special enzyme that is produced by the intestinal mucosa. If it is produced in insufficient quantities, then lactose cannot be fully absorbed. The intestines do not have the necessary environment of microorganisms. Lactose intolerance leads to excessive gas formation. The situation occurs against the background of abdominal pain and bowel movements. The symptoms worsen the baby’s condition, so he becomes capricious.
In infants, this manifestation is called lactase deficiency. Some babies are also allergic to this product. However, experts attribute the situation to improper functioning of the immune system. In this case, characteristic reactions do not occur in the esophagus and stomach.
The disease is dangerous, because against its background there is no possibility of digesting mother's milk. The optimal solution is a special mixture. In newborns, this pathology causes not only severe pain in the stomach and intestines. Lactase leads to malfunctions of some internal organs and systems. Against the background of its consumption, acidity increases sharply, so the intestinal walls can be damaged. The disease prevents the baby from getting all the necessary vitamins and minerals from food. If treatment is not started in time, the child may lag behind in development due to lack of necessary nutrition.
Symptoms and signs of lactase deficiency
The entire clinical picture of this condition is based on symptoms of lactose intolerance. These symptoms may vary in severity for each child. The main symptoms of lactase deficiency in newborns include:
- increased gas formation in the intestines (flatulence);
- loose, foamy stools;
- intestinal colic, accompanied by restlessness and crying of the child;
- symptoms of fluid loss (dehydration);
- frequent regurgitation of food;
- weight loss or slow gain.
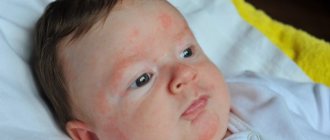
There is no relationship between the degree of deficiency and the severity of symptoms. Some children may experience skin manifestations of lactase deficiency. These include atopic dermatitis. The secondary form of lactase deficiency is characterized by constipation in children.
There are a number of signs, the appearance of which should alert a nursing woman. These signs include:
- holding the baby in their arms, parents can hear the sounds of rumbling in the baby’s intestines;
- during the feeding process, the baby abandons the breast, long before satiation;
- there are fragments of undigested food (lumps) in the child’s stool;
- the baby’s tummy is constantly tense and swollen;
- the child becomes restless, often cries and is capricious for no apparent reason.
Only a pediatrician can make a diagnosis of lactase deficiency after examining the child and assessing the laboratory diagnostic data obtained. The appearance of similar symptoms can be caused by improper organization of breastfeeding or violation of breastfeeding technique.
Main reasons
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the driving mechanisms of intolerance:
- The primary variant of the disease is diagnosed if the enterocytes in the baby’s body are normal. However, they cannot produce enough lactase.
- The gastrointestinal tract is not yet fully formed. This process, as a rule, ends only by the fourth month. After this, the child will be able to absorb lactase in full.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the body are a consequence of gene disorders.
- Functional impairment can also be of an “adult” nature. In this case, lactase will not be digested throughout life. With age, the situation can only get worse. It is important to identify this pathology in time and direct all efforts to eliminate it.
- Lactase deficiency can also occur due to damage to the overall structure of enterocytes. The disease develops against the background of the spread of infection in the intestines and inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Some children develop the pathology due to an allergic reaction to cow's milk or gluten. In this case, these products should be excluded from the diet completely.
In case of lactase deficiency, it is advisable to feed the child with a special mixture
Excess milk sugar is a situation in infants that has symptoms similar to lactose intolerance. In this case, the process of enzyme production occurs normally. However, the body receives an excess of lactose. Against this background, unpleasant symptoms arise. The situation is quite often observed if the baby feeds only on the mother's foremilk. It contains an excessive amount of sugar.
Signs
Symptoms of lactose intolerance in infants become more pronounced as they get older. At the same time, immediately after the baby is born, there are practically none. Only after a certain period do parents begin to notice:
- Excessive gas production, which leads to constant pain in the baby's tummy.
- Mothers periodically begin to notice rumbling in the tummy and its excessive tension.
- Disturbances in the formation of stool. You can observe foam and an unpleasant odor in it. Yellow color also indicates the presence of pathology. Only at the next stage of development of the disease does it become green with an admixture of mucus.
- The process of defecation occurs too often or, conversely, the baby becomes constipated.
- After eating, the process of regurgitation occurs more often than usual.
- Additionally, the baby has poor weight gain. The situation most often occurs in children who are bottle-fed.
If a child cannot digest lactose, this most often does not negatively affect appetite. They begin to eat actively, but after a couple of minutes they refuse to breastfeed. You can also observe periodic crying, spontaneous movements of the legs and arching in the back.
If milk sugar is consumed excessively, the child behaves in a similar way. Among the main differences, good weight gain should be noted.
Let's sum it up
So, lactase deficiency in infants can occur both with artificial and natural feeding. But many doctors argue that the pathology in question simply cannot exist during breastfeeding! And even greenish, foamy stool, intestinal colic and frequent regurgitation are not symptoms of lactase deficiency. Indeed, even “classical” medicine says that the symptoms of the disease in question are nonspecific and may indicate a number of other health problems.
What parents need to know:
- Intestinal colic occurs in almost every newborn, and it does not at all mean lactase deficiency. No diagnosis can be made on this basis alone.
- Frequent regurgitation can occur due to improper feeding (the baby swallows air along with milk).
- Foamy and greenish stools are, of course, not the norm, but this is how the intestines adapt to “adult” life.
- Stool tests for carbohydrates and breath tests for hydrogen often give false-positive results, so these tests are highly questionable in diagnosing lactase deficiency.
- Incomplete digestion of lactose in the first week of a baby’s life is often normal and occurs even in completely healthy children. Sometimes this adaptation period stretches until the child is five months old and this is also considered the norm.

So, let’s conclude: if a newborn baby does not refuse to eat, does not show anxiety, develops within normal limits and gains weight either “according to the table” or with a slight lag, then there is no need to wean him from the breast and run around in search of lactose-free formulas!
And one more thing: if the doctor diagnoses “lactase deficiency”, or the parents themselves (oh, horror!) determine this pathology in their own baby, then they go to specialized stores for lactose-free formula. The cost of such nutrition is quite high, which is why some doctors suspect that the frequent diagnosis of “lactase deficiency” is just a marketing ploy.
Lactase deficiency does exist. Yes, in some cases the child’s condition requires a change in diet, giving up breastfeeding and switching to special formulas. But such measures are considered the most extreme, and in most cases the child simply needs to be given time to adapt to new living conditions. So, parents should be competent and prudent, carefully monitor the condition of their baby and under no circumstances make diagnoses on their own, and certainly not use any special formulas for feeding.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category
6, total, today
( 54 votes, average: 4.46 out of 5)
Groin pain in men: possible causes
Laryngopharyngeal reflux: causes, symptoms, treatment
Related Posts
Features of diagnostics
It is important to recognize lactase intolerance in time. To do this, it is necessary to carry out the following activities:
We recommend reading: Lactase Baby for newborns and reviews about the drug
- It is necessary to take material for research from the mucous membrane of the small intestine. The procedure is called a biopsy. It requires the administration of anesthesia, so it is performed extremely rarely in young children.
- For correct diagnosis, you will need to create a lactose curve and a hydrogen test. This will require an oral dose of lactose. After completing this procedure, you will need to donate blood for analysis. Based on the results, a curve will be drawn up. The method may also involve the study of inhaled air. Unfortunately, the procedure can only cause discomfort in a baby. Additionally, it should be noted that today there are no indicators that would allow one to correctly analyze the amount of hydrogen.
- The analysis must be carried out with stool. At the same time, the hydrogen content in them is assessed. Unfortunately, research in this area does not have a high degree of correctness. Today there are no uniform norms and rules that could be applied to all infants. Such an analysis does not make it possible to study carbohydrates according to all the necessary indicators.
- The coprogram is used to detect hyperacidity or excessive amounts of fatty acids. Lactose intolerance is diagnosed if the level is several times higher than normal.

To make a diagnosis you will need to donate blood
The diagnosis is most often made based on the entire complex of symptoms. Signs can only be assessed correctly by doctors. Parents should not self-medicate, because it can only lead to aggravation of the situation. When diagnosing deficiency, it is advisable to transfer the baby to a special version of the formula that does not contain components harmful to the body.